Chapter 23 additional information
advertisement

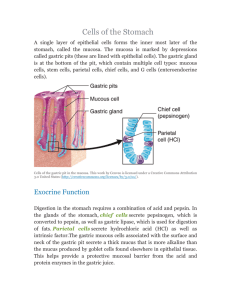
Digestive System Chapter 23 Overview Digestive Processes Functional Concepts Mechanical and Chemical Stimuli Intrinsic and extrinsic Controls Two types of reflexes Short =enteric (local) Long =CNS and autonomic nerves Digestive Anatomy Overview Hepatic portal system 4 layers Mucosa -mucous membrane Submucosa -areolar tissue with blood and lymphatic vessels Muscularis Externa -circular and longitudinal muscle layers Serosa -areolar and simple squamous Enteric Nervous System Submucosal plexus Myenteric plexus Functional Anatomy Functional Anatomy Saliva Greater than 97% water PH 6.75-7.0 Electrolytes Enzymes: Salivary amylase and lingual lipase Mucin -glycoprotein Immune proteins: Lysozyme, definsin, IgA Urea and Uric acid Naturally occurring bacteria http://www.textbookofbacteriology.net/normalflora.ht Salivary Control Intrinsic salivary glands keep mouth moist Extrinsic glands moisten food Food entering mouth activates Parasympathetic innervation triggers enzyme rich saliva Sympathetic triggers thick saliva (mucin rich) Chemical and mechanical stimulate nuclei in pons and medulla Sight and smell of food also activate Lower GI irritation, spicy food, acidic food Teeth and Gums Mechanical breakdown of food Oral disease may cause: Atherosclerotic plaques Clotting within coronary and cerebral arteries Pharynx and Esophagus Pharynx contains friction free stratified squamous epithelia Esophagus is a muscular tube GERD Hiatal hernia Digestive Process: Mouth to Esophagus Mechanical breakdown Deglutition (swallowing) uses 22 muscle groups Buccal phase -voluntary movement within mouth Pharyngeal-esophageal phase -involuntary movement controlled by pons and medulla The Stomach Stomach Simple columnar epithelium -secretes thick alkaline mucous Gastric pits and glands Secretions depend upon location Mucous neck cells -thin mucous Parietal cells -secretes H+, Cl-, intrisic factor Chief cells -pepsinogen and lipases Enteroendocrine cells -histamine, serotonin, somatostatin, gastrin Homeostatic Imbalances Gastric Ulcers 90% caused by Helicobacter pylori 10-20% of infected show symptoms Inhibit or lessen HCl production Damage stomach epithelium Disrupt cell junctions Promote chronic inflammation Digestive Processes in the Stomach Protein digestion begins Alcohol and aspirin absorb into blood stream Secretion of intrinsic factor Required for absorbtion of vitamin B12 B12 is needed for RBC production Regulation of Gastric Secretion Neural mechanisms Hormonal mechanism Stimuli act on brain, stomach, intestine Three phases: cephalic, gastric, intestinal Not mutually exclusive phases Cephalic (Reflex) Phase Short, lasting only minutes Prepares stomach to receive food Sight and smell of food are the trigger Stimulates mucous, chief, parietal and G cells Conditional response Special senses → hypothalamus → medulla → vagus → enteric plexus → stomach glands Gastric Phase 3-4 hours Neural and hormonal response Triggers Distension of stomach Increase in pH (decrease in acidity) Presence of undigested materials (proteins) Gastric Phase Neural response Produces mixing waves Stretch and chemoreceptors trigger short (myenteric) reflexes Ach from parsympathetic neurons stimulates parietal and chief cells Increase in HCl and Pepsinogen Proteins, alcohol, caffine stimulate chemoreceptors Gastric Phase Hormonal response Increasing gastrin levels stimulates parietal and chief cells Gastrin enters blood stream circulates back to stomach Increase in HCl and Pepsinogen Decrease in pH (acidity) Increase in gastric motility Alkaline tide Intestinal Phase Very long, lasting hours Controls gastric emptying Neural and hormonal responses Neural Responses Chyme leaving stomach relieves distension No-longer stimulating stretch receptors Distension of duodenum by chyme stimulates intestinal stretch receptors =enterogastric reflex Inhibits medulla (gastrin secretions) and local reflexes (gastric contractions) Stimulates contraction of pyloric sphincter Mucous production stimulated in duodenum to protect intestine Intestinal Phase Hormonal response Triggered by the arrival of chyme in duodenum Arrival of lipids and carbohydrates Stimulates cholesystokinin (CCK) and gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) CCK inhibits gastric secretion of acids and enzymes GIP inhibits gastric secretion and rate of contraction Meals low in fat enter intestine quicker than those high in fat Decrease in ph stimulates enteroendocrine cells to release secretin Secretin inhibits parietal and chief cells Stimulates pancreas to produce bicarbonate Stimulates liver to secrete bile Partially digested proteins in duodenum stimulate G cells in duodenal wall. Allows more time for lipids to be broken down by intestine G cells produce gastrin which circulates back to stomach increasing acid production Gastric processing meets digestive requirements of specific meals Gastric Motility and Emptying Response to distension of stomach Gastric Contractile Activity Smooth muscle pacemaker cells Interstitial cells of Cajal set basic electrical rhythm (BER) Set maximum rate of contraction Do not initiate contractions Regulation of Gastric Emptying Stomach and duodenum work in conjunction