Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation other particle with force:
advertisement
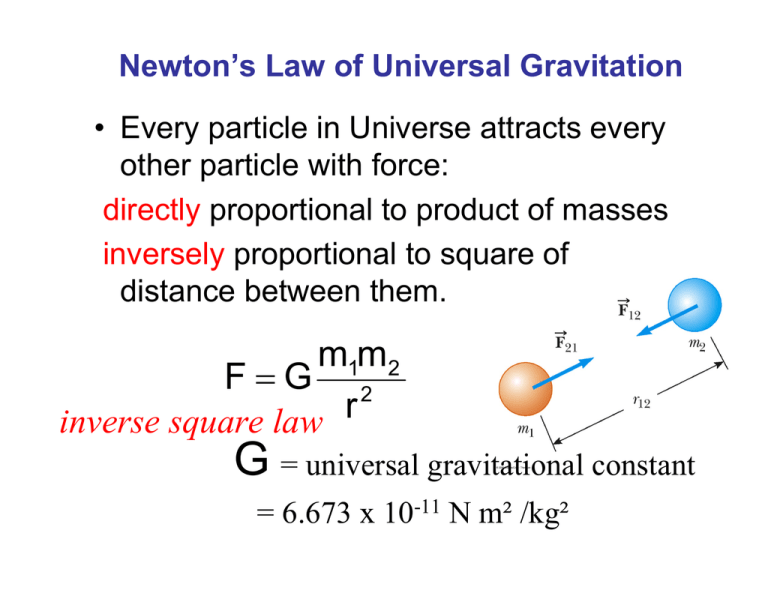
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation • Every particle in Universe attracts every other particle with force: directly proportional to product of masses inversely proportional to square of distance between them. m1m2 FG 2 r inverse square law G = universal gravitational constant = 6.673 x 10-11 N m² /kg² Applications of Universal Gravitation Gravitational force of uniform sphere on particle outside sphere same as force exerted if entire mass of the sphere concentrated at its center--Gauss’ Law • Acceleration due to gravity • g will vary with altitude ME gG 2 r Gravitational Potential Energy • PE = mgy is valid only near the earth’s surface • For objects high above the earth’s surface, an alternate expression is needed MEm PE G r – Zero reference level is infinitely far from the earth Escape Speed • speed needed for an object to “escape” from planet • For the earth, vesc is about 11.2 km/s • Note, v is independent of the mass of the object v esc 2GME RE Black holes, escape speed and the speed of light GM GM 2 R 2 vesc vesc R RBH GM 2 c R ~ 1 cm for Earth R ~ 3 km for Sun Ch. 8 General Torque Formula Component of F r OR r F sin • The lever arm, d, is the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to a line drawn along the direction of the force d = r sin so = F d = F r sin Torque and Equilibrium • First Condition of Equilibrium • The net external force must be zero F 0 or Fx 0 and Fy 0 •The Second Condition of Equilibrium states The net external torque must be zero 0