Lecture 5: CI’s, Three Decisions Generalization Effect Size
advertisement

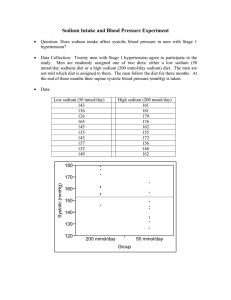
Lecture 5: CI’s, Three Decisions Generalization Effect Size Men with Stage 1 hypertension on a 50 mmol/day Na diet will have lower average blood pressure than men on a 200 mmol/day Na diet. How much lower, on average, will the blood pressure be with the 50 mmol/day diet? 1 Estimated Effect Size 2 Confidence Interval The difference in sample means is an estimate of the difference in population means. 19.9 mmHg lower, on average. 1 ∗ Difference ∗ 1 Std ErrDif 3 t Distribution 4 Confidence Interval 19.9 df 80% 90% 95% 98% 99% 2.101 10.96 2=18 ∗ =2.101 1 10 1 10 –19.9 2.101 4.90 –19.9 10.3→ 30.2, 9.6 5 6 1 Lecture 5: CI’s, Three Decisions Interpretation Generalization We are 95% confident that the difference between the population means is between –30.2 mmHg and –9.6 mmHg. Men with Stage 1 hypertension on a 50 mmol/day Na diet will have an average blood pressure from 9.6 to 30.2 mmHg lower than men with Stage 1 hypertension on a 200 mmol/day Na diet. 7 Generalization 8 3 Principles Control Replication Randomization Note that the generalization is talking about men with Stage 1 hypertension in general not the men who participated in the experiment. 9 3 Decisions 10 Response What is the response? What are the treatments? What is the experimental material? You have to decide what response variable you will use in your experiment. 11 12 2 Lecture 5: CI’s, Three Decisions Example Treatments Blood pressure after three months on the diet. Change in blood pressure. You have to decide what factor you will manipulate to make treatments. 13 Example 14 Experimental Material Manipulated factor – amount of sodium in the diet. Treatments You have to decide what experimental material will be used in the experiment. 50 mmol/day 200 mmol/day 15 Example 16 Caution Experimental material consists of men with Stage 1 hypertension. There is a difference between experimental material and experimental units. 17 18 3 Lecture 5: CI’s, Three Decisions Difference Example Treatments are applied to experimental units. Experimental units can be groups of experimental material. Response: Weight gain of hogs (pounds). Treatments: Normal feed, Feed with additive (Paylean). Experimental Material: hogs. 19 20 Experimental units Experimental units There are 10 hogs is each of 20 pens. Each pen is randomly assigned one of the treatments, Normal or Paylean. Because the treatment, type of feed, is applied to the pen, the pen is the experimental units. Response is really the average weight gain of hogs in a pen. 21 Alternative 22 Caution If pigs were fed individually, then the individual hog would be the experimental unit. Identifying what is the experimental unit is very important! 23 24 4