Flammables/Combustibles and Explosives * Safety Instruction (Year 3)
advertisement

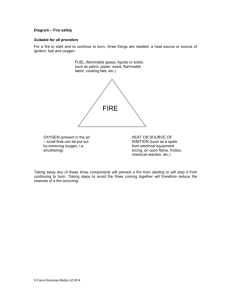
Flammables/Combustibles and Flammables/Explosives – Safety Instruction Tim Styranec, Chemical Storekeeper Safety Instruction and Review Sign In Sheet Review Protective Equipment – Lab coats, gloves, goggles Waste- red cans, waste forms Safety & Emergency- EOHS (x3700), 911 Spill response kits LAW –Review OSHA Lab Standard Occupational Health and Safety Plan Last year MSDS. This session concentrates on class of chemicals- Flamm/Combustible and explosives. Large quantities used in Organic labs and Research Purpose of session - to learn about developing good safety habits when working with flammable/combustible and explosive materials. NFPA LABEL - RED 4-0- Show example – Acetone. FLAMMABLE can be described simply as a substance that will readily catch fire and burn. Flash point below 100 degree F. COMBUSTIBLE- flash point above 100 F.(difference important DOT reg. And shipping) same to us. Flash Point - minimum temp. of liquid at which it gives off vapors sufficient to form an ignitable mixture with the air near the surface of the liquid or container. It is by far the most important property concerned with. Where get this - MSDS, LABEL Flammable Range Lower Flammable Limits is the minimum percentage of vapor to air required for Upper Flammable Limits is the Percentage of vapor to air above which ignition possible.(too rich) ignition.(too lean) is no longer Beware of all Organic Liquids Just because a flash point may be high it does not take it out of the range of hazardous material. Example: Kerosene fp 100F can be just as dangerous as a flammable liquid just a few degrees lower. Flammability Substance will sometimes ignite but other times will not burn. Depends on 1. temperature of substance 2. concentration of that substance in the atomsphere 3. other criteria. - fire triangle - Energy, Oxidizer, FUEL - (Flammable) 3 things necessary to have a fire - fuel -oxygen heat. FIRE TRIANGLE FIRE TRIANGLE - as long as the triangle is not complete, the legs are not touching to form a closed or completed triangle It is impossible to have a fire. Want to control in this case fuel. Flammable Liquids Flammable Liquids - FUEL Types we work with- organics labs and research. Hydrocarbons - Pure compounds as well as mixtures. Pentane, hexane, heptane, decane, benzene, toluene xylenes, cyclohexan, Cycloheptane etc. Alcohols - R-OH, ethanol, methanol,propyl,butyl, Ethers - usually flash point is lower, makes it more dangerous. R-O-R' can become oxidized in unusual and unexpected way Oxygen atom may enter the molecule to form Peroxide R-O-O-R' Which is potentially explosive. DO not open cans - if not sure how long stored. Return for disposal. RULE: once opened it should be used completely or disposed of . Do not store. If must DATE can. Ex. Diethyl ether, methyl ethyl ether, isopropyl ether. Flammable Liquids Ketones Flash point is generally higher. Used as solvents Ex. - ACETONE,( also called Dimethyl ketone, 2-propanone), Methyl butyl ketone, (2Heaxanone) and methyl ethyl ketone.(2-Butanone) Aldehydes -Flash point similar to Ketones. Ex. Formaldehyde, Acetaldehyde Amines - Considered derivatives of ammonia. Most foul-smelling, all toxic to some degree and all have relatively low flash points. Smell of Rotting flesh due to the formation of amines. Ex. Butyl amine, ethyl amine, diethyl amine Esters - Distinctive pleasant odors. Common esters - methyl formate, Methyl acetate, vinyl acetate, ethyl acetate. Beware of all Organic Liquids. Once again - Beware of all Organic Liquids. Even though a strict definition of combustible liquid might not include liquids with flash points above 200 degrees F. Flammable Solids Carbon based -coal, Phosphorus (white), Metals Aluminum, Magnesium Picric Acid - also an explosive Compressed Gases Acetylene- flammmable range is from 2.5 to 83 percent. Every time released in flammable range. Hydrogen - - these gases have same hazards as other flammables but now Under pressure Always check MSDS, now in folder in each room. If not let me know. Explosives Definition: any material or device that is created specifically for the purpose of exploding which it will do upon demand. Definition eliminates all materials that will explode but were not created or designed to function that way Materials that will explode under certain conditions – Materials that will explode under certain conditions Increases in Temperature Decompose quickly Become dangerously reactive Light mechanical shock can begin reactions Certain chemicals when mixed Other Dangers Chemicals impurities ( organic peroxides - from Ether) Ammonium Nitrate Organic Peroxides- Ether forms peroxides – unstable Natural gas Flammable gases Vapors of flammable and combustible liquids Metal and organic powders Monomers- simple, small molecule that has capabiltiy of reacting with itself to form giant molecule called a polymer. Safety – Hazards associated with Flammable/Combustibles and explosives Read the MSDS – protective equipment - what to wear, how stored, how to handle properly and safely, PEL’s, signs and symptoms of exposure. If need additional information – my office(ext. 3665) or EOHS. Read Labels - You are only person who can make the area you work safe as possible. VIDEO - Flammable & Explosives – QUIZ Flammables Xylene example Flash point Limits - Flammability - too lean, too rich Toxic Limits Ignition Temp. Ethyl Ether- hot plate NO OPEN FLAME OR HOT PLATE Use Heating Mantle or Water Bath MSDS- Fp and Ignition temp Static Electricity Adequate Ventilation Flashback - use arresters Storage and Cleanup Secondary Containers Storing - Flammable Cabinets no direct sunlight Label Avoid bench top and hood storage Liter or more store in Flamm. Cabinet - here all flammable in cabinet Gases - not color coded - Read MSDS Clean up - EOHS- we do not fit of want to use respirators. Vermiculite- does not absorb vapors CLEAN UP call me, and I will contact EOHS. Explosives-Know what you are working with MSDS Shock, catalyst Impurities Organic Peroxides - unstable Date Ether Container - look for contaminant Fire - What to do Fire - What to do R A C E (get out) Rescue Alarm Close Door Extinguish. - Exit If feel can extinguish If feel can extinguish P A S S Pull the pin Aim squeeze the handle Sweep PLAN When working with Dangerous chemicals - Take time – PLAN QUESTIONS