Lecture 8: Analysis of Variance Formal Analysis Partitioning Variability
advertisement

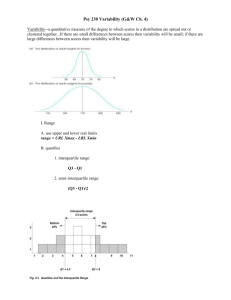
Lecture 8: Analysis of Variance Formal Analysis Partitioning Variability The Analysis of Variance – ANOVA Quantify the total amount of variability and split it among the sources. Total Variability Variability due to treatments effects. + Variability due to chance (random) error. Measurement Experimental Material Planned Systematic 1 Total Variability 2 Total Variability ∑ How much variability is there for the entire set of experimental data? Compute a sample variance. 4140.95 19 1 3 4 Partitioning Variability Partitioning Variability Sum of Squares C Total Degrees of Freedom C Total Sum of Squares Treatments + Degrees of Freedom Treatments Sum of Squares Error 5 + Degrees of Freedom Error 6 1 Lecture 8: Analysis of Variance Treatments SSTreatment Estimated Treatment Effects ̂ 50 mmol Na/day: 143.10 – 153.05 = –9.95 = 10(–9.95)2 + 10(+9.95)2 = 1980.05 200 mmol Na/day: 163.00 – 153.05 = +9.95 7 8 Random Error SSError Pool the sums of squares within each treatment by creating the weighted sum of treatment sample variances. 1 = 9(11.75)2 + 9(10.10)2 = 2160.9 9 Degrees of Freedom 10 Analysis of Variance Source Treatment: number of treatments minus 1, (k – 1) Error: total number of observations minus the number of treatments, (N – k) 11 df Sum of Mean F Ratio Prob > F Squares Square Diet 1 1980.05 1980.05 16.4935 Error 18 2160.90 C. Total 19 4140.95 0.0007* 120.05 12 2 Lecture 8: Analysis of Variance Test of Hypothesis F Ratio F Ratio is the mean square for treatment divided by the mean square error. : : or : : 13 14 F Ratio Prob > F A large F Ratio indicates that differences between treatment sample means are larger than random error. This is the P-value for the F Ratio. 15 16 Prob > F Decision Small P-values (<0.05) indicate that difference in treatment sample means are statistically significant. The F Ratio=16.4935 and Pvalue=0.0007. The small P-value indicates that the difference in treatment sample means is statistically significant. 17 18 3 Lecture 8: Analysis of Variance Generalization JMP For men with Stage 1 hypertension, a low sodium diet (50 mmol Na/day) will result in lower average blood pressure than a high sodium diet (200 mmol Na/day). Analyze Fit Y by X Y, Response: Systolic BP X, Factor: Diet 19 20 Menu next to Oneway Oneway Analysis of Systolic BP (mmHg) By Diet 200 Means and Std Dev Means/ANOVA/pooled t 150 100 050 mmol/day 200 mmol/day Diet 21 22 23 24 Means and Std Dev 4