Homework for Iran
advertisement

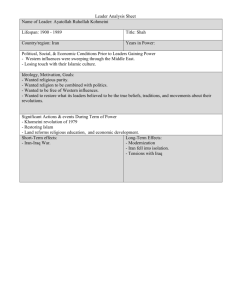
Iran HW – Hand-write answers to the following questions and define the following terms. Use the textbook, Briefing Paper and class notes. Due Monday, April 13. 1. In the West European tradition, Montesquieu argued that government should be divided into legislative, executive, and judicial "branches." The Iranian constitution creates some institutions that don't neatly fit into Montesquieu 's three branches. A. Identify two (2) institutions of national government that do NOT clearly belong in a legislative, executive, or judicial branch of Iranian government. (2 points) B. Explain why each of those institutions do not coincide with Montesquieu's categories. (2 points) 2. a. What is a reason the Iranian Majlis is a representative body? (1 point) b. What is a reason the Iranian Majlis is not representative? (1 point) c. What is a major difference between statute law passed by the Majlis and Islamic sharia? (1 point) 3. What do political scientists mean when they label Iran's economy as "rent seeking?" (2 points) In what way does Iran’s position as a rentier state free the government from being responsive to its citizens’ demands? (2 points) 4. What are two structures in the Iranian regime that provide representation of public opinion in the law and policy making processes? (2 points) What are two structures in the Iranian regime that limit the representation of public opinion in the law and policy making processes? (2 points) 5. The Iranian president is elected nationally and directly. The Prime Minister of the UK is elected from one of over 600 constituencies. Does the manner of election affect the power of these two heads of government? (1 point) If so, how? If not, what are two major factors that account for the differences between the power of the Iranian president and the power of the British PM? (4 points) 6. What is the function of Iran’s Expediency Council? (2 points) Why is it necessary for the state’s functions? (2 points) 7. What are two domestic and two global factors that affect economic policy making in Iran? (4 points) Which are more limiting, the domestic or global factors? Why? (2 points) Questions from Powell (3 points each) 8. Which social groups participated in the revolution of 1978 and 1979, and why? What factors led to the overthrow of the Pahlavi monarchy and support for Ayatollah Khomeini? 9. How do the republican components of Iran’s institutional structure interact with the Islamic ones? Has their relative importance changed over time? 10. What is meant by elite politics being factional politics? What are these factions, what issues divide the elite, and how are their rivalries managed? 11. The founders of the Islamic republic sought to create an Islamic society composed of Islamist citizens. How did they seek to do this, and how successful were they? IRAN – FRQs from previous AP tests 12. There are similarities and differences in the sources of authority for leaders in China and Iran. (2014) a. Describe two formal powers of Iran’s supreme leader. (2 points) b. Identify two official positions that China’s head of state typically holds today. (2 points) c. Describe one similarity in the sources of authority of Iran’s supreme leader and of China’s head of state. (2 points) d. Describe one difference in the sources of authority of Iran’s supreme leader and of China’s head of state. (2 points) 13. Identify one country (hint: Iran) studied in the AP Comparative Government & Politics course that provides for a runoff for the election of its chief executive. Describe how the runoff election system works in the country (Iran) you identified. (2 points) Explain why a country might establish a runoff election system. (2 points) (2014) 14. Define political legitimacy. (2 points) Describe one source of political legitimacy for the office of president in Russia. (1 point) Describe a different source of political legitimacy for the office of the supreme leader in Iran. (1 point) (2013) 15. Identify the institution in Iran that controls which candidates can run for the Majles. (1 point) Describe how this institution controls the selection process. (2 points) Explain how the candidate selection process influences electoral competition. (2 points) (2012) 16. Describe two distinct sources of political legitimacy established by the constitution of the Islamic Republic of Iran. (2 points) Discuss one example of how having both those sources of political legitimacy simultaneously has led to tensions in Iran in the last fifteen years. (2 points) (2011) 17. Political competition and transparency are key concepts that political scientists use when evaluating political systems. (2010) (a) Describe political competition, and describe transparency in the context of politics. (2 points) (b) Explain the function of Iran’s Guardian Council in the electoral process. (2 points) 18. Define theocracy. (1 point) Identify two national-level institutions in Iran for which members are directly elected by citizens. (2 points) (2008) Identify and describe one theocratic institution of government in Iran. (1 point) Terms (from Powell): Basij; Green Movement; Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps IRGC); Islamists; Leader; Majiles; parastatal foundations; multiple power centers; shari’a; Sunnis; Twelver Shiism; ulema; velayat-e faqih (1 point each)