Digestive System
advertisement
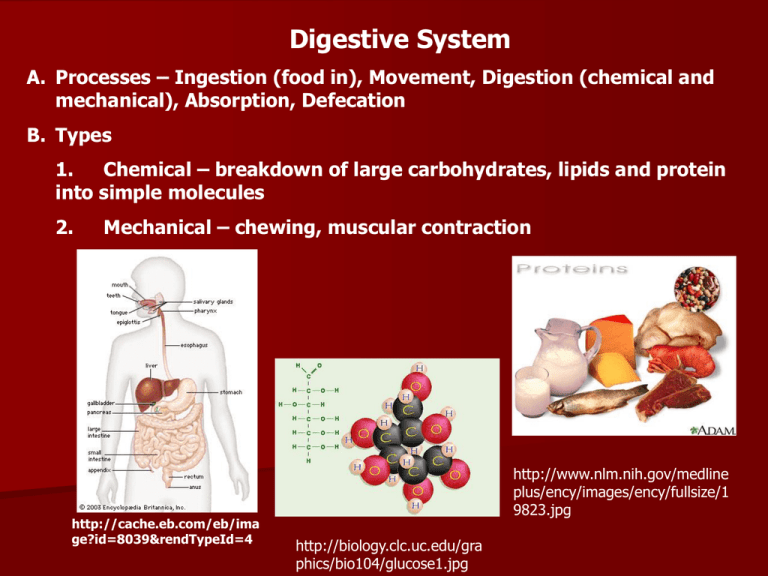
Digestive System A. Processes – Ingestion (food in), Movement, Digestion (chemical and mechanical), Absorption, Defecation B. Types 1. Chemical – breakdown of large carbohydrates, lipids and protein into simple molecules 2. Mechanical – chewing, muscular contraction http://cache.eb.com/eb/ima ge?id=8039&rendTypeId=4 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medline plus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/1 9823.jpg http://biology.clc.uc.edu/gra phics/bio104/glucose1.jpg C. Organization: Gastrointestinal Tract and Accessory Organs 1. GI Tract (Alimentary Canal) – mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine 2. Accessory Organs – teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gall bladder, pancreas http://visual.merriamwebster.com/images/hu manbeing/anatomy/digestivesystem.jpg D. Histology 1. mucosa – inner lining – mucous membrane 2. submucosa – areolar connective tissue binds mucosa to muscle, contains blood and lymphatic tissue 3. muscularis – skeletal – mouth, pharynx, upper esophagus, (swallowing) smooth muscle – the rest of the tract 4. serosa – outermost layer, serous fluid allows for free gliding of the mesentery, omentum and falciform ligament http://cache.eb.com/eb/image?id=74315&rendTypeId=4 E. Digestive Tract: Anatomy and Physiology 1. Mouth – oral or buccal cavity a. Tongue – skeletal muscle covered with mucous membrane Extrinsic muscles – outside and insert in, move tongue side to side and in and out Intrinsic muscles – inside, speech and swallowing b. Salivary glands - 3 pairs – parotid, submandibular, sublingual Saliva – 99.5% H2O, .5% solutes – lubrication and dissolving, Salivary Amylase under nervous control http://academic.kellogg.cc.mi.us/herbran dsonc/bio201_McKinley/f264a_salivary_glands_c.jpg c. Teeth – located in bony sockets of maxilla and mandible - KNOW TYPES AND FUNCTIONS http://www.medem.com/MEDEM /images/AMA/ama_preventive_o ralhealth_lev20_theteeth_01.jpg http://whyfiles.org/shorties/1 47tooth/images/teeth.jpg http://dentistsplans.com/images/health ytooth.jpg d. Digestion in the mouth Mechanical – Mastication (chewing) Chemical – Salivary Amylase – starts breakdown of starch 2. Esophagus – lies behind the trachea a. Function – transports food b. Peristalsis – muscular movements (involuntary) to push food through esophagus c. lower esophageal sphincter – prevents backflow of HCl (heartburn) http://www.massgeneral.org/cancer/c rr/types/thoracic/illustrations/images/ esophagus_front.jpg 3. Stomach – J-shaped a. Anatomy – cardia – superior opening Fundus – up and to the left Body – large central portion Pyloris – narrow, inferior region b. Digestion MECHANICAL – mixing waves = Peristaltic movements every 15-20 seconds, forms chyme CHEMICAL – Pepsin digests proteins, effective at pH of 2 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/en cy/images/ency/fullsize/19223.jpg Gastric Lipase breaks down large lipids (triglycerides) Controlled by nervous and hormonal mechanisms c. Regulation of gastric emptying – Stomach empties all of contents into duodenum within 2-6 hours Carbohydrates spend less time in stomach, proteins more Vomiting – forceful expulsion of contents from upper GI tract 4. Pancreas – behind stomach, secrete into duodenum through pancreatic duct a. Anatomy – Islets of Langerhans and Acini cells, 2 types of cells b. Pancreatic juices EXOCRINE ENDOCRINE Acini cells Islets of Langerhans Produce mixture of digestive Glucagon (converts enzymes = pancreatic enzymes glycogen to glucose) Multiple enzymes for digestion Insulin (transports of carbs, protein, fat glucose into cells and Regulated by nervous system changes glucose into and hormones glycogen http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/ images/ency/fullsize/17194.jpg http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency /images/ency/fullsize/17151.jpg 5. Liver – heaviest gland, supported by falciform ligament a. Functions: Lobules consist of hepatic cells which produce bile Destroys worn out white and red blood cells, bacteria and other toxins http://www.best-vitamin-supplementsguide.com/images/liver.jpg b. Bile – yellow, brownish or olive green, pH of 7.6-8.6, aids in emulsification, conversion of fat into droplets, helps in absorption of fat 6. Gall bladder – concentrates and stores bile until needed by small intestine http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplu s/ency/images/ency/fullsize/1090.j pg 7. Small intestine – most digestion and absorption (90%) occurs here a. Anatomy – 21 ft long in cadaver, 10 ft long in living (muscle tone) Made up of duodenum, jejunum, ileum b. Adaptations - length, mucosa and submucosa are modified to increase digestion and absorption, villi and microvilli increase surface area, circular folds http://www.cudahychamber.com/images /digestive_system.gif http://instruct1.cit.cornell.edu/courses/biog105/page s/demos/105/unit6/media/villus.structure.jpg c. Digestion and absorption of major nutrients CARBOHYDRATES – maltase, sucrase and lactase break disaccharides into monosaccharides, absorbed as such PROTEINS – pepsin fragments proteins into peptides, Peptidase completes the task, absorbed as amino acids LIPIDS – occurs in small intestineby pancreatic lipase, absorbed as monoglycerides and fatty acids NUCLEIC ACIDS – done by intestinal and pancreatic juices http://images.google.com/i mages?hl=en&rlz=1T4DMUS _enUS207US207&resnum=0 &q=nucleic%20acids&um=1 &ie=UTF-8&sa=N&tab=wi http://images.foodnetwork.com/webfood/ima ges/gethealthy/nutritionalallstars/LeanProtei ns_header.jpg 8. Large Intestine – completion of absorption, makes vitamins, forms feces a. Anatomy – 5 feet long, 2.5 in in diameter, ileocecal sphincter, appendix, ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon b. Digestion, absorption, and feces formation – MECHANICAL – following meal chyme is forced into cecum, food intiates mass peristalsis – drives colon contents into the rectum – 3 or 4 times daily 9. Disorders of the digestive system http://immunesupportonline.co m/Images/Digestive%20Syste m%20Anatomy_files/Digestive %20tract%20annotated.jpg http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/th umb/c/c5/Digestive_system_diagram_en.svg/300px -Digestive_system_diagram_en.svg.png






