FCH 532 Study Guide This assignment will not be collected
advertisement

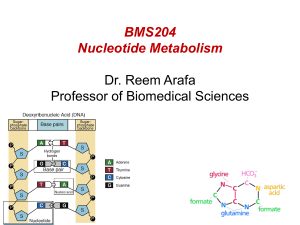
FCH 532 Study Guide This assignment will not be collected 1. Starting out from ribose-5-phosphate, write out the metabolic pathway for the production of inosine monophosphate (IMP). Show all chemical structures and names of substrates. Also show co-factors and enzymes. a. Continue from IMP to produce AMP and GMP. How is pyrimidine synthesis regulated? 2. Show the pathways for the de novo synthesis of pyrimidines. In what ways does this differ from purine synthesis. 3. How is pyrimidine biosynthesis regulated in E. coli as compared to in animals? 4. What is the function of ribonucleotide reductase? Write out a mechanism for this enzyme’s reaction. 5. Write out a plausible mechanism for the inhibition of thymidylate synthetase by FdUMP. 6. Write out the major catabolic pathways for purines and pyrimidines. Show all chemical structures. 7. Write the pathway for the biosynthesis of uridine triphosphate UTP) naming all enzymes, coenzymes, and substrates. You should show the structure of all substrates but need not show the structures of the enzyme intermediates 8. Briefly discuss the biochemical mechanism by which a cell regulates purine biosynthesis so it obtains balanced amounts of both purine nucleotides. 9. Most nucleotide bases are reused rather than synthesized from scratch. Briefly discuss the reutilization pathways for purines and contrast the difference in ATP requirements to reutilize adenine for the synthesis of ATP versus forming a new ATP by de novo synthesis. 10. Inhibitors of one-carbon metabolism (THF) block the synthesis of DNA but not RNA, why? 11. Name the different nucleotides, their nucleosides and their component bases. 12. Define the following terms: Z-scheme, photorespiration, photosystem 2, light harvesting complex, chlorophyll, Calvin cycle, lumen, photoautotroph, Rubisco, etc. 13. One of the classic experiments conducted by Benson, Bassham and Calvin as part of their elucidation of the pathway of dark carbon fixation was to feed the algae 14-C labeled carbon dioxide and then degrade the resulting sugars to determine which carbons are radio-labeled. Indicate which carbons will be radiolabelled in the following sugars after feeding radioactive carbon dioxide. 14. What are the 4 possible routes of dissipation of excitation energy during phototransfer?