Chemistry 201 - C Alkyl Halides
Chemistry 201 - C
Alkyl Halides
This presentation was created by
Professor Carl H. Snyder
Chemistry Department
University of Miami
Coral Gables, FL 33124
CSnyder@miami.edu
Copyright 2004 by Carl H. Snyder,
University of Miami. All rights reserved.
Naming Alkyl Halides
Naming Alkyl Halides
Naming Alkyl Halides Naming Alkyl Halides
1
Alkyl Halides From C=C
Additions
By anti addition of X
2
By Markovnikov addition of HCl, HBr, or
HI
Halogenation of Alkanes - Free
Radical Chlorination of CH
4 chloromethane dichloromethane trichloromethane tetrachloromethane
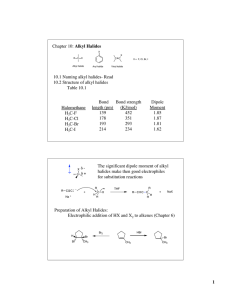
Free radical chlorination of methane gives chloromethane ( methyl chloride ) dichloromethane ( methylene chloride ) trichloromethane ( chloroform ) tetrachloromethane ( carbon tetrachloride ).
Chlorination of Methane: A
Free Radical Reaction
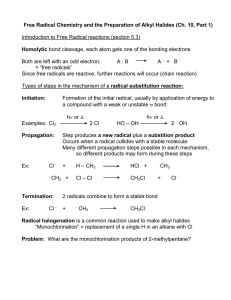
Initiation
The mechanism is initiated by free radicals and proceeds with the creation and reaction of free radicals.
Light , as a reaction condition, can be represented as h
νν where h represents Planck’s constant, and
νν represents the radiation frequency.
Propagation Termination
2
Free Radical Halogenation of
Alkanes: Mechanism
Halogenation of Alkanes with
Multiple Classes of Hydrogens
Rate = (1/E act
) x (conc.) x (probability factor)
Radical Stabilities
Relative Rates of Chlorination:
A Function of Radical
Stabilities
The order of stabilities of alkyl free radicals is the same as the order of stabilities of carbocations.
Free Radical Bromination
Free radical bromination is more selective than chlorination.
Reason: The
Hammond
Postulate.
Bromination is more endothermic
T.S. is more like the free radical product.
T.S. stability reflects free radical stability.
Allylic Bromination With
N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS)
N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS) effects bromination exclusively in the allylic position.
3
NBS Bromination: Free
Radical Mechanism
A Complete Set of Radical
Stabilities
NBS produces a low concentration of Br
2
The result is a free radical bromination at the allylic carbon.
Alcohol to Alkyl Halide: HX
Alcohol to Alkyl Halide: PBr
3
Alcohol to Alkyl Halide: SOCl
2
The Grignard Reagent
Reaction of an alkyl halide, R-X, with magnesium, Mg, yields a Grignard reagent ,
RMgX.
4
Alkyl Halide to Alkane via
Grignard Reagent
R-X + Mg
→
RMgX
RMgX + H
2
O
→
R-H + Mg(OH)X
The H of H
2
Use of D
2
O replaces the MgX of RMgX
O yields R-D, a deuteroalkane
CH
3
CH
2
MgBr + D
2
O
→
CH
3
CH
2
D + Mg(OH)X
The Gilman Reagent
Reaction of RX with Li yields an alkyllithium .
Alkyllithium and CuI produce R
2 reagent .
CuLi, the Gilman
C-C Bond Formation Via The
Gilman Reagent
C-C Bond Formation Via The
Gilman Reagent
Oxidation In Organic
Chemistry
5
Oxidation In Organic
Chemistry
Oxidation In Organic
Chemistry
Reduction In Organic
Chemistry
Reduction In Organic
Chemistry
Reduction In Organic
Chemistry
End
Alkyl Halides
6