8th Grade
advertisement

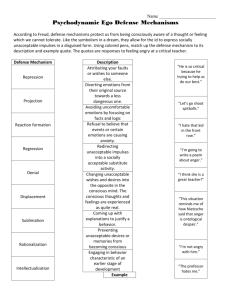
MEH 2.1 & 2.2 Objective 2.1 Evaluate the uses of defense mechanisms is terms of whether they are healthy or unhealthy Defense Mechanisms Defense mechanisms are behaviors that an individual might use to cope with an uncomfortable situation or problem. Defense Mechanisms Compensation A person tries to make up for his/ her weaknesses by developing strengths in other areas. Daydreaming A person escapes unpleasant, boring, or frustrating situations by imagining that he or she is doing something else. Defense Mechanisms Denial Refusal to accept reality. Displacement A person transfers the emotions he or she feels from the original situation or object to another situation or object. Humor A person focuses on the funny aspects of a painful situation. Defense Mechanisms Identification A person tries to assume the qualities of someone that is admired. Projection A person shifts the blame and/or responsibility for his/her actions or thoughts to another person. Rationalization An attempt to justify one’s actions with an excuse rather than by admitting one’s failure or mistake. Defense Mechanisms Regression Retreating to an earlier time that seems less threatening and requires less responsibility. Repression Blocking out thoughts about unpleasant things or experiences. Repression is actually an unconscious method of escaping something unpleasant. Defense Mechanisms Sublimation Transforming unacceptable behaviors into acceptable ones. Sublimation can involve redirecting specific behaviors. Suppression The effort to hide and control unacceptable thoughts and feelings. Objective 2.2 Critque personal use of structured thinking to enhance emotional well-being (based on appropriateness, effectiveness, and consistency). 8 Steps to Healthy Decisions 1) Identify the problem. 2) Gather relevant information. 3) Consider the alternatives 4) Assess positive and negative consequences. 5) Determine who is affected by the decision. 6) Determine who is influencing the decision. 7) Make an informed decision. 8) Evaluate the decision.