Unit 5 Part 1 The Brain: Biological Basis of Behavior
advertisement

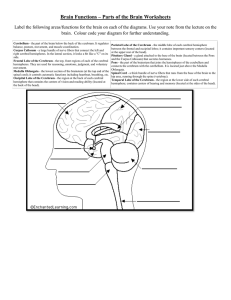
Unit 5 Part 1 The Brain: Biological Basis of Behavior Anatomy Function 1. Hypothalamus 2. Cerebral Hemispheres A. Auditory/hearing, language memory and speech capacity B. Primary visual area 3. Cerebrum C. 4. Cerebral Cortex D. Bridge connecting various parts of the brain 5. Cerebellum E. Relay station for all sensory information except smell 6. Frontal Lobe F. Helps to maintain homeostasis (body temperature, body fluid, hormone secretion) 7. Temporal Lobe G. Center that controls heart rate and reflex actions, regulates Controls motor activities and interprets sensation blood pressure and breathing 8. Parietal Lobe H. “Master gland”; releases hormones controlling many body 9. Occipital Lobe I. 10. Spinal Cord activities & Influences activities of many endocrine glands Two bundles of axons that connect the hemispheres of the brain so right & left sides can communicate J. 11. Medulla Oblongata Controls skeletal muscles, formation of words, and personality K. Branched fibers that receive neural impulses 12. Pons L. 13. Dendrites M. Thought to secrete melatonin (which is believed to play part 14. Axons N. Four cavities in brain that contains cerebrospinal fluid and protects the brain O. Responsible for coordination movements, makes movements smooth, helps maintain muscle tone and equilibrium P. Transmits neural messages from cell body towards another neuron Q. Controls many reflex activities of body; transmits Organized to receive sensory information & control muscles mostly from contralateral (opposite) side of body in regulation of sleep) 15. Central Nervous System 16. Corpus Callosum 17. Pineal Gland information back and forth from nerves of PNS to brain 19. Thalamus R. Control center for entire organism; integrates incoming information and determines appropriate responses. S. Most highly evolved portion of brain 20. Pituitary Gland T. 18. Ventricles Sensory Association area – impulses from skin such as pain and temperature are interpreted; area for estimation of distances, sizes and shapes 21. The Central Nervous System (CNS) is comprised of the ____ and ______ 22. The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) is made up of outside the CNS and _________ ______ _______. such as the eyes, ears, taste buds, olfactory receptors and touch receptors 23. The largest part of the human brain is the __________________ 24. The thin outer layer of the cerebrum is the ________l ______ 25. The four lobes of the cerebrum or brain are the _______ and the _________ . , _____ , ________ lobes. 26. The cerebral hemispheres are connected by the ______ ________ 27. Damage to the occipital lobe can result in _________ 28. Damage to the temporal lobe can result in _______ 29. Dysfunction of the hypothalamus can cause ________ ____________ . __________ . . , _____ , and ________ problem. 30. Damage to the frontal lobe can cause changes in ___________ . 31. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) is produced by a structure called _______ located in the __________ 32. The ventricles excrete _____ and away from the brain. . ______ . ________ from Cerebrospinal Fluid to the blood ,