Testing “Everyday” Items for Radioactivity Hands-on Investigation:
advertisement

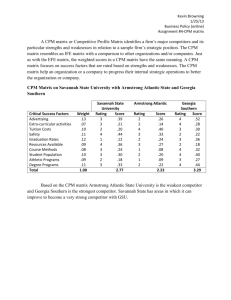
Name Date Hands-on Investigation: Testing “Everyday” Items for Radioactivity In this investigation, you will be working with a digital radiation monitor that contains a GM tube. You will explore how this monitor works by measuring some of the ionizing radiation in your classroom. This monitor detects , and radiation. The window at the front of the monitor is made of mica and is fragile! Please do not let anything (especially a pointed object) touch this window. For accurate readings of substances with low levels of radioactivity, the mica window should face the material and be placed close to the substance in question, without actually Figure 1: Vernier Digital Radiation Monitor. Image Source: Digital Radiation Monitor manual. touching the substance. Watch your teacher’s demonstration of how to set the counter to count for 6 minutes using the timed count mode and then set your counter to count for 6 minutes. 1. Select your first object or substance to be tested for radioactivity. Set it about 1 cm in front of the mica window and turn the monitor ON as described by your teacher. Start your stopwatch as soon as you activate the monitor for counting. Keep your stopwatch running and complete the data table. NOTE: If the substance to be tested is in a container, the walls of the container may block some of the radioactivity so the monitor has to be positioned in such a way as to measure the substance directly. Item or Substance __________________ Time (min) Total Counts Change in Counts (from previous value) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Since your measurements were made at 1 minute intervals, your Change in Counts column represents the counts per minute (CPM). 2. Use the data from the table to determine the following: Min CPM = ________ Max CPM = ________ Avg CPM = ________ 3. Now repeat this procedure for two more items or substances you think may be radioactive. Item or Substance __________________ Time (min) Total Counts CPM Item or Substance __________________ Time (min) Total Counts CPM 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 Min CPM = _______ Max CPM = _______ Min CPM = _______ Max CPM = _______ Average CPM = __________ Average CPM = __________ 4. Compare your results with other groups. Describe any similarities or differences you found by comparing the items you tested with items tested by other groups. BE SPECIFIC. 5. Is there anything that your group or any other group found that you think may be radioactive? Explain your answer using data you collected. 6. Repeat the procedure one more time and this time do not put anything in front of the radiation monitor. Item or Substance __________________ Time (min) Total Counts CPM 0 1 2 3 7. How do these results compare with the items and substances that have been measured so far? Do you think any of the items measured so far are radioactive? Why or why not? 4 5 6 Min CPM = _______ Max CPM = _______ Average CPM = __________ The radioactivity measured by a radiation monitor when nothing is in front of it is called “background radiation.” When testing for the presence of radioactivity one must always measure the background radiation first and then subtract it from any radioactivity measurements recorded. 8. Using this information, now test two more items/substances to see if they are radioactive: Item or Substance __________________ CPM Time Total CPM Corrected (min) Counts Item or Substance __________________ CPM Time Total CPM Corrected (min) Counts 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 Min CPM = _______ Max CPM = _______ Min CPM = _______ Max CPM = _______ Average CPM = __________ Average CPM = __________ 9. Now test some of the items supplied by your teacher for the presence of radioactivity using what you have learned so far in this activity. Item or Substance __________________ CPM Time Total CPM Corrected (min) Counts Item or Substance __________________ CPM Time Total CPM Corrected (min) Counts 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 Min CPM = _______ Max CPM = _______ Min CPM = _______ Max CPM = _______ Average CPM = __________ Average CPM = __________ 10. Which items tested in this lab activity are emitting radioactivity? Use data to support EACH of your conclusions. 11. Which items are you uncertain about? Why? Use your data to support your answer. 12. If time allows, determine if several other materials are radioactive. (Your teacher may have additional data tables OR you can create your own on your own paper.)