Developmental Psychology
advertisement

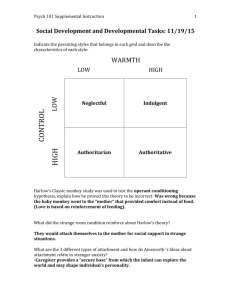
Infancy and Childhood Social Development Maturation • Maturation is the physical development of a person. • First you roll over, then crawl, then walk, then run. • Some babies skip crawling but that can be bad for cognitive development. Stranger Anxiety Attachment • An emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress in separation. Factors of Attachment • Body Contact • Familiarity • Responsive Parenting Body Contact • It was first assumed that infants became attached to those who satisfied their need for nourishment. Then this guy came along…….. Harry Harlow and his Discovered that monkeys preferred the soft body contact comfort of a cloth mother, over the nourishment of a hard/wirily mother. Familiarity • Attachments based on familiarity are formed during our critical periods. . • In general, a critical period is a limited time in which an event can occur, usually to result in some kind of transformation. A "critical period" in developmental psychology is a time in the early stages of an organism's life during which it displays a heightened sensitivity to certain environmental stimuli, and develops in particular ways due to experiences at this time. If the organism does not receive the appropriate stimulus during this "critical period", it may be difficult, ultimately less successful, or even impossible, to develop some functions later in life the optimal period shortly after birth when an organism’s exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produce proper development Konrad Lorenz • Konrad Lorenz studied how goslings (baby geese) will imprint themselves to a human if they get human exposure during a critical period Same with dogs Responsive Parenting Do parents play a part in your attachment? •Mary Ainsworth Stranger Paradigm •Van den Boom’s Research Deprivation of Attachment • Often withdrawn, frightened and in extreme cases speechless. •Harlow’s monkeys would either cower in fright or act extremely aggressive. Many could not mate and if they could, the mothers were unresponsive parents. •Is there a connection between crime and lack of childhood attachment? Daycare • High Quality daycare has shown no detrimental effects on children over the age of two. •The studies go both ways for children under the age of two- no clear answer yet. Self - Concept • A sense of one’s identity and selfworth. When does self-awareness start? Child Attachment Styles based on Ainsworth’s (1971) “The Strange Situation” studies • Mary Ainsworth studied children's’ attachment styles. She would place a mother and young child in a room. The independent variable was a “strange situation” like a stranger or have the mother leave the room. The dependent variable was how the child would react. Ainsworth’s attachment styles • Mary Ainsworth would have a stranger enter the room. Children with a secure attachment would go to the mother for comfort when a stranger entered the room. The child would cry when the mother left but was happy when the mother returned. • Most common (66%) Ainsworth’s attachment styles • Insecure-avoidant (20%) – not distressed at mother leaving or stranger arriving; cool response when mother returns • Probably caused by distant mothers Ainsworth’s attachment styles • insecure- resistant (12%) – clingy to mother; traumatized by every stage of the experiment; distrustful of their mothers • Caused by over-bearing, controlling mothers General Parenting Styles • • • • • Based on Diana Baumrind’s studies They are: Permissive Authoritarian Authoritative Permissive Parents • Parents submit to their children’s desires, make few demands and use little punishment. Authoritarian Parents • Impose rules and expect obedience. •“Why, because I said so!!!!” •What word that begins with A describes an authoritarian? Authoritative Parents • Parents are both demanding and responsive. • Exert control by setting rules, but explain reasoning behind the rules. • Encourage open discussion.