Project Time Management

SOFTWARE PROJECT
MANAGEMENT
Project Time Management
Dr. Ahmet TÜMAY, PMP
Project Time Management
Project Time Management includes the processes required to manage timely completion of the project.
The planning effort for time management is part of the Develop Project Management Plan process
(Section 4.3), which produces a schedule management plan that sets the format and establishes criteria for developing and controlling the project schedule.
Plan Schedule Management
• Establishes policies and procedures for planning, developing, managing, executing and controlling the Project schedule
Define Activities
The Activity Definition process will identify the deliverables at the lowest level in the work breakdown structure (WBS), which is called the work package.
Project work packages are planned (decomposed) into smaller components called schedule activities to provide a basis for estimating, scheduling, executing, and monitoring and controlling the project work.
Define Activities
• Process of identifying and documenting the specific actions to be performed to produce the Project deliverables
Activity Definition Tools
Decomposition; Subdividing the work packages into smaller, more manageable components, activities. This activity definition is often performed by the project team members responsible for the work package.
Rolling Wave Planning; Rolling wave planning is a form of progressive elaboration planning where the work to be accomplished in the near term is planned in detail at a low level of the WBS, while work far in the future is planned for WBS components that are at a relatively high level of the WBS.
Activity Definition Outputs
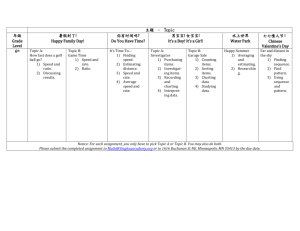
Activity List; The activity list includes the activity identifier and a scope of work description for each schedule activity in sufficient detail to ensure that project team members understand what work is required to be completed.
Activity Attributes; These attributes are used for project schedule development and for selecting, ordering, and sorting the planned schedule activities in various ways within reports.
Milestone List; Significant point or event in the project. May be mandatory or optional.
Sequence Activities
Activity sequencing involves identifying and documenting the logical relationships among project activities.
Schedule activities can be logically sequenced with proper precedence relationships, as well as leads and lags to support later development of a realistic and achievable project schedule.
Activity Sequencing Techniques
.1 Precedence Diagramming Method (AON)
4 Type Dependencies FS,FF,SS,SF
.2 Dependency Determination
Mandatory Dependencies; hard logic, inherent in the nature of the work being done (a built prototype before test) or contractually required.
Discretionary Dependencies; preferred logic, or soft logic, usually established based on knowledge of best practices within a particular application area where a specific sequence is desired, even though there are other acceptable sequences.
External Dependencies; those that involve a relationship between project activities and non-project activities.
.3 Leads and Lags
Estimate Activity Resources
Estimating schedule activity resources involves determining what resources (persons, equipment, or materiel) and what quantities of each resource will be used, and when each resource will be available to perform project activities.
Resource Estimating Techniques
Alternatives Analysis
Bottom-up Estimating
The resource needs of each lower, more detailed piece of work are estimated, and these estimates are then aggregated into a total quantity for each of the schedule activity’s resources.
Published Estimating Data
Estimate Activity Durations
The process of approximating the number of work periods needed to complete individual activities with estimated resources
Estimate Activity Duration Inputs
• Activity Resource Requirements,
• Resource Calendars,
• Project Scope Statement, constraints and assumptions
– Available skilled resources,
– Contract terms and requirements,
– Existing conditions,
– Availability of information,
– Length of the reporting periods.
• Project Risks
Duration Estimating Techniques
• Analogous Estimating; Analogous estimating uses parameters such as duration, budget, size, weight, and complexity, from a previous, similar project, as the basis for estimating the same parameter or measure for a future project. Frequently used for the early phases of project. Less costly, fast but less accurate.
• Parametric Estimating; Uses statistical relationships between historical data and other variables to calculate an estimate for activity parameters, like cost, duration
• Three Point Estimates (PERT);
• Reserve Analysis; Project teams can choose to incorporate additional time referred to as contingency reserves, time reserves or buffers, into the overall project schedule as recognition of schedule risk.
Develop Schedule
An iterative process of analysing activity sequences, durations, resource requirements and schedule contraints to create the Project schedule model. Model defines activities start and finish dates.
Schedule Development Techniques
• Schedule Network Analysis
– Critical Path Method
– Schedule Compression
• Crashing
• Fast Tracking
– What-If-Scenario Analysis
– Resource Leveling
Control Schedule
Schedule control is the process of monitoring the status of the project and manage changes to the schedule baseline and concerned with:
•Determining the current status of the project schedule,
•Influencing the factors that create schedule changes,
•Determining that the project schedule has changed,
•Managing the actual changes as they occur.
Control Schedule Techniques
• Performance Reviews; measure compare and analyse schedule performance – EV (Earned Value
Analysis, Kazanılmış Değer Analizi)
• Variance Analysis
• Project Management Software