South Asia: Culture and Lifestyles
advertisement

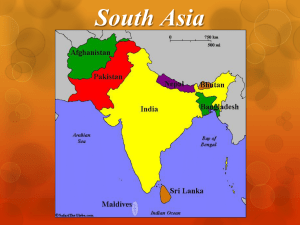
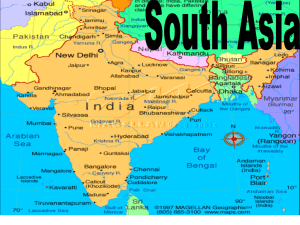
SOUTH ASIA: CULTURE AND LIFESTYLES LANGUAGES __________Major languages spoken in South Asia English is widely spoken in the area, particularly in: ________________________________________ Tourism Parts of South Asia once under British rule __________________________________ Hindi (India), Urdu (Pakistan), Bengali (Bangladesh) Trace roots back to Aryan invaders of 3,000 years ago, and are related to the major languages of Europe Dravidian Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam Spoken in __________________ and __________________ Draw roots back to the earliest inhabitants of South Asia RELIGION Hinduism Main religion of _____________ and __________________ ____________________ Pakistan, Bangladesh, and the Maldives were all founded as Islamic states; thus, the majority of the population in these areas is Muslim. Founded by guru ___________________ in the 1500s Teaches there is one God, and the only way to break away from reincarnation is through meditation, and good deeds. Christians Came out of _________________________ Preaches strict _____________________, because everything has a soul Sikhism Strongest in Sri Lanka, Bhutan, and Nepal Follows the teachings of Siddhārtha Gautama, or ____________________. Jainism There are also almost 120 million Muslim in India Buddhism Also practiced in Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, and Bangladesh About 17 million Concentrated in ______________________ in southern and northeastern India Zoroastrianism An ancient Iranian religion and a religious philosophy. The Indian city of ___________________ houses the last living Zoroastrianism followers. RELIGION AND DAILY LIFE Bhutan and Nepal Prayer flags and prayer wheels can be seen on the streets Monks can be heard chanting ___________________, or repetitive prayers India _____________________, or Hindu holy men, can be seen walking from temple to temple carrying only their blankets and begging bowls _____________________, considered holy, can be seen roaming freely in the streets and markets. Pakistan and Bangladesh Women can be seen wearing their _____________, an enveloping robe that Islamic tradition require for modesty LITERATURE India Epic Poems Written between 1500 and 500 BCE ___________________________ (muh-hah-Bah-ruh-tuh) ___________________________ (rah-MAH-yah-nuh) Muhammad Iqbal Philosopher and writer Wrote in early 1900s Proposed the idea of an ____________________in South Asia Rabindranath Tagore Wrote fiction, poetry, and drama Won Nobel Prize in Literature Wrote India’s _________________________ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jana_Gana_Mana INDIA – DANCE & MUSIC Dance Most dance styles in India are based from themes of Hindu mythology __________________________________ (bah-Rah-tah-NAHT-yam) Based on the devotional postures of sacred temple dancers, these dances involve rapid whirling, stamping feet, and elaborate language of hand gestures called mudras. Dancers, usually women, wear bright silk saris and jingling gold jewelry. __________________________________(kah-tha-KAHL-lee) Male dancers wear huge, colorful masks, and their violent movements are rooted in martial art postures Music – two basic types Hindustani – in the _______________ Karnatic – in the __________________ Melody called ____________ Rhythm called ___________ INDIA – THE MOVIES ______________________ Nickname given to India’s film industry centered in Mumbai Mixture of Bombay (now called Mumbai) and Hollywood World’s largest producing film industry More than 800 full-length films a year VISUAL ARTS AND ARCHITECTURE Visual Arts Traditionally South Asians visual arts have been used to express ________________________, and to document daily life. Architecture _____________ – Buddhist domed temples in Nepal and Sri Lanka _____________ – fortified monasteries in Bhutan Taj Mahal – is a white marble mausoleum located in Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India. It was built by Muslim emperor ______________________in memory of his third wife, Mumtaz Mahal. The Harmandir Sahib - informally referred to as the __________________________is a prominent Sikh Gurdwara located in the city of Amritsar, Punjab, India. It was built by the fifth Sikh guru, Guru Arjan, in the 15th Century. In 1604, Guru Arjun completed the Adi Granth, the holy scripture of Sikhism, and installed it in the Gurdwara. Modern Art and Architecture A blend of traditional and _____________________styles SPORT - CRICKET http://www.ted.com/talks/harsha_bhogle_the_rise _of_cricket_the_rise_of_india