Running Water- Rivers (transport and erosion)
advertisement

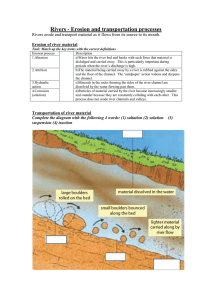
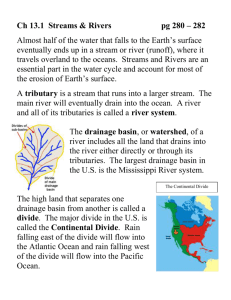
Running water: • The major force of erosion acting on Earth today. • If it weren’t for the mountainbuilding activity of plate tectonics, Earth would be completely flat. • Running water takes the form of rivers, groundwater, and glaciers. • Rivers are formed by the run off of higher elevations. • Drainage Basin- the area of land from which a stream gets its water supply. • As rivers flow over land they erode the landscape in 4 main ways: • Abrasion- occurs when rock particles buff/scrape the bedrock. • Attrition- occurs when particles in the water collide and break down into smaller pieces. • Corrosion- is the dissolving of soluble materials (materials that are easily dissolved in water). • Hydraulic Action- is the breaking down of rock by water pounding on it’s surface. The erosion and transportation of material • Streams transport material through traction- the rolling of larger sediments along the river bed. • Saltation- is the bouncing of particles along the river bed. • Suspension- is the carrying of smaller sediments in the water by turbulent flow. • Solution- is the dissolving of materials in the water. Classification of Rivers: • Rivers evolve through a series of stages from youth to maturity to old age. • Youthful Rivers: • dominated by vertical erosion. This allows rivers to cut down into the landscape forming V-shaped valleys. • Tend to be fairly straight • Have rapids and waterfalls • Have a turbulent flow Mature Rivers: • Dominated by lateral erosion. This allows the river to widen the valley. • Meanders begin to form • The river is smoother and the flow more gentle. Old Age Rivers: • Dominated by deposition and lateral erosion. • The meandering river has created a wide floodplain (good for farming) • Oxbow lakes, back swamps, and natural levees form • Deltas are found at the mouth of the rivers where they enter large bodies of water. Oxbow Lake • Back swamps is the section of a floodplain where deposits of fine silts and clays settle after a flood. • They are usually behind a stream’s natural levees. Delta Deltas: • A landform that forms at the mouth of a river. • This occurs where the fresh water of the river flows into the ocean, sea, lake, or reservoir. • Deposition of sediment occurs as the river flow leaves the mouth of the river. • Over long periods of time, this deposition builds the characteristic geographic patterns of a river delta. • *Reminder* Deposition= the process by which sediments, sand, soils, and rocks are added (deposited) to a landform. (This process may transport the material via water, wind, or through mass wasting).