PROJECT TIME MANAGEMENT

B U D I L U H U R U N I V E R S I T Y
POST GRADUATE PROGRAM OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
IT PROJECT MANAGEMENT
PROJECT TIME
MANAGEMENT
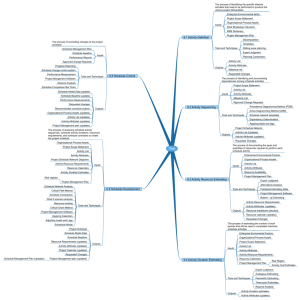
Project Time Management Processes
• Project time management involves the processes required to ensure timely completion of a project.
Processes include:
1. Define activity
2. Sequence activity
3. Estimate activity resources
4. Estimate activity durations
5. Develop schedule
6. Control schedule
3
Define Activity
• Identifying the specific schedule activities that need to be performed to produce the various project deliverables
• Project work packages are planned into smaller components (decomposed) called schedule activities to provide a basis for estimating, scheduling, executing, and monitoring and controlling the project.
4
Define Activities
INPUT
1. Scope baseline
2. Enterprise environmental factors
3. Organizational process assets
OUTPUT
1. Activity list
2. Activity attributes
3. Milestone list
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES
1.
Decomposition
2.
Rolling wave planning
3.
Templates
4.
Expert judgment
5
Activity Definition
Input (1)
1. Scope baseline
Project deliverables, constraints & assumptions documented in the scope statement
2. Enterprise environmental factors
Availability of project IS
Scheduling S/W tools, etc
3. Organizational process assets
Activity planning-related policies, procedures, guidelines that are considered in developing activity definitions
6
Define Activity
Outputs
Activity list
Comprehensive list of schedule activities
Activity attributes
1 Identifier 6 Logical relationship
2 Codes
3 Description
4 Predecessor
5 Successor
7 Leads and lags
8 Resource requirement
9 Imposed dates
10 Constraints & assumptions
Milestone list
Component of the PM plan
Indicates whether mandatory or optional milestone
7
Define Activities
Tools & Techniques
Decomposition
Subdividing the project work packages into smaller more manageable components called schedule activities
Rolling wave planning
A form of progressive elaboration planning where the work to be accomplished in the near term is planned in detail at a low level of the WBS
Templates
Expert judgment
8
Sequence Activities
• Identifying and documenting dependencies among schedule activities
9
Sequence Activities
INPUT
1. Activity list
2. Activity attributes
3. Milestone list
4. Project scope statement
5. Organizational process assets
OUTPUT
1. Project schedule network diagram
2. Project document updates
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES
1. Precedence diagramming method (PDM)
2. Dependency determination
3. Applying leads and lags
4. Schedule network templates
10
Sequence Activities
Tools & Techniques
P recedence D iagramming M ethod
• Activities are represented by boxes
• Arrows show relationships between activities
• More popular than ADM method and used by project management software
• Better at showing different types of dependencies
11
Sequence Activities
Tools & Techniques
Determine dependencies between tasks
FS : Finish-to-start
A
B cannot start until A finishes
B
SS : Start-to-start
A B cannot start until A starts
B
FF : Finish-to-finish
A
B cannot finish until A finishes
B
SS : Start-to-finish
A
B cannot finish until A starts
B
12
13
Sequence Activities
Tools & Techniques
14
Sequence Activities
Tools & Techniques
Dependency determination
– Mandatory dependencies (inherent in the nature of the work being done)
– Discretionary dependency (prefer logic / preferential logic / soft logic)
– External dependency (the project activities are dependent on non-project activities
Applying leads & lags
• A lead allows an acceleration of the successor activity
• A lag directs a delay in the successor activity
15
Schedule network templates
– Templates for the entire project
– Templates for sub network (fragment network)
16
Estimate Activity Resources
• Estimating the type and quantities of resources required to perform each schedule activity
Inputs
1. Activity lists
2. Activity attributes
3. Resource availability
4. Enterprise environmental factors
5. Organizational process assets
Outputs
1. Activity resource requirements
2. Resource breakdown structure
3. Project document updates
17
Estimate Activity Resources
Output
Activity resource requirements
Identification and description of the types and quantities of resources required of each schedule activity in a work package
Resource breakdown structure
A hierarchical structure of the identified resources by resource category and resource type
Project documents updates
18
Estimate Activity Resources
Tools & Techniques
Expert judgments
Alternatives analysis
Many schedule activities have alternative methods of accomplishment
Published estimating data
Production rates, unit cost of resources, etc
Project management software
Bottom-up estimating
• Decompose the schedule activities into more details; estimate the resource needed to complete each detailed piece of work. Aggregate bottom-up wise
19
Estimate Activity Duration
• Estimating the number of work periods that will be needed to complete individual schedule activities
Inputs
1.
Enterprise environmental factors
2.
Organizational process assets
3.
Project scope statements
4.
Activity lists
5.
Activity attributes
6.
Activity resource requirements
7.
Resource calendars
8.
Project management plan:
– Risk register
– Activity cost estimate
Outputs
1.
Activity duration estimates
2.
Activity attributes
20
Estimate Activity Duration
Tools & Techniques
Expert judgment
Analogous estimating
Using actual previous data and expert judgment
Parametric estimation
Duration
= Quantity of work to be performed x productivity rate
21
Estimate Activity Duration
Tools & Techniques
Three-Points estimates
• Most likely (M)
• Optimistic (O)
• Pessimistic (P)
Formula in CPM:
Duration = ( O + 4M + P)/6
Reserve analysis
22
Develop Schedule
Analyzing :
• activity sequences,
• activity durations,
• activity resources requirements,
• schedule constraints to create the project schedule
23
Develop Schedule
Inputs
1. Organizational process assets
2. Project scope statements
3. Activity lists
4. Activity attributes
5. Project schedule network diagram
6. Activity resource requirements
7. Resource calendars
8. Activity duration estimates
9. Project management plan:
– Risk register
Outputs
1.Project schedule
2.Schedule model data
3.Schedule baseline
4.Resource requirements
(updates)
5.Activity attributes (updates)
6.Project calendars (updates)
7.Requested changes
8.Project management plan
(updates)
– Schedule management plan
(updates)
24
Develop Schedule
Output
Project schedule
Often presented graphically,
– Project schedule network diagram
– Bar charts & Milestone chart
Schedule baseline
Project schedule, with additional information
– Baseline start date
– Baseline finish date
25
Develop Schedule
Output
Schedule data
Supporting data for the project schedule:
• Schedule milestones
• Schedule activities
• Activity attributes
• Assumption & constraints
• Resource requirements by time period
• Alternative schedule (best case, worst case)
• Schedule contingency reserves
26
Develop Schedule
Tools & Techniques
1.
Schedule network analysis
2.
Critical path method
3.
Critical chain method
4.
Resource leveling
5.
What-if scenario analysis
6.
Applying leads and lags
7.
Schedule compression
8.
Scheduling model
27
Develop Schedule
Tools & Techniques
Schedule Network Analysis
Employs a schedule model and various analytical techniques:
– CPM (critical path method)
– Critical chain method
– What-if analysis
– Resource leveling to calculate:
– Early start (ES) & late start (LS) dates
– Early finish (EF) & late finish (LF) dates
28
Develop Schedule
Tools & Techniques
Critical Path Method (CPM)
• A project network analysis technique used to predict total project duration
• A critical path for a project is the series of activities that determines the earliest time by which the project can be completed
• The critical path is the longest path through the network diagram and has the least amount of slack or floa t
29
Develop Schedule
Tools & Techniques
Finding the Critical Path
1.
Develop a good project network diagram
2.
Add the durations for all activities on each path through the project network diagram
3.
The longest path is the critical path
30
Develop Schedule
Tools & Techniques
Schedule compression
Shorten the project schedule without changing the project scope to meet the schedule constraints, imposed dates, or other schedule objectives
Techniques:
Crashing: Cost and schedule tradeoffs are analyzed to determine how to obtain the greatest amount of compression for the least incremental cost
Fast tracking: Phases of activities that normally would be done in sequence are performed in paralel
31
Develop Schedule
Tools & Techniques
Source: Schwalbe, ITPM , 3 rd ed
Original schedule
Shortened duration thru crashing
Overlapped
Tasks or fast tracking
32
Develop Schedule
Tools & Techniques
Buffers and Critical Chain
• A buffer is additional time to complete a task
• Murphy’s Law states that if something can go wrong, it will , and Parkinson’s Law states that work expands to fill the time allowed . In traditional estimates, people often add a buffer and use it if it’s needed or not
• Critical chain schedule removes buffers from individual tasks and instead creates
– A project buffer , which is additional time added before the project’s due date
– Feeding buffers , which are addition time added before tasks on the critical path
33
Source: Schwalbe, ITPM , 3 rd ed
34
Develop Schedule
Tools & Techniques
Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
• A network analysis technique used to estimate project duration when there is a high degree of uncertainty about the individual activity duration estimates
• Uses probabilistic time estimates based on using :
– optimistic (O),
– most likely (M),
– pessimistic (P) estimates of activity durations
• PERT weighted average formula:
O + 4 M + P
6
35
Control Schedule
• Controlling changes to the project schedule
Inputs
1. Schedule management plan
2. Schedule baseline
3. Performance reports
4. Approved change requests
Outputs
1. Work performance measurements
2. Organizational process assets updates
3. Change requests
4. Project mgmt plan updates
5. Project managements updates
36
Control Schedule
Input
Schedule management plan
• Establishes how the project schedule will be manage and control
• Component of the project management plan
Schedule baseline
• Latest, approved schedule
• Component of the project management plan
Performance reports
• Provide information on schedule performance
• Alert to issues that may cause schedule performance problems in the future
Approved change requests
37
Control Schedule
Output
Work Performance Measurements
• SV (schedule variance)
• SPI (schedule performance index)
Organizational Process Assets Updates
Lesson learned documentation
(cause of variance, the reasoning behind the corrective actions chosen)
38
Control Schedule
Output
Change Requests
Processed for review and disposition through the integrated change control process
Project Management Plan Updates
Schedule baseline updates
Schedule management plan updates
Project Documents Updates
Schedule data
Project schedule
39
Control Schedule
Tools & Techniques
1.
Performance reviews
2.
Variance analysis
3.
Project management software
4.
Resource levelling
5.
What-if scenario analysis
6.
Adjusting leads and lags
7.
Schedule compression
8.
Scheduling tool
40
Control Schedule
Tools & Techniques
Project management software
Provides the ability
– To track planned dates vs actual dates
– To forecast the effects of project schedule changes
41
42
Control Schedule
Tools & Techniques
Variance analysis
– Schedule control
Schedule comparison bar chart
– Displays current status bar & approved project schedule baseline
43
B U D I L U H U R U N I V E R S I T Y
POST GRADUATE PROGRAM OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY