PersuasiveTerms 6th Reading printable chart
advertisement
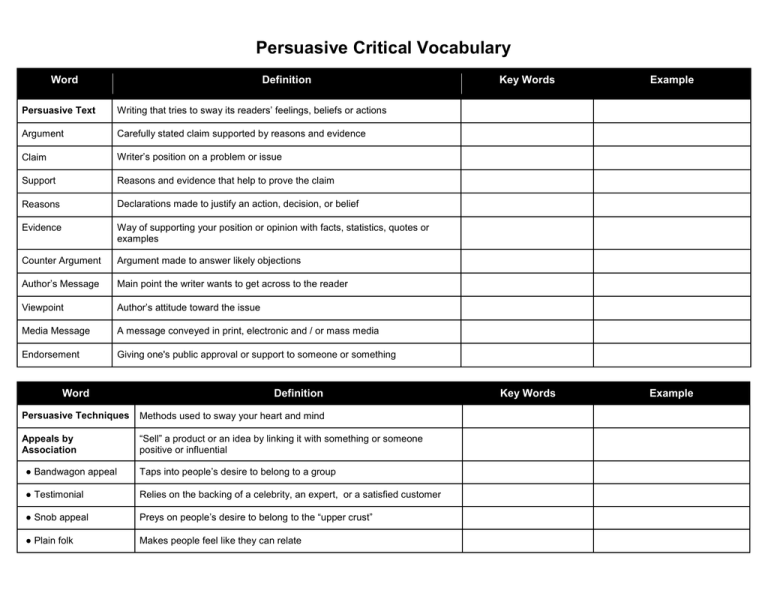
Persuasive Critical Vocabulary Word Definition Persuasive Text Writing that tries to sway its readers’ feelings, beliefs or actions Argument Carefully stated claim supported by reasons and evidence Claim Writer’s position on a problem or issue Support Reasons and evidence that help to prove the claim Reasons Declarations made to justify an action, decision, or belief Evidence Way of supporting your position or opinion with facts, statistics, quotes or examples Counter Argument Argument made to answer likely objections Author’s Message Main point the writer wants to get across to the reader Viewpoint Author’s attitude toward the issue Media Message A message conveyed in print, electronic and / or mass media Endorsement Giving one's public approval or support to someone or something Word Definition Persuasive Techniques Methods used to sway your heart and mind Appeals by Association “Sell” a product or an idea by linking it with something or someone positive or influential ● Bandwagon appeal Taps into people’s desire to belong to a group ● Testimonial Relies on the backing of a celebrity, an expert, or a satisfied customer ● Snob appeal Preys on people’s desire to belong to the “upper crust” ● Plain folk Makes people feel like they can relate Key Words Example Key Words Example ● Appeals to authority Argues that a statement is correct because the statement is made by a person or source that is commonly regarded as authoritative ● Appeals to logic A rhetorical strategy where the argument is made by presenting facts that lead the audience to a specific conclusion Emotional Appeal “Sell” a product or an idea by evoking an emotional reaction ● Appeal to Fear Makes people feel as if their safety, security, or health is in danger. ● Appeal to Vanity Uses flattery to win people over. Loaded Language Relies on words with strongly positive or negative associations. ● Words with Positive Associations Words that bring to mind something exciting, comforting, or desirable. ● Words with Negative Associations Words that evoke strong negative feelings in the reader or remind people of unpleasant images, experiences, or feelings. Faulty Reasoning Claim based on information that is incorrect, biased, or simply does not make sense. ● logical fallacy Mistaken ways of reasoning ● hasty generalization Conclusion drawn from too little evidence ● overgeneralization Broad conclusion using all-or-nothing words like every, always, and never ● circular reasoning Reasons that say the same thing over and over again using different words ● false cause Assumption that one event caused another because it ocurred earlier in time ● vague language Statements that are unclear ● irrelevant examples Examples that do not directly relate to the claim ● rhetorical questions Questions that have an obvious answer, to suggest that anyone with common sense must agree ● stereotyping Applying a conventional, formulaic, and oversimplified conception, opinion, or image of a person or group of people ● name calling Trying to win support by referring to the opposition in negative terms