Phase 2 Site Investigation Management Plan : Firing Ranges
advertisement

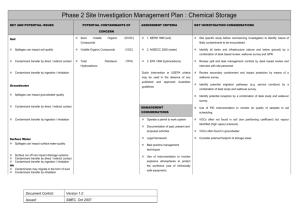
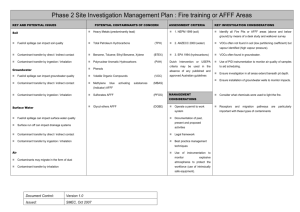
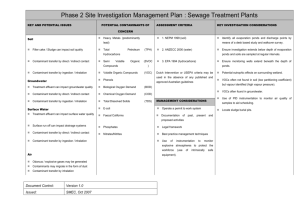
Phase 2 Site Investigation Management Plan : Firing Ranges KEY AND POTENTIAL ISSUES POTENTIAL CONTAMINANTS OF CONCERN ASSESSMENT CRITERIA KEY INVESTIGATION CONSIDERATIONS 1. NEPM 1999 (soil) Identify likely contaminants from desk study Soil Heavy Metals Contaminants can impact soil quality Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TPH) 2. ANZECC 2000 (water) Determine extents of investigation from desk study Contaminant transfer by direct / indirect contact Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) 3. EPA 1994 (hydrocarbons) Undertake a UXO survey before commencing investigation to protect the workforce. Contaminant transfer by ingestion / inhalation Semi Volatile Organic Compounds (SVOC) Dutch Intervention or USEPA criteria may be used in the absence of any Groundwater Benzene, Toluene, Ethyl Benzene, Xylene HMX, Contaminants can impact groundwater quality PETN, RDX, Tetryl, (BTEX) published and approved Australian guidelines nitrated Metals contaminants may not necessarily leach from munitions casings. Consider investigation of likely munition fall out zones Consider investigation of stop butts Use GPR to determine depth of investigation compounds Contaminant transfer by direct / indirect contact Phosphorous Contaminant transfer by ingestion / inhalation Strontium Sulphate Perchlorate Surface Water Contaminants can impact surface water quality Surface run off can impact drainage systems Contaminant transfer by direct / indirect contact USEPA (2005) Region IX Preliminary Remediation Goals represent the main source of HILs for explosives residues. MANAGEMENT CONSIDERATIONS Contaminant transfer by ingestion / inhalation Air Operate a permit to work system Documentation of past, present and proposed activities Contaminants may migrate in the form of dust Legal framework Contaminant transfer by inhalation Best practice management techniques Document Control: Version 1.0 Issued: SMEC, Oct 2007