Mineral Review Mineral – a naturally occurring, inorganic solid that
advertisement

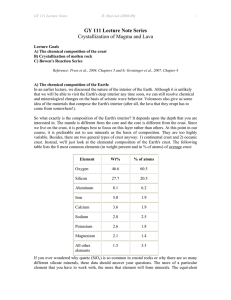
Mineral Review Mineral – a naturally occurring, inorganic solid that has a crystal structure and a definite chemical composition. Characteristics (inside-genetic make-up) Solid – definite shape and volume Inorganic – never alive Naturally Occurring – no help from humans Crystalline Structure – particles of a mineral line up in a pattern that repeats Chemical Composition – compounds that are made up of one or more elements Properties (outside - physical) How minerals are identified Streak – the color of the powdered form of the mineral Luster – way a mineral reflects light – metallic, nonmetallic, glassy, dull, and shiny Hardness – how easily a mineral scratches materials – Mohs Hardness Scale Cleavage – minerals breaks along smooth, flat surface Fracture – minerals that break at random with rough or jagged edges Color – color and appearance are not enough to distinguish minerals Crystal – solid with atoms arranged in an orderly, repeating pattern Crystals form 1) Colling of hot, liquid rock called magma causing compounds to combine a. Magma cools slowly = crystals are large (intrusive igneous) b. Magma cools quickly = crystals are small (extrusive igneous) 2) The evaporation of water that has minerals dissolved in it Special Properties – Florescent, magnetic, optical properties, chemical reactions, taste, radioactive Mineral Compositions and Groups – There are 90 elements that make up Earth’s Crust. About 98% of the crust is made up of only 8 of these elements (Oxygen, Silicon, Aluminum, Iron, Calcium, Sodium, Potassium, and Magnesium) How are minerals grouped? - Grouped by elements – Silicon and oxygen are the two most abundant elements in the Earth’s crust, the minerals are called silicates.