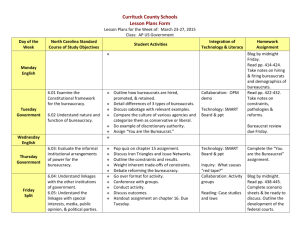
American Government Chapter 12 Bureaucracy in a Democracy
advertisement

American
Government
Chapter 12
Bureaucracy in a Democracy
Federal Civilian Employment
Bureaucracy
{
Government run by desks
{
Administration
{
{
Actual offices, tasks, and principles of organization
that are employed in the most formal and sustained
administration system to implement government
policy
Division of labor-workers are specialized
Key Questions
{
{
{
{
What role do the executive branch and its
officials play in American democracy?
What role should they play?
What are the political considerations and
contexts in which departments and agencies act?
How do we seek to control agencies and
departments?
Proper Role of Politics in Governmental
Administration
{
19th Century Æ Patronage
z
z
Emphasis of democracy over efficiency
Meshed with party system of the day
Proper Role of Politics in Governmental
Administration
{
20th Century ÆProfessionalized
z
z
Created by Pendleton Act of 1883
Life-long bureaucrats are exempt from
political control.
{
Merit based system
z
z
Exams govern hiring and promotion.
Staffed with experts from industry
{ Ex-military in the Department of Defense
{ Oil workers in the Department of Energy
Changes in Federal Civilian Employment
4000
3500
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
1821 1841 1861 1881 1901 1921 1941 1961 1981 2001
Origin of Cabinet-Level Departments
Department
Established
Budget (2005)
(billions)
War
1789
State
1789
28.0
Treasury
1789
403.8
Navy
1798
Interior
1849
8.9
Justice
1870
20.7
Agriculture
1889
81.8
Labor
1903
57.0
Commerce
1903
6.2
Defense
1947
428.9
Housing and Urban Development
1965
38.9
Transportation
1966
59.0
Energy
1977
23.3
Health and Human Services
1979
574.7
Education
1979
64.3
Veterans’ Affairs
1988
67.3
Homeland Security
2002
31.0
Non-Cabinet Agencies
{
Independent Executive
Agencies
{
Regulatory Commissions
{
Government
Corporations
Alan Greenspan
FED Chairman
Independent Regulatory Commissions
Achieving Democratic Control Over a
Professional Bureaucracy
{
{
Politics get in the way of efficiency
and sound management
Ideally, bureaucrats would use their
expertise to make govt. better
z
z
Requires discretion and leeway
Policymakers set broad direction, while
bureaucrats implement policies in most
efficient way
Bureaucratic Arrangements are Both
Valuable and Problematic
{
Benefits
z
z
z
{
Expertise
Efficiency
Economies of scale
Problems
z
z
Responsiveness
Accountability
Inefficiency of Bureaucracies
{
Additional constraints imposed on public
agencies to ensure compliance and faithfulness
z
Hierarchical chain of command must be obvious
z
Flow of information must be orderly and monitored
z
Need way of identifying individual responsibility
Principal-Agent Problem
{
{
{
{
Expertise and Efficiency conflict with
Responsiveness and Accountability
Delegation of authority must be
accompanied by oversight
Principal = Congress & President
Agent = Bureaucracy
Goals of Agents (Bureaucracy)
{
{
{
{
A bureaucrat is an office manager.
The bureau chief attempts to
maximize his/her department’s
budget.
Prestige and salary
Belief in department’s mission
Avoiding Agency Slippage
{
Before the Fact Political Weapons
z
{
Getting the right individuals
After the Fact Political Weapons
z
Punishment
Before and After Controls
{
President
z
Before-the-Fact
{
z
After-the-Fact
{
{
{
Appointment Power
Executive Orders
Budgetary and Administrative Clearance
Congress
z
Before-the-Fact
{
{
z
Specificity of Legislative Language
Delegation to President
After-the-Fact
{
{
{
Power of the Purse
Oversight
Agency Creation
Types of Congressional Oversight
{
Police Patrol
{
Fire Alarm
America’s Unique Bureaucracy
{
Hostile Political Culture
z
{
Incoherent Organization
z
{
Overlapping jurisdiction
Divided Control
z
{
Americans “hate” big government
Two bosses: president and Congress
Open Bureaucracy
z
Freedom of Information Act