week5bkgd
advertisement

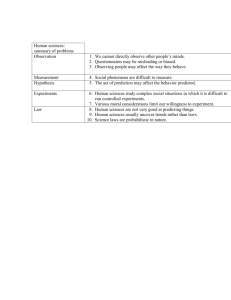
60-207 • Assignment #2 is now posted, due Thursday • This week: How good is the evidence: Personal Observation, Case Studies, Research Studies, and Analogies *and* Are There Rival Causes? • NOTE change for test: OCTOBER 17th • • • Assignment #2: Due date: October 8th in class. Instructions: Search the web for articles using the google search engine by clicking on the link below. 1. In your search find web pages which deal with the following: On July 17, 1996, TWA Flight 800, a Boeing 747 bound for Paris, exploded shortly after taking off from New York's Kennedy Airport, killing all 230 people on board. The National Transportation Safety Board, as recently as last year, has not determined the cause of the crash. (hint: simply plugging in "TWA" in the search parameters will return too many pages of little or no relevance.) Submit the URL from the Google search result. 2. From your search (confine yourself to the first two or three screen results) find two articles with conflicting claims about the cause of the crash and answer: How good is the evidence? Remember to submit the web pages with your assignment. Research Studies as Evidence • systematic collection of observations by people trained to do scientific research • Scientific method tends to seek publicly verifiable data • Extraneous factors are minimized by the use of controls • Experimental design Limitations of Scientific Research • Research varies greatly in quality • Research findings often contradict one another • Research findings do not prove conclusions (at best they support conclusions) • Researchers are biased • Web authors often distort or simplify research conclusions • Research “facts”change over time – especially claims about human behaviour • Research varies in how artificial it is Questions to raise regarding research studies 1. 2. What is the quality of the source of the report? Usually, but not always, the more reputable the source, the better designed the study. Other than the quality of the source, are there other clues included in the communication suggesting the research was well done? E.g., does the report detail any special strengths of the research? 3. 4. Do other findings support the conclusion of the the study? How selective has the communicator been? I.e., has the communicator only selected studies which support his or her point? 5. Is there evidence of a critical attitude in the author/speaker? 6. Is there any reason for someone t have distorted the research? 7. Are conditions in the research artificial and, thus, distorted? (link between lab and the world?) 8. How far can we generalize given the research sample? • Are there any biases or distortions in the surveys, questionnaires, ratings, or other measurements that the researcher uses? Biased Surveys and Questionnaires • Meant to measure people’s attitudes and beliefs … • 1. Participants need to respond honestly. Why wouldn’t they? • 2. Wording in questions can be ambiguous or vague – so they are open to multiple interpretations. How were the questions worded? • 3. Questionnaires may contain built-in biases, including biased wording and biased context. • 4. Placement of items relative to other items. • 5. Length of survey • 6…