Checkpoint Chapter 1 – Force Review
advertisement

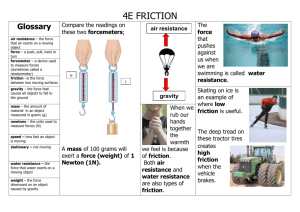
Checkpoint Earth’s Forces Dr. Browne Check Point 1. What is a force? A _________ or __________ 2. To describe a force both the _______________ and the ________________ are needed. 3. Unbalanced forces occur when . . . 4. Balanced forces are ______________ in size and ________________ in direction. 5. _______________ forces do not cause a change in an objects motion. 6. The _________________ of an object is the amount of gravity pulling on it. 7. Look at the diagram below and answer the question that follow: 3 N 10 N 9N a. What is the net force acting on the box? ________ b. Draw the resultant vector: 8. The Gravity is the force of ___________________ between objects in the universe. 9. What is Universal gravitation? Who came up with it? 10. If the mass of an object increases, gravity will _______________. An object with less mass will have _______________ gravity than an object with greater mass. 11. As the distance between objects increases, the gravity will _____________________. 12. The measure of the pull of gravity on an object is known as _________________. ( ___ = m x g) 13. As gravity changes, an objects _____ will change, but its _____ will not change. 14. A spring scale is used to measure ____________, now label the missing parts of the spring scale below: : a. __________ b. __________ c. __________ d. __________ The Coal Family: 15. Friction moves in the _______________________ direction of motion. 16. The friction of an object at rest is called _________________ friction. 17. The friction of two solid surfaces moving over each other is called ________________ friction. 18. The friction of wheels is an example ____________ friction. 19. The friction caused by moving through liquids and gases is called _____________ friction. 20. Friction is affected by ________________ and how ______________ they are pushed together. 21. To reduce friction a ______________________ is used. 22. The amount of force applied to a specific area is known as ___________________. 23. The pressure caused by the force exerted by Earth’s atmosphere is called _______________________. 24. To calculate pressure you would use the formula: _______ 25. The SI units of pressure are: ___________________ 26. To change or manipulate pressure two factors are considered: __________________ and/or ____________________ 27. Both gases and liquids exert pressure, this is known as _______________ pressure. 28. It is the ___________________ in gases and liquids bumping into _________________ that cause the pressure. 29. A ______ is an object that travels around another object. 30. The ____ is an example of a natural satellite. An artificial satellites has been launched into space to gather ____. 31. A satellite that has a higher orbit will take ___ to travel around Earth than lower orbiting satellites. 32. Orbits are created by _____ and ____ which pull on the object, causing it to travel in an _____ path between the two forces. Answer Key Answer Key 1. What is a force? A PUSH or PULL 2. To describe a force both the MAGNITUDE (SIZE) and the DIRECTION are needed. 3. Unbalanced forces occur when FORCES ARE UNEQUAL IN SIZE. Net Force < 1N and causes a change in motion. 4. Balanced forces are EQUAL in size and OPPOSITE in direction. 5. BALANCED forces do not cause a change in an objects motion. 6. The WEIGHT of an object is the amount of gravity pulling on it. 7. Look at the diagram below and answer the question that follow: 3 N 10 N 9N a. What is the net force acting on the box? [2 N, Left] b. Draw the resultant vector: 2N 8. The Gravity is the force of ATTRACTION between objects in the universe. 9. What is Universal gravitation? NEWTON’S LAW OF GRAVITY THAT STATES THAT ALL OBJECTS IN THE UNIVERSE ARE AFFECTED BY GRAVITY. Who came up with it? ISAAC NEWTON 10. If the mass of an object increases, gravity will INCREASE. An object with less mass will have LESS gravity than an object with greater mass. 11. As the distance between objects increases, the gravity will DECREASE. 12. The measure of the pull of gravity on an object is known as WEIGHT. ( W = m x g) 13. As gravity changes, an objects WEIGHT will change, but its MASS will not change. 14. A spring scale is used to measure FORCE, now label the missing parts of the spring scale below: : a. POINTER b. SCALE c. SPRING d. MASS 15. Friction moves in the OPPOSITE direction of motion. 16. The friction of an object at rest is called STATIC friction. 17. The friction of two solid surfaces moving over each other is called SLIDING friction. 18. The friction of wheels is an example ROLLING friction. 19. The friction caused by moving through liquids and gases is called FLUID friction. 20. Friction is affected by SURFACES and how HARD they are pushed together. 21. To reduce friction a LUBRICANT is used. 22. The amount of force applied to a specific area is known as PRESSURE. 23. The pressure caused by the force exerted by Earth’s atmosphere is called AIR PRESSURE. 24. To calculate pressure you would use the formula: P = F / A 25. The SI units of pressure are: PASCAL (Pa) 26. To change or manipulate pressure two factors are considered: AMOUNT OF FORCE and/or SURFACE AREA 27. Both gases and liquids exert pressure, this is known as FLUID pressure. 28. It is the MOLECULES in gases and liquids bumping into SURFACES that cause the pressure. 29. A SATELLITE is an object that travels around another object. 30. The MOON is an example of a natural satellite. An artificial satellites has been launched into space to gather DATA. 31. A satellite that has a higher orbit will take LONGER to travel around Earth than lower orbiting satellites. 32. Orbits are created by FORWARD MOTION and GRAVITY which pull on the object, causing it to travel in an ELLIPTICAL path between the two forces.