Bios 1030 Sunday week 10 Blood review: 1What are the three main
advertisement

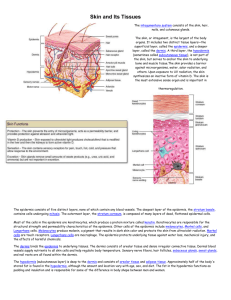
Bios 1030 Sunday week 10 Blood review: 1What are the three main functions of blood? 2. Name four things that make up blood. 3. Where do the elements formed in blood come from? 4. What does the term “form-function” mean? 5. What shape are red blood cells? 6. Why do you think red blood cells are short lived? 7. What does protein do for blood? Be specific. 8. About what percentage of your blood consists of red blood cells? 9. What function in RBC’s allows it to be flexible? 10. Old blood cells are removed by the _________________ and _________________. 11. RBC production is regulated by a hormone called ______________________ which is produced by the ________________. 12. What is anemia? Why is it important when talking about blood? 13. What is Sickle-cell anemia? When/why would you possibly want to have Sickle cell anemia? 14. Describe the two ways discussed in class in which people are able to blood dope. a) b) 15. What are the normal hematocrit levels for females and males? 16. Why do you think blood doping is popular among professional athletes? 17. Where are white blood cells made? 18. List the two long lived and the three short live classifications of white blood cells. 19. What type of blood cells are considered the first responder? Are these cells short or long lived? 20. How does Phagocytosis cells get rid of foreign objects in the body? 21. How does Eosinophil cells get rid of foreign objects in the body? 22. What does hematocrit mean? 23. Macrophages are developed _______________. 24. What are macrophages? Where are they stored? What do they do? 25. What is the longest lived white blood cell? 26. What are the three categories that lymphocytes can differentiate into? 27. Where does leukemia form? This is the cancer of what? 28. Platelets are fragments of what? What do you think the most important function of platelets is? 29. What two things are important to take in consideration when matching blood types? 30. You have a patient who needs blood. The recipient has type AB blood, who can donate to them? 31. Why is it important to recognize blood types during pregnancies? Exam review: 1. Name and describe each of the four main tissue types a) b) c) d) 2. What are the four specialized connective tissues? 3. Which of the three muscle types is not striated? 4. Draw and label a neuron including: axon, dendrites, myelin sheaths, and nodes of Ranvier. 5. Nerve impulses travel ___________ on unmyelinated than on myelinated nerves. 6. What is the largest organ in the body? 7. The two main layers of the skin consist of the _________________ and the ________________, and below the skin is the ___________________. 8. What type of tissue is the epidermis made of? 9. What role does keratin play in the epidermis? 10. True or False. The epidermis contains blood vessels. 11. Give three characteristics of the dermis. 12. What is the main function of the hypodermis? 13. What are fingerprints? What layer of the skin are they created from? 14. How is normal flora helpful in forensics? 15. Why do you think cancer originates in the epidermis and not the dermis? 16. Name the most common and the most deadly types of skin cancer. 17. What are the ABCD’s of skin cancer? 18. Why do adults have fewer bones in their bodies than newborns do? 19. What are the four main functions of the skeletal system? 21. What are ligaments and tendons? 22. Where are blood cells formed? What do they come from? 23. Draw and label a long bone, include: head, shaft, and marrow (red and yellow) 24. Describe the following: OsteoblastsOsteoclastsOsteocytes25. Why is it important that our bones are able to remodel themselves? 26. What are the stages of bone repair? 27. Describe each stage. a) b) c) d) 28. Why are bones more vulnerable to breakage right after bone has been repaired? 29. Fill out the chart Nucleated? Voluntary? Skeletal Smooth Cardiac 30. Describe the order of muscle structure from largest to smallest. Striated? 31. Draw a relaxed sarcomere. 32. Draw a contracted sarcomere. 33. What are the steps that need to take place before a muscle can be excited? 34. List the three places described in lecture where ATP can come from along with the amount of time each one will last. 35. Fill out the chart Fast Twitch Slow Twitch Uses Metabolism Color Fatigue 36. List three things that are increased from anaerobic training. 37. List three things that are increased from aerobic training. 38. Give the path blood flow takes through the body starting from the left atrium. 39. What are the characteristics of arteries? 40. What are the characteristics of veins? 41. What are capillaries? 42. How does the body keep blood flow upward in veins? 43. What is the difference between Pulmonary and Systemic pathways? Pulmonary- Systemic44. What is the SA node? Were is it located? 45. What is the average blood pressure? What are these two numbers called and what does each one measure? 46. What is the number one killer from CVD’s? 47. What is hypertension? Why is it called the “silent killer”? 48. What is a stroke? 49. Describe the differences between LDL and HDL? LDLHDL50. Give three risk factors for developing a CVD.