Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports Group Lead: Sponsor:
advertisement
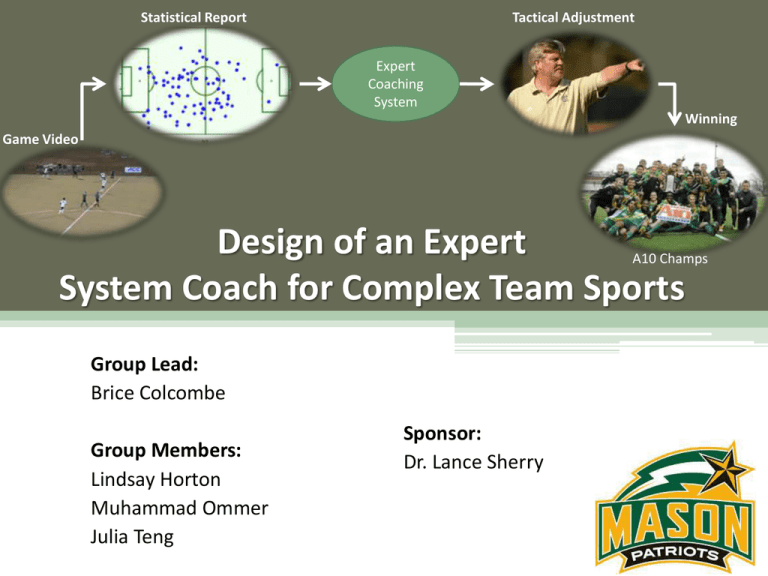
Statistical Report Tactical Adjustment Expert Coaching System Winning Game Video Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports A10 Champs Group Lead: Brice Colcombe Group Members: Lindsay Horton Muhammad Ommer Julia Teng Sponsor: Dr. Lance Sherry 2 Agenda • • • • • • • • • Context Stakeholder Analysis Problem/ Need Statements Concept of Operations Mission/Functional/Design Requirements Simulation Risks Project Plan Next Steps Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 3 Objective of Game • Soccer: Game between two teams of ten field players and one goalie per team • Main Focus: George Mason University Men’s Soccer Team • Field: A standard NCAA regulated field is 115-120 yds (length) by 70-75 yds (width) including two goals that are defended on either side of the field. • Objective: The object of the game is to score more goals than the other team Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 4 Strategy • Offense: ▫ Connect a series of passes to get around and through the opposing team’s defense by using numerical advantage • Defense: ▫ Win the ball back from opposing team ▫ Do not allow the opposing team to get near your goal with the ball causing them to not score any goals 5 Strategies: Common Formations 4-3-3 4-4-2 Coaching Rules Inverting the Pyramid: A History of Football Tactics (Jonathan Wilson) Figure 4: 4-3-3 Formation Figure 3: 4-4-2 Formation Types: Numerical Advantages: Types: Numerical Advantages: • • • • • • • • • • • Flat Wide Diamond Narrow Diamond Numbers out wide Support for attacking Disadvantages: • Flat 2 Holding Midfielders 2 Attack Midfielders High/Low Wings Outnumbered in middle Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports Attack-centric Strong central midfield presence Disadvantages: • • Open to counterattack Open on outside 6 Complexity of Soccer • Baseball vs. Soccer: Discrete vs. Flowing • Players have to make own decisions in order to benefit the team • Players have to adapt to the situations around them • No instructions/stoppages until halftime • Network Complexity of Soccer: Netcentricity Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 7 How Coaching is Done • Traditional ▫ Use coaching expertise ▫ Watch practices/games, make changes accordingly ▫ Cannot ‘see’ full complexity of game • New Generation ▫ Use data analysis to find holes in strategy, make changes accordingly ▫ Able to ‘see’ patterns and complexity of game • Hybrid Mix of Traditional and New Generation ▫ Use a mix of the two coaching strategies Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 8 Current Process Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 9 NCAA Tournament • It is a single elimination tournament with a total of 48 teams • 22 teams get an automatic bid from winning their conference championships • The remaining 26 teams get an at large bid based on their teams rating percentage index (RPI) score Source: NCAA (2015) Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 10 Rating Percentage Index [RPI] • Consists of Three Parts: 1. Teams Winning Percentage (Expert Coaching System) 𝑊+ 𝑇 2 𝑊+𝐿+𝑇 W = win, L = loss, and T = tie 2. Opponents Average Winning Percentage (Schedule Planning) 𝑂𝑊+ 𝑂𝑇 2 𝑂𝑊+ 𝑂𝑇 −1 2 (𝑂𝑊−1)+ 𝑂𝑇 2 , , 𝑂𝑊+ 𝑂𝐿−1 +𝑂𝑇 𝑂𝑊+𝑂𝐿+(𝑂𝑇−1) (𝑂𝑊−1)+𝑂𝐿+𝑂𝑇 (win , tie, loss) OW = Opponent’s win, OL = opponents loss, and OT = opponents tie 3. Teams A’s Opponent’s Opponents Average Winning Percentage (Schedule Planning) 𝑥 of Team A’s opponents’ part 2 Combine the three parts: 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡 1 + 2 ∙ 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡 2 + 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑡 3 𝑹𝑷𝑰 = 4 Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 11 Historical Atlantic 10 Data (2004-2014) GMU vs SLU Winning Percentage A-10 Historic Winning Percentages 80% 74% 100% 90% 60% 50% 44% 51% 52% 52% 57% 37% 37% 40% 30% 46% 48% 55% 23% 20% 60% 80% Winning Percentage Winning Percentage (past ten years) 70% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 10% 0% 0% 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 GMU Winning Percentage: 𝑊+ 𝑇 2 𝑊+𝐿+𝑇 Saint Louis GMU Average Saint Louis Source: Atlantic 10 Team Archives (2015) Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 12 What a Win is Worth School UCLA Maryland UI UNC URI VCU UVA GMU UMASS Salary Win % 205,000 75% 206,000 71% 176,225 62% 88,044 58% 72,500 55% 90,640 55% 115,400 52% 90,855 51% 108,681 47% Conference Wins 4 4 1 1 2 0 2 2 1 NCAA Years Coaching Total Championships at School Experience 4 12 14 2 23 25 3 6 12 2 5 23 0 3 12 0 6 15 2 20 26 0 11 24 0 1 24 Average Salary: $158,133.80 Average Atlantic 10 Coach: $90,676.50 GMU Head Coach worth per win: $9,085 A national championship level coach gets paid on average $67,457.30 per year more than an Atlantic 10 coach. Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 13 Gap Analysis Replicate Saint Louis Success By: 1. Win Atlantic 10 Conference Championship 2 times every 5 years 2. Receive an NCAA Bid 6 times every 10 years 3. Average RPI Score of .56 Resulting success will help close head coaches salary gap of $67,000 Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 14 Agenda • • • • • • • • • Context Stakeholder Analysis Problem/ Need Statements Concept of Operations Mission/Functional/Design Requirements Simulation Risks Project Plan Next Steps Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 15 Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 16 Stakeholder Analysis Class Stakeholder Goals Tensions Head Coach Produce a team that gives highest probability of winning Keep job, get next big job Assistant Coaches Scout best players for the team Prepare the team for games Become head coach Player Perform at highest level Get to next level (pro) Pressure from University to win Old school coaching ideals Disagreements with head coach Doesn’t always have a say in decisions Not getting played by coach Playing on a losing team Trainers Have as few injuries as possible Rehab injured players Can’t always control how hard coach pushes players Investors (University) Fund a winning team Make money through ticket and memorabilia sales Market the University in a positive fashion Want immediate success (not always possible) Budget is only so big Primary Secondary Parents Academies Tertiary Data Analytic Companies Invest money in youth development in hopes of college scholarships and professional contracts Train youth players in hopes of signing with professional clubs Earn revenue from data software sales Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports Can’t be involved with coaches like at the youth level Players move, go onto college Multiple data companies competing with one another 17 Problem Statement George Mason University Men’s Soccer Team is not consistently achieving NCAA Tournament bids at a high rate (2 bids out of last 10 years). Need Statement There is a need for a coaching tool that uses coaching expertise and uses soccer game data to understand the complexity of soccer and seek a competitive advantage in order to increase the probability of an NCAA Tournament bid to 3 bids out of every 5 years. Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 18 Solution Concept of Operations Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 19 Mission Requirements Mission Requirement # Requirement Description MR. 1.0 The Expert Coaching System (ECS) shall recommend XX possible strategies based on game data gathered in real time. MR. 2.0 The ECS shall recommend XX possible strategies based on gameplay data gathered by half-time MR. 3.0 The ECS shall recommend XX possible strategies based on gameplay data gathered by overtime. Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 20 Functional Requirements Functional Requirement # FR. 1.0 Requirement Description The ECS shall run a simulated soccer game derived from collected gameplay data. FR. 2.0 The ECS shall accurately recognize soccer field patterns using probability maps 90% of the time. FR. 3.0 The ECS shall accurately quantify pass rate probabilities inbetween the 14 zones from game data 95% of the time. FR. 4.0 The ECS shall accurately determine goal probability rates that can be made from each of the 14 zones. Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 21 Design Requirements (Input/Output) Input Requirement # Requirement Description IR. 1.0 The ECS shall input statistics from Sports Data company providers. IR. 2.0 The ECS shall input zone graph percentages from InStat to run the simulation. IR. 3.0 The ECS shall input XX coaching rules to be used to make adjustments. Output Requirement # Requirement Description The ECS shall output a table showing the relationship between OR. 1.0 current formations utilized and possible adjustments that are recommended by the system. The ECS shall output correct coaching adjustments that result in OR. 2.0 30% greater chance of winning OR. 3.0 The ECS shall output tactical adjustments xx amount of hours after receiving game data from Data analytics’ providers. Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 22 Agenda • • • • • • • • • Context Stakeholder Analysis Problem/ Need Statements Concept of Operations Mission/Functional/Design Requirements Simulation Risks Next Steps Project Plan Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 23 Simulation • Objective: To simulate a game based on game data and see if the coaching system rules will impact the outcome of the game. • Input: Input passing data that is transformed into probability maps that are inputted into the simulation • Output: table of passing percentages and strategy changes • Simulates a 90 minute game (two 45 minute halves) using passing probability maps and different ball movements • Simulation based on previous refereeing senior design project: Assessment of soccer Referee Proficiency in Time-Sensitive Decision Making Jones et.al.(2013) • Currently over 10,000 lines of code Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 24 Simulation Requirements Simulation Requirements # Requirement Description The simulation shall input zone graph data consisting of 14 zones of SR 1.0 a standard NCAA soccer field. SR 2.0 The simulation shall follow strategies of George Mason University Men’s Soccer Team formations. SR 3.0 The simulation shall follow 1 set of probability maps per strategy. SR 4.0 The simulation shall update the probability map of successful passing rate percentages once the ball moves from one zone to another. SR 5.0 The simulation shall change the possession of the ball after a shot or intercepted pass. SR 6.0 The simulation shall calculate average player location within 1 of the 14 zones in order to determine feasible pass rates from zone to zone. Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 25 Probability Maps • Total of 15 probability maps per strategy • 14 cell grid • 13 possible passing opportunities per map • Once the ball has successfully been passed to a new zone the probability map will change Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 26 Netcentricity – (Flow Centrality) SHOT Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 27 Ball Movement Interaction Diagram Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 28 Simulation Interface Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 29 Output Table Time From Zone To Zone Possession Action Successful 80:08 7 6 Home Pass Yes 80:10 6 7 Home Pass Yes 80:11 7 7 Home Dribble Yes 80:15 7 10 Home Pass No 80:17 10 13 Away Pass No 80:21 13 13 Home Dribble Yes 80:25 13 14 Home Pass Yes 80.29 14 14 Home SHOT GOAL Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 30 Field Functions Function Zones 4-3-3 Flat 4-3-3 Triangle 4-4-2 Flat 4-4-2 narrow Diamond Right Wing Zone 10 - 13 40% 30% 30% 25% Left Wing Zone 0-3 40% 30% 30% 25% Middle Zone 4-9 20% 40% 40% 50% Defense Zone 0,4,5,10 20% 25% 20% 20% Midfield Zone 1,2,6,7,11,12 50% 55% 50% 55% Forward Zone 3,8,9,13 30% 20% 30% 25% 31 Coaching Rules (Numerical Advantage) Current Strategy 4-3-3 Flat RWZone <= 40% and LWZone<= 40% Tactical Change 4-3-3 Triangle Message: Ball needs to get out wide because passing in wing zones is xx change formation Dzone > 20% and Fzone is <= 30% 4-4-2 Flat Message: Ball is being passed to much in the defensive zone and not enough attacking is occurring. Switch formation to 422 flat. Current Strategy meets criteria Message: continue to play with current strategy. Current Strategy 4-3-3 Flat Tactical Change RWZone <= 40% and LWZone<= 40% 4-3-3 Triangle Dzone > 20% and Fzone is <= 30% Message: Ball needs to get out wide because passing in wing zones is xx change formation 4-4-2 Flat Current Strategy meets criteria Message: Ball is being passed to much in the defensive zone and not enough attacking is occurring. Switch formation to 422 flat. Message: continue to play with current strategy. Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 32 Coaching Rules (Numerical Advantage) Current Strategy 4-4-2 Flat RWZone <= 30% and LWZone<= 30% Dzone > 20% and Mzone is <= 50% Current Strategy meets criteria Tactical Change 4-2-2 Diamond Message: Ball needs to get out wide because passing in wing zones is xx change formation 4-4-2 Diamond Message: Ball is being passed too much in the defensive zone and not enough attacking is occurring. Switch formation to 4-4-2 diamond to get the ball in the midfield and forward. Message: continue to play with current strategy. Current Strategy 4-4-2 Narrow Diamond Tactical Change MidZone<= 50% 4-3-3 Triangle Midzone <= 50% Message: Need to find central midfielders with the ball. Change to a 4-3-3 triangle and get ball inside. 4-4-2 Flat Current Strategy meets criteria Message: Ball needs to go through the middle more. Switch to a 4-4-2 flat to get the ball to the wider flanks. Message: continue to play with current strategy. 33 Validation of Concept of Operations Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 34 Score Differential from Monte Carlo Simulation 35 Design of Experiment Formations Replications Flat Right Wing Zone Left Wing Zone Middle Zone Flat ≤ 30% ≤ 40% Get ball wide 4-4-2 Diamond > 30% > 30% > 40% Continue Strategy None ≤ 25% ≤ 25% ≤ 50% Find central players 4-3-3 Triangle > 25% > 25% > 50% Continue Strategy None ≤ 40% ≤ 40% ≤ 20% > 40% > 40% > 20% Continue Strategy None ≤ 30% ≤ 30% ≤ 40% Find central players 4-4-2 Flat > 30% > 30% > 40% Continue Strategy None 250 250 250 4-3-3 Triangle Tactical Change ≤ 30% 4-4-2 Diamond Message 250 Get ball wide 4-3-3 Triangle The above design of experiment focuses on the various formations and the equivalent right, left and middle zone passing percentages 36 Design of Experiment Formations Flat Replications Defense Zone Midfield Zone Forward Zone Message Tactical Change ≥ 20% ≤ 50% ≤ 30% Get ball higher 4-4-2 Diamond < 20% > 50% > 30% Continue Strategy None ≥ 20% ≤ 55% ≤ 25% Find central players 4-4-2 Flat < 20% > 55% > 25% Continue Strategy None ≥ 20% ≤ 50% ≤ 30% Get ball high 4-4-2 Flat < 20% > 50% > 30% Continue Strategy None ≥ 25% ≤ 55% ≤ 20% Find higher players 4-4-2 Diamond < 25% > 55% > 20% Continue Strategy None 250 4-4-2 Diamond Flat 250 250 4-3-3 Triangle 250 The above design of experiment focuses more on the defensive, midfield and forward zone passing percentages in order to run the various different formations 37 System Risks Risk Category Safety Money Bad Advice Expert System Rules Simulation What is the risk Risk Mitigation Will this system hurt someone? Verify the system doesn’t put human life into risk Will this system lose money? Compare win probability using system with how much each win is worth Test system with XX scenarios Will this system give bad advice? and verify accurate results with coaches Talk to XX coaches to get Will accurate rules input into the various opinions of accurate system? rules Will the simulation of the system Create XX scenarios to test be accurate? simulation Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 38 Agenda • • • • • • • • • Context Stakeholder Analysis Problem/ Need Statements Concept of Operations Mission/Functional/Design Requirements Simulation Risks Project Plan Next Steps Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 39 Work Breakdown Structure Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 40 Critical Path Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 41 Budget Task Number Tasks Predicted Hours 1 Expert Coaching System 2326 $ 116,300.00 1.1 Management 70 $ 3,500.00 1.2 Research 308 $ 15,400.00 1.3 CONOPS 93 $ 4,650.00 1.4 Originating Requirements 80 $ 4,000.00 1.5 Design Alternatives 85 $ 4,250.00 1.6 Design Of Experiment 88 $ 4,400.00 1.7 Simulation 995 $ 49,750.00 1.8 Analysis 130 $ 6,500.00 1.9 1.1 Conclusion 100 $ 5,000.00 Presentations 107 $ 5,350.00 1.11 Documentation 270 $ 13,500.00 Total Cost = (Average Junior SE salary per hour) * Overhead Cost * Predicted Hours Source : GMU Office of Budget and Planning Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports Cost 42 Project Cost Analysis (week 1-14) $60.00 Cost (Thousands) $50.00 $40.00 $30.00 $20.00 $10.00 $0 2 4 Planned Value 6 8 Time (weeks) Actual Cost 10 Earned Value Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 12 14 16 43 Performance Indices (week 1-14) 1.80 1.60 Performance Index 1.40 1.20 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 0.00 0 2 4 6 Cost Performance Index (CPI) 8 Time (weeks) 10 12 Schedule Performance Index (SPI) Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 14 16 44 Project Risks Critical Tasks Data Collection Coaching Rules Develop Simulation Cost Analysis Foreseeable Risks Mitigation • Unable to get GMU Men’s Soccer Team data • Use Instat dashboard to look at other college Team’s data • Inaccurate rules input in the system • Talk to XX coaches to get various opinions of accurate rules • Unable to run simulation • correctly The simulation of the system is • inaccurate Test and debug while developing simulation Using Monte Carlos simulation to test it XX times • Work more hours than planed to ensure project is on schedule Work more hours than planned to ensure actual cost is under budget • • • Schedule Variance is negative Cost Variance is negative • Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 45 Next Steps (WBS) • • • • • • Design of Experiment (1.6) Continue to add complexity to simulation (1.7.2.3) Analysis (1.8) Validation and Verification (1.9.2) Recommendations (1.9.4) Documentation (1.11) Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports “Only those who can see the invisible can do the impossible” 46 -Frank L. Gaines Special Thanks • 2014 Referee Proficiency Senior Design Project (Jones, Cann, Almashhadi, Popal) Tom Morrell Design of • an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 47 References • [1] Virginiasports.com, 'VIRGINIASPORTS.COM - The University of Virginia Official Athletic Site - UVa Men's Soccer', 2015. [Online]. Available: http://www.virginiasports.com/sports/m-soccer/archive/va-m-soccerarchive.html. [Accessed: 25- Oct- 2015]. • [2] Uclabruins.com, 'Men's Soccer - Schedule - UCLA Bruins Official Athletic Site | UCLABruins.com', 2015. [Online]. Available: http://www.uclabruins.com/SportSelect.dbml?SPSID=749841&SPID=126914&DB_OEM_ID=30500&Q_SEASON =2013. [Accessed: 25- Oct- 2015]. • [3] Atlantic10.com, 'Men's Soccer - News - Atlantic 10 Conference Official Athletic Site', 2015. [Online]. Available: http://www.atlantic10.com/SportSelect.dbml?DB_OEM_ID=31600&SPID=136213&SPSID=799925. [Accessed: 25- Oct- 2015]. • [4] Soccer-training-guide.com, 'The 4-3-3 is a Highly Popular Formation', 2015. [Online]. Available: http://www.soccer-training-guide.com/4-3-3.html#.Vi1ul36rTIU. [Accessed: 25- Oct- 2015]. • [5] J. Duch, J. Waitzman and L. Amaral, 'Quantifying the Performance of Individual Players in a Team Activity', PLoS ONE, vol. 5, no. 6, p. e10937, 2010. • [6] J. Perez, Concepts and Coaching Guidelines, 1st ed. U.S Soccer Curriculum, 2015 [Online]. Available: http://resources.ussoccer.com/n7v8b8j3/cds/downloads/Part%202%20%20Concepts%20and%20Coaching%20Guidelines%20U.S.%20Soccer%20Coaching%20Curriculum.pdf. [Accessed: 20- Oct- 2015] • [7] J. Maxcy and J. Drayer, Sports Analytics: Advancing Decision Making Through Technology and Data, 1st ed. Philadelphia: Fox School of Business, 2014 [Online]. Available: http://ibit.temple.edu/wpcontent/uploads/2014/04/IBITSportsanalytics.pdf. [Accessed: 20- Oct- 2015] • [8] Sites.google.com, 'RPI: Formula - RPI for Division I Women's Soccer', 2015. [Online]. Available: https://sites.google.com/site/rpifordivisioniwomenssoccer/rpi-formula. [Accessed: 20- Oct- 2015] • [9] Budget, 'Fiscal Year 2015-2016', 2015. [Online]. Available: http://budget.gmu.edu/fiscal-year-2015-2016/. [Accessed: 16- Nov- 2015]. Back-Up 49 Complexity of Coaching Figure 2: Coaches role in sports team dynamics Source : Concepts and Coaching Guidelines Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 50 Soccer Analytics 10/21/2015 • Not much is known about Soccer Analytics before 1996. – Influenced by the movement of data analytics in other major sports – The Sabermetrics model in MLB got the ball rolling in the 1970’s (Oakland Athletics first used) • Using big data to make decisions in areas such as : pricing, management, player development, and training. Figure 5: Percentages of sports that employ data analysis Source : Sports Analytic: Advancing Decision Making Through Technology and Data Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 51 Soccer Analytics (cont’d) 10/21/2015 • The emergence of modern sports data companies – Opta – 1996 – began collecting data for English Premier league teams • Initial Data Collection approach – Number of passes – Number of tackles – Distance travelled – Prozone – 1998 – providing multiple performance analysis packages to major football clubs including: » Manchester United (1999) » Real Madrid (2006) » US Major League Soccer (2008) Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 52 Current Process Challenges: • Patterns are inconsistent from game to game • A lot of pressure on coaches to make successful decisions • Limited time between games 52 53 What a Win is Worth 10/21/2015 Winning Percentage vs. Salary 80% Coference Win Percentage 70% 60% 50% 40% y = 1E-06x + 0.3963 R² = 0.6994 30% 20% 10% 0% 0 50,000 100,000 150,000 200,000 Head Coaches Salary Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 250,000 54 Statistical Data (InStat) Team Individual Player Stats Challenges, lost ball, recoveries 130 Total actions 25 Participating Attacks 52 Challenges 9 Set pieces 13 Indexes 4 Passes 13 Passes 11 Action Maps 12 Action Graph (time x actions) 12 Ball Possession 10 Successful Actions Graph (time x actions) 12 Attacks 14 Average Position Player Maps 3 Above data time in game (15min) Pass Distribution Table 1 Zones Pass Distribution Maps 1 Actions Successful 14 Dangerous attack maps 10 Passes Accurate 14 Challenges won 14 % Challenges won 14 Overall Player tables 104 Overall Player Maps 16 Overall Player Zones 97 Total of 707 Statistics for each team evaluated 102 54 55 InStat Data 56 Input Data 57 10/21/2015 Statement of Work • Scope of work includes all planning, design, implementation, risk mitigation and validation of the expert coach system • Responsible for allocating the proper resources to the proper phases in creating the system. Design of an Expert System Coach for Complex Team Sports 58 Cost Analysis $140.00 $120.00 Cost (Thousands) $100.00 $80.00 $60.00 $40.00 $20.00 $0 5 10 Planned Value 15 20 Time (weeks) Actual Cost 25 Earned Value 30 35 40 59 Critical Path 60 Critical Path 61 Critical Path 62 Critical Path