SHORT STORY/NOVEL TERMS PLOT PLOT OUTLINE INTRODUCTION
advertisement

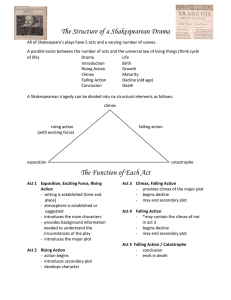
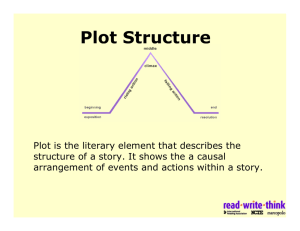
SHORT STORY/NOVEL TERMS PLOT - a series of events leading to a major crisis or resolution. PLOT OUTLINE - introduction, trigger incident, rising action, major climax, falling action, resolution. INTRODUCTION: setting and characters are introduced. TRIGGER INCIDENT: the event that introduces a problem or conflict. RISING ACTION: events leading to a major crisis. MAJOR CRISIS: the turning point in the plot. CLIMAX: the most exciting or emotional high - sometimes occurs at the same time as the major crisis. FALLING ACTION: events fall into place. RESOLUTION: also called conclusion, where the problem or conflict is completely resolved or better understood. SHORT STORY TERMS continued CONFLICT: someone/something opposing someone/something else TYPES OF CONFLICT: Internal - personal struggle Types: personal vs. self External - person(thing) struggles against an outside force or person Types: person vs. person person vs. nature person vs. machine person vs. society person vs. supernatural person vs. technology nature vs. nature machine vs. machine EXPOSITION: giving necessary background information throughout the story. SETTING: the time, place and circumstance of the story. ATMOSPHERE: the mood or general feeling of the story. TONE: feeling conveyed by the author’s attitude. THEME: the central idea, general truth or commentary on life or people, the MESSAGE or MEANING of a piece of work. TECHNIQUES USED IN WRITING SATIRE: criticizing anybody/anything by ridiculing them. Blending a critical attitude with humour and wit. IRONY: intended meaning is opposite to what is expressed, a situation which develops in an unexpected way. FORESHADOWING: a hint of something that will happen in the future. PERSONIFICATION: human qualities given to non-living things. SIMILE: comparison of two unlike things using “like”, “as” or “than” METAPHOR: comparison of two unlike things without using like or as CHARACTER In a Short Story there is a main character involved in a single conflict. PROTAGONIST: main character ANTAGONIST: someone or something that opposes the main character. DYNAMIC CHARACTER: goes through a CHANGE of character or LEARNS something. STATIC CHARACTER: does not learn or change. Character is revealed by: 1) ACTION - what the character does 2) WORDS - what the character says 3) REACTIONS - by other characters 4) REPORTING - what other characters say 5) NARRATION - what the story teller tells us