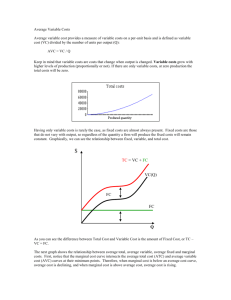
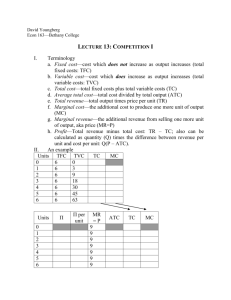
Relation of Average Variable Cost and Average Total Cost to Schedule:
advertisement
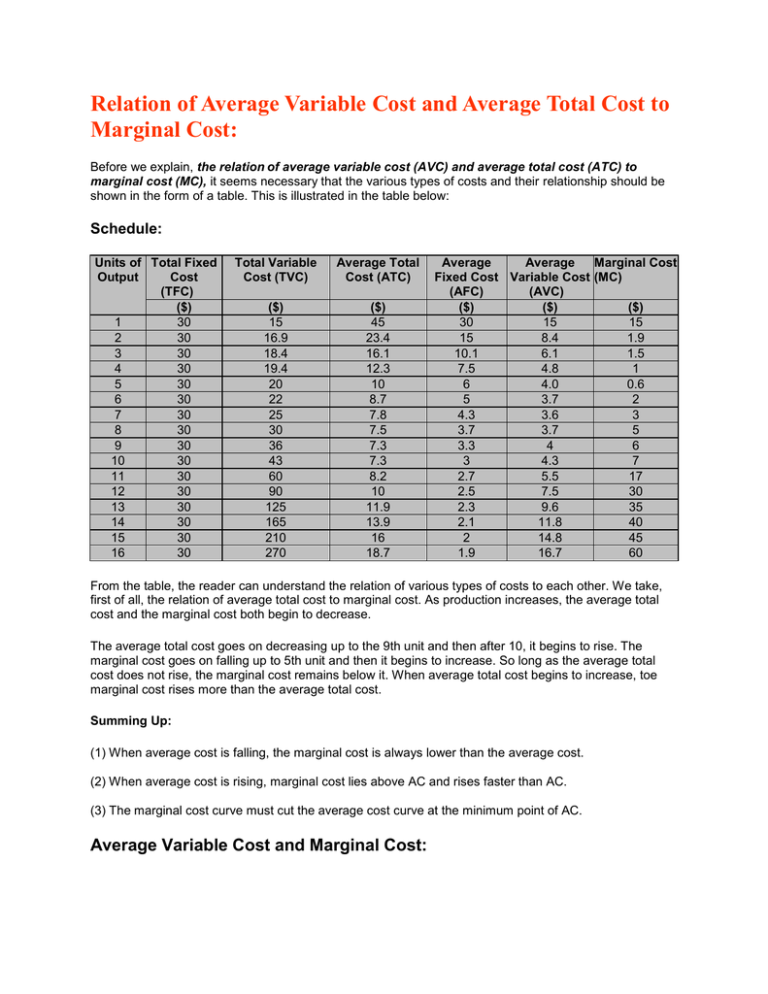
Relation of Average Variable Cost and Average Total Cost to Marginal Cost: Before we explain, the relation of average variable cost (AVC) and average total cost (ATC) to marginal cost (MC), it seems necessary that the various types of costs and their relationship should be shown in the form of a table. This is illustrated in the table below: Schedule: Units of Total Fixed Output Cost (TFC) ($) 1 30 2 30 3 30 4 30 5 30 6 30 7 30 8 30 9 30 10 30 11 30 12 30 13 30 14 30 15 30 16 30 Total Variable Cost (TVC) Average Total Cost (ATC) ($) 15 16.9 18.4 19.4 20 22 25 30 36 43 60 90 125 165 210 270 ($) 45 23.4 16.1 12.3 10 8.7 7.8 7.5 7.3 7.3 8.2 10 11.9 13.9 16 18.7 Average Average Marginal Cost Fixed Cost Variable Cost (MC) (AFC) (AVC) ($) ($) ($) 30 15 15 15 8.4 1.9 10.1 6.1 1.5 7.5 4.8 1 6 4.0 0.6 5 3.7 2 4.3 3.6 3 3.7 3.7 5 3.3 4 6 3 4.3 7 2.7 5.5 17 2.5 7.5 30 2.3 9.6 35 2.1 11.8 40 2 14.8 45 1.9 16.7 60 From the table, the reader can understand the relation of various types of costs to each other. We take, first of all, the relation of average total cost to marginal cost. As production increases, the average total cost and the marginal cost both begin to decrease. The average total cost goes on decreasing up to the 9th unit and then after 10, it begins to rise. The marginal cost goes on falling up to 5th unit and then it begins to increase. So long as the average total cost does not rise, the marginal cost remains below it. When average total cost begins to increase, toe marginal cost rises more than the average total cost. Summing Up: (1) When average cost is falling, the marginal cost is always lower than the average cost. (2) When average cost is rising, marginal cost lies above AC and rises faster than AC. (3) The marginal cost curve must cut the average cost curve at the minimum point of AC. Average Variable Cost and Marginal Cost: The relation of average variable cost and marginal cost is also very clear from the diagram given below. The AVC goes on falling up to the 7th unit, and then it steadily moves upwards. On the other hand the marginal cost falls up to the 5th unit and then rises more rapidly than average variable cost. Diagram/Figure: In the diagram (13.10) AFC, AVC, ATC and MC curves are shown. Here, units of production are measured along OX and cost along OY. ATC and AVC both fall in the beginning, reach a minimum point and then begin to rise. So is the case with the marginal cost curve. It first falls and then after rising, sharply crosses through the lowest point of average variable cost and average total cost and rises.