contaminant
advertisement

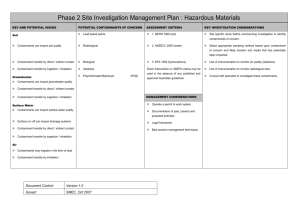
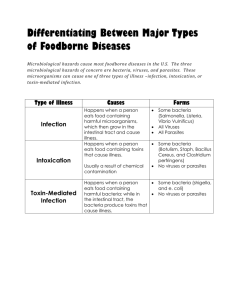
Chapter 6: Food Safety & Sanitation Sources of Food Bourne Illness Sources of Food Bourne Illness Key Terms: • • • • • • • Contaminant Contaminated food Physical Contaminant Chemical contaminant Biological contaminant Pathogen Microorganism • Incubation period • Bacteria • Potentially hazardous foods • Virus • Transmit • Parasite • Host Sources of Food Bourne Illness • A contaminant is a substance in food that does not belong to food • Contaminants in food can cause: – Illness – Death Sources of Food Bourne Illness • Contaminated food is food that contains contaminants. • The three types of contaminants are: – Physical – Chemical – Biological Physical Contaminants • A physical contaminant is an item that accidentally gets into food • Examples include: – Hair – Insects – Fingernails – Metal – Glass • Physical contaminants can cause serious injury Chemical Contaminants • A chemical contaminant is a chemical that is toxic or not usually found in food. • There are several types of chemical contaminants such as: – Pesticides (bug killers) – Cleaning Agents (bleach, ammonia, silver polish) – Metals in solution (ex. copper, lead, and cadmium) Chemical Contaminants • Any cleaning chemical accidently used in a food would cause immediate and severe illness • Chemical contaminants can cause cancer and nervous disorders Biological Contaminants • Biological contaminants are responsible for most cases of foodborne illness. • A biological contaminant is a microscopic living substance that accidently gets into food. • Types of biological contaminants include: – – – – – Bacteria Parasites Viruses Molds Fungi Biological Contaminants • A biological contaminant that causes disease is called a pathogen. • Pathogens are sometimes called diseasecausing microorganisms. • A microorganism is a living substance so small that you must use a microscope to see it. Biological Contaminants • Not all microorganisms cause disease or are biological contaminants. • Many microorganisms are used to create tasty and healthful foods. – Example: Yeast • There are three groups of pathogens that are responsible for foodborne illnesses: – Bacteria – Viruses – Parasites Biological Contaminants • The five main symptoms of foodborne illnesses caused by pathogens are: – Nausea – Vomiting – Diarrhea – Cramps – Fever Biological Contaminants Type Organism Name Incubation Period Bacteria Clostridium botulinum 12 to 36 hours Escherichia coli (E. coli) 2 to 5 days Salmonella 6 to 48 hours Staphylococcus aureus 2 to 4 hours Hepatitis virus A 10 to 50 days Norwalk virus 1 to 2 days Cryptosporidium parvum 2 to 10 days Cyclospora cayetanesis 7 days Trichinella spiralis 4 to 28 days Virus Parasite *The incubation period is the length of time between ingesting the pathogen and the appearance of symptoms. Bacteria • Bacteria are the most common cause of foodborne illnesses that managers are concerned with. • Bacteria are single-celled, microscopic organisms that grow rapidly under ideal conditions. • Not all bacteria cause disease or harmful to humans. Bacteria • Foods in which bacteria grow well are called potentially hazardous foods. • The foods can be raw or cooked, and include: – Meat – Poultry – Fish – Shellfish – Eggs – Dairy Products Bacteria • Temperatures between 40°F to 140°F are called the temperature danger zone • Room temperature is a temperature around 70°F. – Room temperature is in the danger zone. Viruses • A virus is a microorganism that reproduces in the cells of other living things. • Viruses are much, much smaller than bacteria. • Foods can transmit viruses to people. • Transmit means to carry from one place to another • People can transmit viruses to each other. Parasites • A parasite is an organism that must live in another living thing in order to survive. • The living thing that a parasite lives in is called a host. • A host can be a person, animal, or plant. • Parasites can live inside some of the animals that humans eat, such as: – – – – Poultry Cattle Pigs Fish THE END