MAE-2104 – Engineering Mechanics II
advertisement
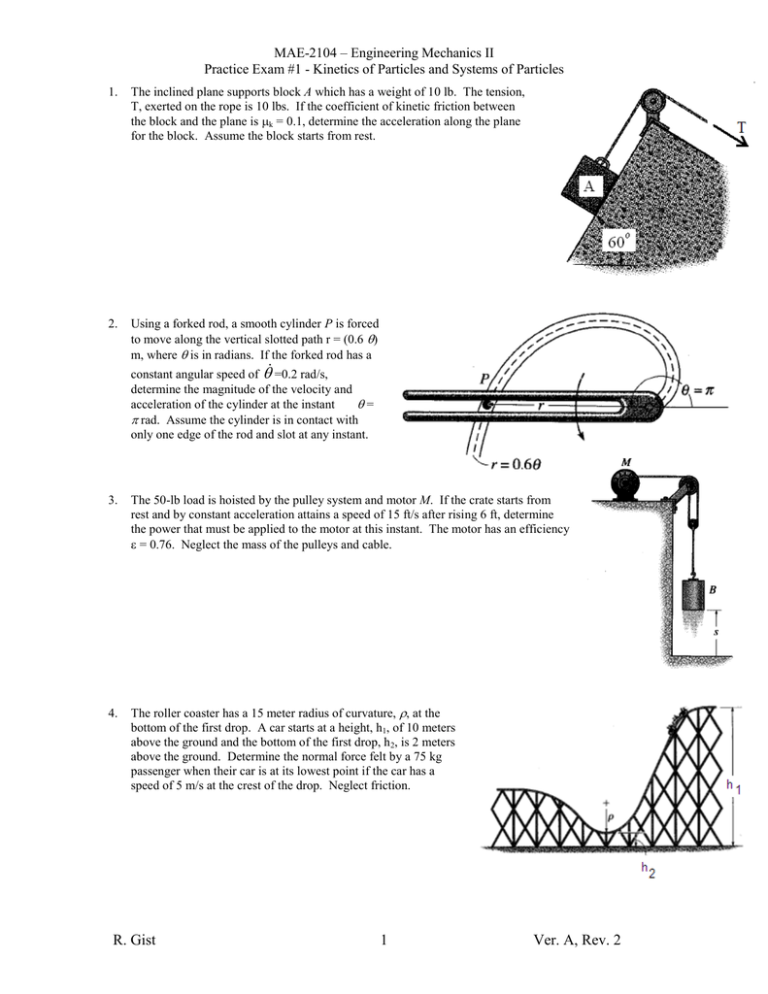
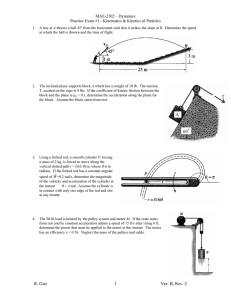
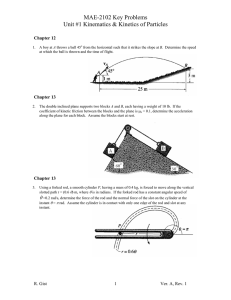
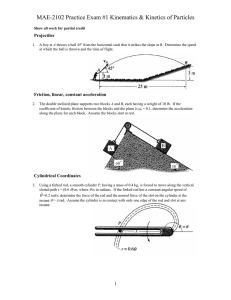
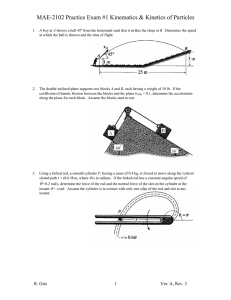
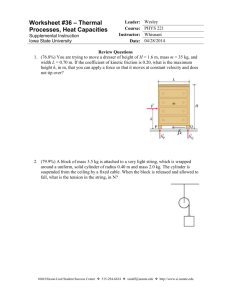
MAE-2104 – Engineering Mechanics II Practice Exam #1 - Kinetics of Particles and Systems of Particles 1. The inclined plane supports block A which has a weight of 10 lb. The tension, T, exerted on the rope is 10 lbs. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane is k = 0.1, determine the acceleration along the plane for the block. Assume the block starts from rest. 2. Using a forked rod, a smooth cylinder P is forced to move along the vertical slotted path r = (0.6 ) m, where is in radians. If the forked rod has a constant angular speed of =0.2 rad/s, determine the magnitude of the velocity and acceleration of the cylinder at the instant = rad. Assume the cylinder is in contact with only one edge of the rod and slot at any instant. 3. The 50-lb load is hoisted by the pulley system and motor M. If the crate starts from rest and by constant acceleration attains a speed of 15 ft/s after rising 6 ft, determine the power that must be applied to the motor at this instant. The motor has an efficiency = 0.76. Neglect the mass of the pulleys and cable. 4. The roller coaster has a 15 meter radius of curvature, , at the bottom of the first drop. A car starts at a height, h1, of 10 meters above the ground and the bottom of the first drop, h2, is 2 meters above the ground. Determine the normal force felt by a 75 kg passenger when their car is at its lowest point if the car has a speed of 5 m/s at the crest of the drop. Neglect friction. R. Gist 1 Ver. A, Rev. 2 MAE-2104 – Engineering Mechanics II Practice Exam #1 - Kinetics of Particles and Systems of Particles 5. The 20-lb cart B is supported on rollers of negligible size. If a 10-lb suitcase A is thrown horizontally on it at 10 ft/s, determine the time t interval before A stops relative to B. The coefficient of kinetic friction between A and B is k =0.4. 6. Determine the magnitude of the angular momentum of the 2.5-kg particle about point O. 7. Disk A has a mass of 1 kg and is sliding forward on a smooth surface with a velocity (A)1 = 5 m/s when it strikes the 3 kg disk B, which is sliding towards A at (B)1 = 2 m/s, with direct central impact. If the coefficient of restitution between the disks is e = 0.4, compute the velocities of A and B just after collision. 8. A 2-kg collar is on a horizontal straight rod, starting at position A. A linear spring attaches the collar to a point above the rod. The spring has a spring constant, k, of 20 N/m. Its natural length, l0, is 30 cm. At position A the spring is stretched to a total length of 50 cm. At position B, the spring is a total length of 30 cm. When at A, the collar is moving at a speed vA of 3 m/s toward B. How fast is the collar moving at B? R. Gist 2 Ver. A, Rev. 2