UCCS S O P
advertisement

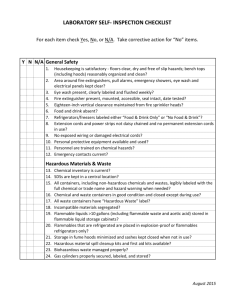
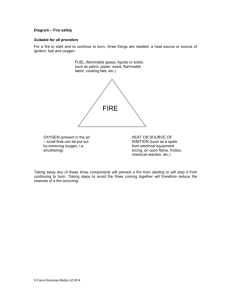
UCCS SAFE OPERATING PROCEDURE 25. SAFE STORAGE AND HANDLING OF FLAMMABLE AND COMBUSTIBLE CHEMICALS (For assistance, please contact Environmental Health & Safety) Flammable and combustible chemicals are materials that, under standard conditions, can generate sufficient vapors to cause a fire in the presence of an ignition source. Materials that generate sufficient vapors to ignite at temperatures below 100°F (38°C) are "flammables," whereas materials that require temperatures above 100°F to provide sufficient vapors for ignition are "combustibles." Typical flammable liquids, classes 1A, 1B, and 1C, are listed below. Depending on density, vapor trails can rise, sink, or traverse horizontally to reach an ignition source, which can result in a flashback fire. Fire can also result from reactions between flammables or combustibles and oxidizers. CABINETS Shall not be vented without prior approval by EH&S and Facilities Services. Are to be vented only with stainless steel piping with joints and seams sealed such that they will not leak under fire conditions. Shall have the vent caps screwed securely in place, unless appropriately vented. Shall contain no more than 60-gallons, or the rated capacity of the cabinet, whichever is less. USE Never use food containers, or containers that look like food containers, for flammable liquid storage or use. Eliminate ignition sources such as open flames, hot surfaces, operation of electrical equipment, and static electricity from areas in which flammable materials are used. Ensure that there is proper bonding and grounding when transferring between containers. Avoid the buildup of static electricity when transferring between plastic containers by avoiding the “free-fall” of liquids -- pour carefully in a steady stream down the sides of the container. Ensure that there is a functional fire extinguisher in the area where UCCS.SOP 25 Flammables Page 1 of 6 flammable liquids are used or dispensed. The fire extinguisher should be rated at least "3B". Never heat flammable substances with an open flame. Preferred heat sources include hot air, oil, salt, sand, steam, water, or wax baths; and heating mantles. Keep containers tightly closed at all times when not in use. Transfers should be carried out only in fume hoods or in other areas where ventilation is sufficient to avoid a buildup of flammable vapor concentrations. Always provide secondary containment to prevent accidental spillage and ignition. Spent or used flammable and combustible liquids should be kept in containers essentially the same as the original When a hazardous waste is added to a container, it must be labeled as hazardous waste at the time the first drop of hazardous waste is added to the container and the label must be dated. Hazardous Waste labels will be used on all waste containers. The container must clearly be labeled with the fully written chemical name and generator’s name. If the collection container contents contain a mixture, all components must be listed by percent or volume on the hazardous waste label. STORAGE A maximum of one gallon of flammable liquid per room can be in “normal storage” (shelves or countertops) in “common containers” (glass, plastic, metal). Quantities greater than one gallon located outside of a flammable liquid storage cabinet must be contained in a self-closing flammable container (“safety can”). Quantities 10 gallons and over will be stored in flammable liquid storage cabinets that meet the design specifications of NFPA 30. Secondary containment – sufficient to hold the entire contents of the storage container and impervious to the material – must be used whenever a glass or plastic container is used for flammables. It is highly recommended in all cases. Flammable and combustible liquids in glass containers shall not exceed 1 liter. When chemical purity must be protected, up to 4 liter quantities are permissible, and EH&S must be notified. UCCS.SOP 25 Flammables Page 2 of 6 Flammables that do not meet the above requirements, and flammables used outside the laboratory setting, must be stored in approved safety cans or the original container. Segregate flammables from oxidizing acids and oxidizers. Replace caps on containers immediately following dispensing. Flammable and Combustibles should be placed under a hood, or other well ventilated area, as soon as practical considering the required process. DO NOT EVAPORATE FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS (EVEN IN A FUME HOOD) AS A MEANS OF DISPOSAL. This is an illegal act – a violation of numerous regulations. Eliminate ignition sources such as open flames, hot surfaces, electrical equipment not certified for use with flammables, and static electricity from areas in which flammable or combustible materials are stored. Post conspicuous "No Smoking" signs in the vicinity of flammable storage & operations. Even though campus buildings are smoke-free facilities this serves as a valuable reminder to employees, students, and visitors. Flammable liquids requiring cooling must be stored in refrigerators or freezers that meet the design specifications of NFPA 45 9-2.2. The manufacturer prominently labels such devices to indicate that the unit is suitable for such use. Ensure that there is proper bonding and grounding when transferring between containers for dispensing a flammable liquid from a large container or drum. UCCS.SOP 25 Flammables Page 3 of 6 FLAMMABLE LIQUID CLASSES Class IA Flammable Liquids Flashpoints below 73° F and a boiling point below 100° F Acetaldehyde Amylene Butadiene Butane Butene Cellulose Nitrate Crude Oil Dimethyl Amine Dimethyl Propane Dimethyl Sulfide Dioborane 1,2Epoxy-3Phenoxypropane UCCS.SOP 25 Flammables Ethyl Chloride Ethyl Ether Ethyl Nitrite Ethyl Vinyl Ether Ethylamine Ethylene Oxide Furan Hydrocyanic Acid 3-Methyl-1-Butene Methyl Ether Methyl Ethyl Ether Methyl Formate Methyl Mercaptan Methyl Vinyl Ether Monomethylamine iso-Pentane Pentane n-Pentane Petroleum Ethers Phosgene Solutions in Benzene Propylene Propane isoPropylamine Trimethyl Amine Vinyl Chloride Vinylidene Chloride Page 4 of 6 FLAMMABLE LIQUID CLASSES Class IB Flammable Liquids Flashpoints below 73° F and a boiling point at or above 100° F Acetone Acetonitrile Acetyl Chloride Acrolein Acronitrile Allyl Acetate Allyl Alcohol Allyl Amine Allyl Bromide Allyl Chloride Amyl Alcohol Amylamine Amyl Mercaptan Amyl Nitrate Azirdine Benzene Benzotriflouride iso-Butyl Acetate tert-Butyl Alcohol Butyl Amine isoButylamine nButyl Bromide nButyl Chloride isoButyl Formate nButyl Formate tertButyl Chloride Butyl Mercaptan Butyl Vinyl Ether Isobutyl Methyl Ketone n-Butylraldehyde isoButylraldehyde Butryl Chloride Carbon Disulfide p-Chloro-m-cresol Chloroprene Cyclohexane Cyclohexene Cyclopentane Dibutyl Peroxide UCCS.SOP 25 Flammables 1,1-Dichloroethane 1,2-Dichloroethylene 1,2-Dichloropropane 1,1-Diethoxyethane Diethylamine Diethyl Ketone 2,4Dihydro-2H-Pyran Diisopropyl Amine Diisopropyl Ether Dimethoxymethane Dimethoxypropane 2,2-Dimethyl Butane Dimethyl Carbonate 1,4-Dioxane Ethoxy Acetylene Ethyl Acetate Ethyl Acrylate Ethyl Benzene Ethyl Crotonate Ethyl Chloroformate Ethylene Dichloride Ethyl Formate Gasoline Heptane Hexane 1-Hexene 2-Hexene Isoprene Lacquer Diluents Methyl Acetate Methyl Acrylate Methyl Alcohol 2Methyl-1-Butene 2Methyl-2-Butene NMethylbutylamine Methyl Butyrate Methyl Cyclohexane Methyl Chloroformate Methyl Ethyl Ketone 4-Methyl Cyclohexene 2-Methyl Furan Methyl Isobutyrate Methyl Methacrylates Methyl-n-Propyl Ketone 1-Methylpyrrole Regular Naphtha Octane Piperidine Piperylene Propargyl Bromide iso-Propenyl Acetate Propionaldehyde Propionitrile Propionyl Chloride iso-Propyl Acetate n-Propyl Acetate iso-Propyl Alcohol Propylamine Propyl Chloride iso-Propyl Ether iso-Propyl Formate Propyl Nitrate Pyradine Pyrrolidine Pyruvic Acid Tetrahydrofuran Thiophene Toluene Triethyl Aluminum Triethyl Amine Triisobutyl Aluminum 2,2,4-Trimethyl Pentane Valeraldehyde Unsymmetrical Dimethyl Hydrazine Vinyl Acetate 2,4,4-Trimethyl-2Pentane Vinyl Ether Page 5 of 6 FLAMMABLE LIQUID CLASSES Class IC Flammable Liquids Flashpoints at or above 73° F and a boiling point below 100° F Allyl Chloroformate n-Amyl Acetate iso-Amyl Acetate sec-Amyl Acetate n-Amyl Alcohol Amyl Bromide iso-Amyl Formate n-Butyl Acetate sec-Butyl Acetate n-Butyl Alcohol isoButyl Alcohol secButyl Alcohol Butyl Hydroperoxide tertButyl Peracetate nButyronitrile Cyclohexylamine Chlorobenzene Cyclopentanone Din-Butyl Ether 1,3Dichloro-2-Butene 1,3Dichloropropane Endrin Dicyclopentadiene Ethanethiol Ethyl Butyrate nEthylmorpholine Hexyl Amine Mesityl Oxide Methyl Butyl Ketone Methyl Hydrazine Methyl Isobutyl Ketone Naphtha, High Flash Nitroethane Nitromethane Pentaborane Paraldehyde 2-Pinene 1,3-Propanediamine Propargyl Alcohol n-Propyl Alcohol Propyl Benzene Styrene Styrene monomer Trichloroethylene Triethyl o-Formate Trimethyl Borate m-Xylene o-Xylene p-Xylene Last reviewed by Cynthia Norton on December 15, 2015 UCCS.SOP 25 Flammables Page 6 of 6