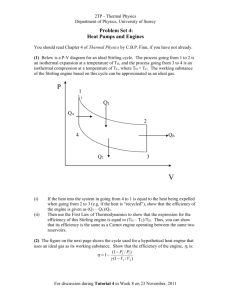
PES S 213 Gen eral Physi ics III
advertisement
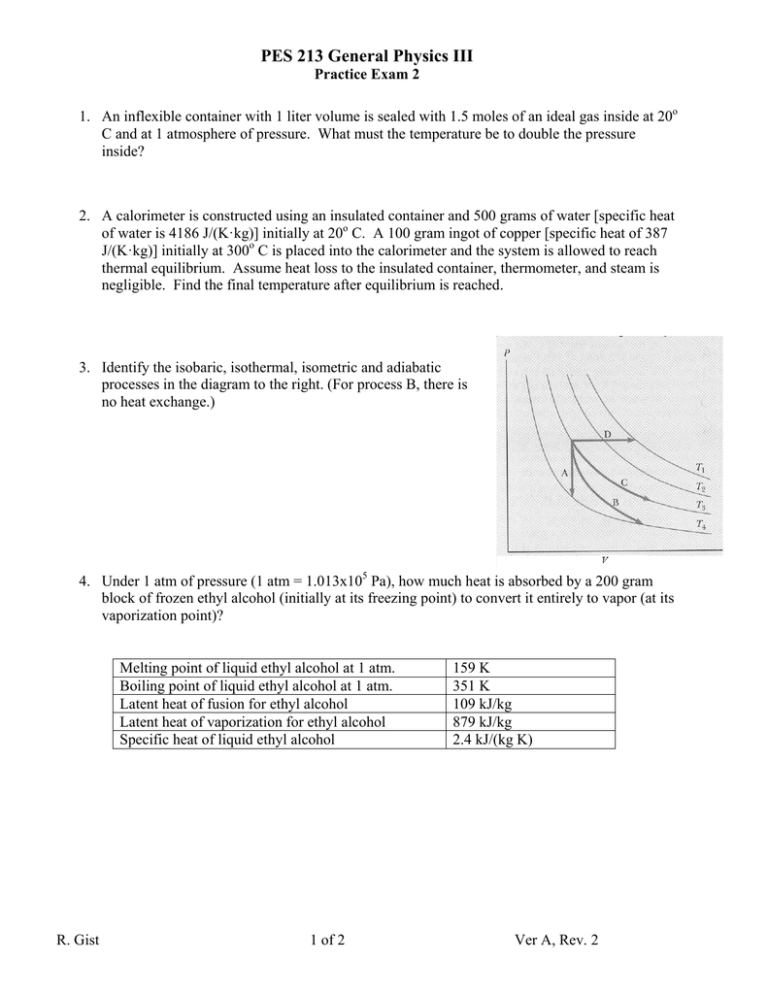
PES S 213 General Physiics III Practicce Exam 2 1. An infllexible contaainer with 1 liter volumee is sealed wiith 1.5 moles of an ideall gas inside at a 20o C and at a 1 atmosph here of pressure. What must m the tem mperature be to double thhe pressure inside?? 2. A calorrimeter is co onstructed ussing an insullated containner and 500 grams g of waater [specific heat of wateer is 4186 J/((K·kg)] initially at 20o C. C A 100 graam ingot of copper c [speccific heat of 387 J/(K·kgg)] initially at a 300o C is placed p into the t calorimeter and the system s is alloowed to reacch thermal equilibrium m. Assume heat h loss to the t insulatedd container, thermometer t r, and steam is negligible. Find th he final tempperature afterr equilibrium m is reached.. 3. Identifyy the isobariic, isothermaal, isometric and adiabatic processses in the diaagram to thee right. (For process p B, thhere is no heatt exchange.) 4. Under 1 atm of preessure (1 atm m = 1.013x1005 Pa), how much m heat iss absorbed by a 200 gram m block of o frozen eth hyl alcohol (iinitially at itss freezing pooint) to convvert it entirelly to vapor (at its vaporizzation point))? Mellting point off liquid ethyl alcohol at 1 atm. Boilling point off liquid ethyll alcohol at 1 atm. Lateent heat of fu usion for ethhyl alcohol Lateent heat of vaaporization for f ethyl alcohol Speccific heat off liquid ethyl alcohol R. Gist 1 of 2 159 K 351 K 109 kJ/kkg 879 kJ/kkg 2.4 kJ/(kkg K) Ver A, Reev. 2 PES 213 General Physics III Practice Exam 2 5. A 2 mole sample of an ideal gas is subjected to compression at a constant pressure of 1.5 atmospheres from a volume of 1 liter to a volume of 0.5 liters. How much work was required for this compression? If the temperature only rises from 20o C to 23o C during this process, how much heat flowed out of the ideal gas? [Universal Gas Constant: R=8.314 J/(mol·K)=0.08206 L atm/(mol·K), 1 atm = 1.013x105 Pa] 6. A particular heat engine operates between two temperatures, 100 o C and 300o C. Each engine cycle takes 0.1 seconds to complete. During each cycle, 120 J is transferred out of the hot reservoir and 100 J is transferred into the cold reservoir. What is the efficiency of this heat engine? What power is generated by this engine? What is the efficiency of a perfect (Carnot) engine operating between these two reservoirs? 7. A heat pump is running as a refrigerator. It is found that for each cycle, 10 J of heat are extracted from the cold reservoir and 15 J of heat enter the hot reservoir. What is the coefficient of performance of this heat pump? 8. A 3 mol sample of an ideal gas at 20o C contained in a .25 L jar. The jar is then connected to a 1 L evacuated chamber (by a tube of negligible volume) and allowed to expand into the chamber with a negligible temperature change. How much has the entropy of the universe changed in this process? How much potential work is forever lost? [possible processes on exam: isothermal & isobaric phase change, free expansion of ideal gas, or heat transfer from one reservoir to another] 9. How much longer will a slot in a copper plate be if it is 2 cm at 20o C after the plate is heated to 1000o C [Coefficient of linear thermal expansion for copper is 17x10-6 1/K]? 10. A bunker wall is constructed of concrete, an air gap, and an inner layer of steel. The concrete wall is 8 cm thick [thermal conductivity of concrete is 0.15 W/(m·K)]. The inner wall is 1 cm thick and made of steel [thermal conductivity=46 W/(m·K)]. The air gap between the two walls is 1 cm wide [thermal conductivity of still air at 27o C is 0.026 W/(m·K)]. What is the rate of heat loss through an area 4 meters by 1 meter if the interior temperature is 27o C and the exterior temperature is 0o C? R. Gist 2 of 2 Ver A, Rev. 2