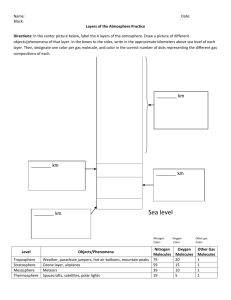
Atmosphere and Weather Notes I. Composition if the atmosphere:
advertisement

Atmosphere and Weather Notes - #1 Volcanic Eruptions played the main role in forming the Earth’s early atmosphere. - We call the mixture of many gases in Earth’s lower atmosphere #2 Air. - The amount of #3 water vapor in the air varies with location, season, and time of day and is therefore not included in the pie chart below. I. Composition if the atmosphere: Composition of the atmosphere 1% 21% 78% Nitrogen Oxygen Ar, CO2, Ne, He, Xe, others a. The composition of the atmosphere has remained stable due to Earth’s natural and #7 efficient recycling systems. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. Animals breathe out the gas #8 CO2 and breath in the gas #9 O2 Plants breathe out the gas #10 O2 and breath in #11 CO2 The amount of #12 CO2 in the atmosphere has steadily increased. #13 CO2 have increased due to the burning of fossil fuels such as i. #14 coal ii. #15 gasoline iii. #16 natural gas Energy from the #17 sun drives the #18 weather and is essential to almost all life on earth. Radiation is the transfer of energy through space in the form of #19 visible light, #20 UV rays and other types of #21 electromagnetic waves. #22 Conduction is the transfer of heat through the collisions of the atoms or molecules of a substance. #23 Convection is the transfer of heat energy in a liquid or gas through the motion of the fluid caused by differences in density. #24 Heat and Temperature are related, they are not the same. A large cup of tea has more #25 heat than a small cup of tea even though they are at the same temperature. A thermometer measures #26 temperature not #27 heat. Ice melts at #28 0ºC and boils at #29 100ºC II. Layers of the atmosphere: #30 Exosphere Decreasing Air Pressure #39 600 Altitude (km) #31 Thermosphere #40 90 #32 Mesosphere #41 50 #35 Ionosphere #36 Mesopause #37Stratopause #33 Stratosphere #38Tropopause #42 15 #34 Troposphere -100 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. -80 -60 -40 -20 0 20 Temperature (C) #43 Troposphere-closest to earth i. Nearly 80% of the total mass of the atmosphere ii. most weather occurs in this layer iii. most pollutants stay here #44 Stratosphere i. solar energy absorbed by ozone layer 1. Ozone = O3 absorbs harmful UV rays 2. Without it skin cancer would be high 3. destroyed by chlorofluorocarbons and aircraft fuel ii. #45 volcanic gases remain here #46 Mesosphere i. meteors burn up here #47 Ionosphere i. highly #48 ionized from UV rays from the sun knocking electrons off oxygen and Nitrogen ii. can disrupt #49 radio communications. iii. northern lights-Aurora Borealis Thermosphere i. Temp. increases to above 1000C Exosphere-outermost layer i. most satellites are here, basically like space The pauses-transitions between layers and temperature remains same i. #50 Tropopause ii. #51 Stratopause iii. #52 Mesopause