Document 10290804
advertisement

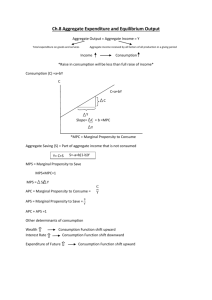
Econ 1: Macroeconomics Asatar Bair, abair@ccsf.edu In-class Exercise: Investment and Aggregate Expenditures 1. In Figure 1, what is real investment when the interest rate is 6%? _________ Figure 1 2. How would you describe the relationship between the interest rate and real investment? Interest rate b 10% a 6% Investment demand curve 10 30 real investment ($ bil) Real aggregate expenditure ($ tril) Figure 2 AE = Y AE2 AE1 _________________ 3. Each of the following shifts the investment demand curve. For each, label which direction the curve shifts. a. Fear of a recession turns investor expectations negative. b. Low inflation gives rise to positive investor expectations. c. New technology creates opportunities in new markets. d. Congress passes an increase in business taxes. 4. (See Fig. 2) What is the real aggregate expenditure and real GDP when AE1 = Y? 5. What is the initial change in aggregate expenditures that shifts the line from AE1 to AE2? (hint: look at the vertical distance between the lines) 3 1.5 45 O 1 3 Real GDP ($ tril) 6 Full employment 6. What is the change in real GDP as aggregate expenditures goes from AE1 to AE2? 7. What is the ratio between your answer for #6 and your answer for #5? Econ 1: Macroeconomics Asatar Bair, abair@ccsf.edu change in equilibrium output initial change in aggregate expenditures ΔY $1,000 bil e.g. Spending multiplier = = =2 ΔG $500 bil 1 1 Spending multiplier = = 1− MPC MPS 1 1 1 e.g. = = =4 1− MPC 1− 0.75 0.25 Spending multiplier = Fill in € the following table: MPC MPS Spending multiplier 0.5 0.4 2/ 3 0.25 4/ 5 0.1 0.95 0.01 4 5 8