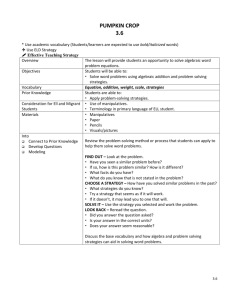
Dana Mitchell Southern Research Station Forest Operations Research Unit
advertisement

Dana Mitchell Southern Research Station Forest Operations Research Unit Participants SRS‐ SRS Center for Bottomland Hardwoods C f B l d H d d SRS‐Forest Operations Mississippi State University Louisiana Tech University Outline Study Site S d Si Equipment Overview Next Steps for Harvesting Implementation Study Site LOWER MISSISSIPPI ALLUVIAL VALLEY (LMAV) History Ecologically degraded area Afforestation efforts Important wetlands Bosco Site LMAV Photo credit: Ducks Unlimited Photo credit: NASA Study Site LMAV Army Corp of Engineers 100 acres SRWC established in 2.5 acre plots 3 replicates of each species/ spacing Plot rows = 660’ long, 165’ wide Climate Winter Flooding Summer Drought Study Site LMAV Species p Eastern cottonwood Black willow Red maple American sycamore Source: Gardiner and Oliver, 2005 Study Site LMAV Spacing p g 3’ x 3’ (4100 cuttings/ac) 2.5’ within/between row pairs, 6’ between double rows Harvest years 4, 7 & 10 6’ x 9’ (807 cuttings/ac) Thin year 3, CC year 5 y 3, y 5 Reestablish for 2nd rotation 12’ x 12’ (302 cuttings/ac) Harvest year 10 Harvest Nov/Dec Equipment Overview Criteria Cut stems in a row High production rate with limited backward movement (not drive‐to‐tree) High floatation, low psi Effectiveness with Effectiveness with ‘bushy’ bushy stems? Effectiveness with single stems? Hydro Ax Feller‐Buncher Hyd‐Mech Prototype Equipment Overview MULCHING WITH BALING Claas 2‐pass system Mulch Collect/bale Netting used to secure bales Transport bale to roadside Impurities, Ash Equipment Overview MULCHING WITH BALING FLD WB‐55 Bio‐baler 55 7.5’ cutting swath Tractor‐powered (185 hp) 4.3 minutes/bale (pmh) 4 3 minutes/bale (pmh) 14.7 bales/pmh 1,000 lb bales (green wt) Photo credit: Anderson Group Baling twine Stop to drop bale Transport bale to roadside p Photo credit: Anderson Group Equipment Overview MULCHING WITH TRAILER Fecon 1‐pass system Operational characteristics Transport chips to landing p p g Size / turning radius Low psi on prime mover, tracks offers flotation on wet soils Trafficability of trailer on wet soils? Cutting action = teeth C i i h Impact of tooth type on stool re‐sprouting Equipment Overview MOBILE CHIPPING Fecon RTC‐22 Bio‐Mass Chipper 2‐pass system Production remains focused on chipping System would include a felling operation and trailer transport to roadside S Source: www.fecon.com f Equipment Overview MOBILE CHIPPING Bruks 2‐pass system Second machine needed for felling Available with an integrated chip bin Machine width 8.2 ft Machine width – 8 2 ft Weight, size, maneuverability Transport trailer to roadside 805.2 STC Photo credit: www.bruks.com Equipment Overview MOBILE MULCH/BALING GyroTrac y (BBS) 1000 1‐pass system Chips Cutting action from knives Re‐sizer Round bales 88” cutting width Bale transport could require a second machine PSI on baler? Turning radius? Equipment Overview SINGLE STEM HARVEST (COTTONWOOD) Felling Machine g No backing movement Tracked for floatation Boom reach reduces trafficking of site Accumulating arms High production with Hi h d ti ith specifically‐designed shears Skidder Light payload , numerous stems medium hp skidder large grapples. Source: explainthatstuff.com Equipment Overview SUMMARY # of passes p Machine Width Stem Impacts ‐ Willow Turning radius d Floatation Photo credit: Anderson Group Kisatchie NF Strip Thinning Project Next Step: Equipment Selection Trial harvest‐ stool integrity g y for coppice sprouting Multiple Systems? Single vs multi‐stem Feedstock specifications at processing facility (chipping vs mulching) Source: backyardbutterflygarden.com S Source: explainthatstuff.com l i h ff Next Step: SRWC Harvesting Implementation l Production and Cost Studies Carbon Footprint for Entire Project p j Stool Impacts Site Impacts Growth, yield, neo‐tropical migrants, non‐game birds g Thank you Dana Mitchell, Research Engineer US Forest Service, Southern Research Station Forest Operations Research Unit Auburn, AL 36849 (334) 826‐8700 danamitchell@fs.fed.us www.srs.fs.usda.gov/forestops