Chapter 4: Latin America
advertisement

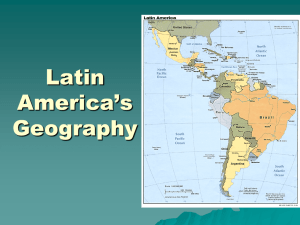
The region begins in Mexico & extends to tip of South America. Shared cultural history is a centripetal force for the region. (remember that term from Ch 1??) Bound by religious homogeneity (Catholicism) & common languages (Sp. & Port.) Deeply impacted by Atlantic Slave trade – LA is one of world’s most racially mixed regions; Poised to become a significant part of global trade (FTAA)http://www.ftaa-alca.org/alca_e.asp STILL NOT APPROVED!! Dominated by its MEGACITIES (over 40 cities with >1,000,000 residents). CITIES: the region’s worst environmental problems are found in its cities. › Mexico city: located in the Valley of Mexico (former site of Aztec civilization) >18 million people; problems include air quality, water stress & subsidence (its sinking!!) **Its geography is a main cause of its problems (city is build over for lake sites & they still draw from underground aquifers for water) http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/earthgwlandsubside.html › Living in Mexico City › Other urban environmental challenges: include air pollution, water stress, garbage removal, significant population density; vulnerability to natural hazards; industrial pollution. Exception = Brazil’s Curitaba – “Green City” http://www.dac.dk/en/dac-cities/sustainable-cities-2/show-theme/greencity/curitiba-the-green-capital/?bbredirect=true DEFORESTATION: This issue is most associated with the region b/c loss of tropical rainforest is most critical here. Rain forests only acct. for 6% of earth’s landmass, but are home to over 50% of worlds’ species. CAUSES: govts. Have encouraged settlement; slash & burn agriculture; cattle ranching (grassification); search for mineral wealth; logging; coca production. Brazil is the biggest offender due its rate of rain forest clearing. Rainforest link RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: When compared to other world regions, LA is not the worst in terms of resource management. However, their major concerns are preserving forests & the biodiversity of the ecosystems within those forests; preserving water & maintaining good water quality (especially in and around the major cities); and stopping the degradation of farmland while at the same time modernizing their agriculture (p. 132) THE ANDES: Extending nearly 5,000 miles the Andes contain 30 peaks that are above 20,000 feet (highest are in the South) as well as active volcanoes. They are also very earthquake prone and contain many precious metals & minerals. Today a major economic activity among countries in the Andean region is drug production (coca & marijuana). Peru Drug Trade Paraguay http://www.whitehouse.gov/ondcp/targeting-cocaine-at-the-source AMAZON BASIN – “Basin” is a term used to describe the entire area through which a river system flows. The Amazon Basin has the largest river system in the world by volume (amt. of water) and the second longest in length. Rainfall is extreme throughout the Amazon Basin, which has no dry season. The Amazon River is not entirely navigable & that’s why despite its immense size, the Amazon Basin has never been a great place for settlement OR a great source of economic profit. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KseAAIsJLQ Although the entire region is within the tropical climate zone (generally warm and adequate rainfall) the geography also brings into play the concept of… ALTITUDINAL ZONATION: this is the relationship between cooler temps at higher elevations and the accompanying changes in elevation. The above concepts tracks changes in temps & rainfall as you ascend to higher elevations. It lead to the notion of the ENVIRONMENTAL LAPSE RATE…which simply is that the higher you go the colder and drier it becomes. Once this concept is understood it becomes the basis for agricultural activity within the specific zones. The 4 zones are TIERRA HELADA (frozen land at highest elevations); TIERRA FRIA (the next highest zone “cold land”); TIERRA TEMPLADA (temperate land at 3 to 6 thousand feet); and TIERRA CALIENTE (the hottest, wettest zone from sea level to 3,000 feet). SEE TEXT P. 140 El Nino is a weather phenomenon used to explain changes in the arrival of warm pacific current that usually comes to the region’s west coast in December. Every decade of so this current is larger (or smaller “La Nina”) and warmer (or colder) and that causes major changes in weather around the region & the globe. El Nino page El Nino Clip Drought – Not really a significant factor in this region, especially when compared with sub-Saharan Africa. It is significant when it occurs because of the impact it has on agriculture (losses and/or disruptions in crop production). Peru Brazil Rio Forum on Problems in LA cities