09D Visual Examination - Educational Excellence
advertisement

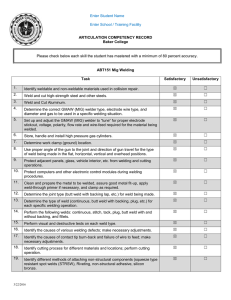
Course Title: Agricultural Mechanics and Metal Technologies Lesson Title: Visual Inspection of Welds – Weld Certification TEKS Addressed in Lesson: 130.22 c 9 D http://ritter.tea.state.tx.us/rules/tac/chapter130/index.html Lesson Objectives. The student will be able to: 1 2 3 identify by sight weld size, alignment, surface contamination, cracks, porosity, and other surface discontinuities, examine various welds for specific criteria, and evaluate welds for quality. Tools and Equipment PPE Appropriate welding machines and electrodes for process Practice metal or projects in progress Visual Inspection PPT Visual Inspection Basics PPT Key Terms / Vocabulary Arc Strikes Blow Hole Porosity Lack of Fusion Lack of Penetration Weld Spatter Undercut Underfill Weld Size Cracks Misalignment Non-destructive evaluation (NDE) or Non-destructive testing (NDT) Engage / Interest Approach/Anticipatory Set Typically, 70% to 80% of surface defects in welds are found and repaired prior to examination by other NDE methods. Effective visual examination must be performed before, during, and after welding. Use visual examination to evaluate welds at every stage of the fabrication process. Show Visual Inspection (VT) PPT at this point. Explore & Explain / Teaching Plan and Strategy / Presentation of New Material Show Visual Inspection Basics PPT for this part of lesson. A. Checklist Before Welding Review applicable documentation Check welding procedures Check welder qualifications Establish hold points (if required) Develop Inspection Plan (if required) Develop plan for recording inspection results Develop system for identification of rejected welds Check condition of welding equipment Check quality and condition of base and filler metals to be used Check weld preparations Check weld joint fit-up Check adequacy of alignment devices Check pre-heat and calibration of equipment when required Check gas and gas flow when required B. Checklist During Welding Check welding variables for compliance with welding procedure Check quality of root pass Check quality of individual weld passes Check interpass cleaning and temperature Check placement and sequencing of individual weld passes Check back gouged surfaces (if required) Elaborate / Activity/Application/ Student Engagement /Laboratory Ask students to develop their own Weld Inspection Reports, either singly or in groups. Ask students to develop their own Non-conformance Reports. Ask students to count the number of welds made in a particular piece, and calculate personal Weld Rejection Rates. Evaluation / Summary C. Checklist After Welding Check finished weld appearance Check weld size and length when required Check dimensional accuracy of weldments Monitor in-process NDT (if required) Monitor post weld heat treatment (if required) Prepare Inspection Reports (if required) References/Additional Materials / Extended Learning Opportunities/ Enrichment ASME Section XI, AWS A3.0 College & Career Readiness Standard ©Texas Education Agency, 2015