Unit Review Guide
advertisement

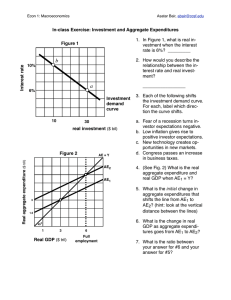
AS/AD, Phillips Curve, and Fiscal Policy Review Guide GDP=AD=C+I+G+Xn Definition of Aggregate Demand: Explain the equation above. Shifters of Aggregate Demand: Definition of Aggregate Supply: Shifters of Aggregate Supply: Keynesian AS Curve: Draw and Explain. Classical AS Curve: Draw and Explain. Draw a AS/AD model in LONG RUN Equilibrium: Draw a Short Run Phillips Curve: What is this model showing? How is SRPC connected to AS/AD model? Classical/Neo-Classical/Monetarist Theory: Economy will SELF-ADJUST back to Long Run Equilibrium During Time of Recession. Show and explain this theory. Keynesian Theory: In the “long run” we are all dead. Wages can be “sticky” and not allow for the economy to adjust itself during a time of recession. Government action is needed. Show and explain this theory. Classical/Neo-Classical/Monetarist Theory: Economy will SELF-ADJUST back to Long Run Equilibrium during an inflationary gap. Show and explain this theory. Keynesian Theory: Due to the “ratchet effect”, prices move up easily, but it is hard to bring them down. Government intervention is necessary. Show and explain this theory. What types of changes can lead to a rightward shift of the Long Run Aggregate Supply Curve? Illustrate how these changes affect the Long Run Phillips Curve: Illustrate how these changes affect a production possibilities curve. Illustrate a rightward shift of the LRAS. Define Fiscal Policy: Fiscal action during a recessionary gap: Overall Goal: AD – What are the two tools: Real GDPPrice Level – Business Cycle – Fiscal action during an inflationary gap: Explain how the multiplier effect works: Marginal Propensity to Consume: Overall Goal: AD – Real GDP- Marginal Propensity to Save: Price Level – Business Cycle – Formula for Spending Multiplier: Formula for Tax Multiplier: Explain why government spending has a greater impact that changing taxes. Explain why the effectiveness of expansionary fiscal policy is reduced as MPC gets lower. MPC = .5 MPC = .5 What is the spending multiplier? What is the tax multiplier? Assume there is a recessionary gap of $20 billion. How much should government spend to close the gap? Assume there is a recessionary gap of $20 billion. By how much should government cut taxes to close the gap? Criticisms of Fiscal Policy: Differentiate between discretionary and nondiscretionary fiscal policy. (Be sure to address automatic stabilizers.) Define budget deficit: Types of Taxes: Progressive: Define national debt: Regressive: Proportional: What is the relationship between the national debt and budget deficits? How do sales taxes affect different income groups