Different Zones of the Amazon Basin wiki
advertisement

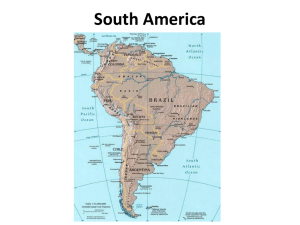
Different Zones of the Amazon Basin: Andes: Fold Mountains created by the collision and subduction of continental plates. The Andes are made of soft sedimentary rock and therefore are eroded easily. The slopes of the Andes is where many rivers have their source and v-shaped valleys are evident in this region e.g Napo valley. Scree slopes are present along with some Volcanic cones e.g. Mt Sangay. Glaciers and Permanent ice is a real feature of the Andes. Due to the thin infertile soil and cold climatic conditions vegetation on the upper slopes is sparse and not very dense. Altitudinal zonation exists with mosses and lichens dominating the highest slopes. The foothills and lowers slopes gradually merge into tropical rainforest. The average height of the Andes mountain range is 4000 metres. The eroded material carried from the Andes flows down the river white in colour. Basin: The Amazon Basin is a formation created by the deposition of transported alluvial sediment. The large rivers that dominate this region are the main feature as they act as the transporters of the sediment. The basin is a flat area that only drops 100 metres from the base of the Andes to the coastal fringe. The Amazon basin is a large flood plain called the Varzea which fuels the region with its seasonal floods. Features that dominate here are the large meandering rivers and there many tribuataries. The meandering rivers have created Ox bow lakes which are scattered throughout the Basin. The Vegetation that dominates here is the dense and large Amazon rainforest. There is clear stratification with very tall trees. Rosewood and Kapok can measure up to 65 metres tall. Ancient Plateau’s: Coastal Fringes: