CH 25 - Biloxi Public Schools
advertisement

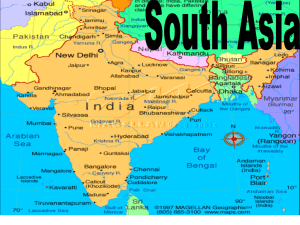
Southern Asia (India and the Indian Perimeter) Chapters 25 and 26 Countries of South Asia Pakistan India Nepal Bangladesh Bhutan Sri Lanka India Natural Environment Three major landforms – The Himalaya Mountains – The Gangetic Plain – The Deccan Peninsula Himalaya Mountains Cotton – 2nd largest exporter in world – India’s largest export is textiles (cloth) Animals – Bengal Tigers, Indian elephants, monkeys, and cobras. https://www.yo utube.com/wat ch?v=I64LLdmHRc (5:00) Indian Elephant https://www.yo utube.com/wat ch?v=vWWXx 5XGAUE (2:00) Common Indian Monkey https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=rJFmLtM GSqs (3:18) Cobra India’s History Aryans (nomadic Central Asian cattle herders) conquered India in 1500 B.C. They introduced Sanskrit language to the area. By 1000 AD the Islamic Empires took over the area. They built the Taj Mahal. By the 1700’s, the British gained control of the area from the French in the “Seven Years War” Sanskrit Taj Mahal Agra, India 1632 Built by Mughal emperor Shah Jahan as a tomb for his second and favorite wife Mumtaz Mahal. She died giving birth to their 14th child. Took 22 years to build. The British East India Company controlled India for the British in the 1700’s Sepoy Rebellion – Many Indians did not like British rule. – In 1857 there was a rebellion from Indian sepoys (Indian troops under the command of British officers) – The sepoys killed the officers and their families. – Both sides reported vicious acts of cruelty, but in the end the British crushed the revolt. – Because of the sepoy revolt, the British did not treat the Indians as equals. In 1885 the Indian National Congress was formed to request more rights from the British, but the request was denied. The Sepoy Rebellion Mohandas K. Gandhi – A young lawyer who led the independence movement in the 20th century. – He was known as Mahatma (great soul) Gandhi. – Gandhi believed that nonviolent noncooperation was the best way to bring positive change. – He led hunger strikes, boycott of British goods, and protests. – His efforts were effective and Britain granted independence to India after World War II. Mahatma Gandhi Partition of India – Britain and the Indian congress wanted India to be one country. – Muslims in India wanted to be a separate state. – Tensions grew, and to avoid war, Britain divided the colony into the countries of India and Pakistan. – Pakistan became mostly Muslim. – India became mostly Hindu. – This left many Hindus in Pakistan and many Muslims in India. – About 14 million were displaced in the world’s largest mass migration – Panic let out and 1 million people died in massacres and riots trying to get to the country of their religion. – These riots even killed Gandhi, when he was shot and killed by Hindu extremist in 1948. – There is religious tension between the areas to this day. Hinduism Aryan religion included the basic ideals that became part of Hinduism. A pantheon is all the gods of a religion. Hindi is the major language of India Hinduism consists of thousands of deities (gods). Hindu Temple in Singapore Hindu Temple Hinduism centers on 3 beliefs: – Reincarnation (being reborn in different forms) – Dharma (doing one’s duty in life) – Karma (positive and negative forces caused by a person’s actions) Brahma – god of creation Vishnu god of protection Shiva – the destroyer Caste system – Brahmins (priests and intellectuals) – Kshatriyas (warriors) – Vaisyas (traders and merchants) – Sudras (laborers) – Dalits (unclean or oppressed) World’s Largest Hindu Temple in New Delhi, India Temple in Delhi, India A Sadhu or holy man India Today One out of every 6 people live in India (1.3 billion people) India’s economy is extremely varied – Outsourcing – make many products for other countries for cheaper than the country using them Farming is the basis of the economy, but online merchandising is growing. Cities are overcrowded, noisy, and smog filled. 70% of India lives in villages that have not changed much for generations. Electricity and paved roads are recent developments. India’s Issues and concerns Rapid growth /Over Population (33% of the country is younger than 14) Poverty (many never attend school and do not have basic standards of life) Political violence (particularly with Pakistan and the Muslim culture – Both countries now have nuclear capabilities) Bombay The Indian Perimeter The countries of the Indian Perimeter are: – Pakistan – Bhutan (landlocked) – Nepal (landlocked) – Bangladesh – Sri Lanka Monsoons greatly affect the climate and vegetation of the area. Mount Everest (29,035ft) is located in Nepal Mount Everest is the highest mountain in the world. Mount Everest, Nepal By the 1500’s the Aryans had moved into the area. The Muslim Mughal Empire ruled the 1500’s to the 1700’s Over time Great Britain controlled almost the entire subcontinent. The British gave up control in 1947 Bangladesh gained independence from Pakistan in 1971. Sri Lanka became independent in 1948. Bhutan became fully independent in 1949. The area has 3 main religions (Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam) Christianity though publicly outlawed is practiced by some. Temple in Nepal Bangladesh is overwhelmingly agricultural. Nepal and Bhutan are very poor and still mainly agricultural. Pakistan and Bangladesh have more than 130 million people. The streets of Bangladesh Katmandu, Nepal Sri Lanka India Perimeter Issues and Challenges The greatest challenge of the Indian Perimeter is poverty. Political issues over Kashmir region between India and Pakistan. Military leaders have overthrown the Pakistan government three times in recent years. Sri Lanka faces issue between Hindu Tamil minority and Buddhist Sinhalese majority.