Puritan New England and Middle Colonies with
advertisement

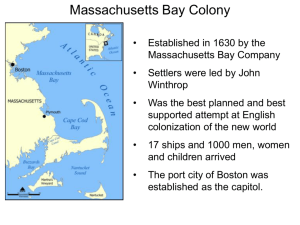
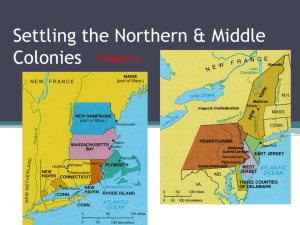
New England and the Middle Colonies 1601–1700 Puritan Origins: The English Reformation • Henry VIII uses the Reformation for political (and personal) means. England breaks with the Catholic Church • English (Anglican) church keeps most practices of Catholicism • Others (Puritans) wanted a full reforming of the church. Wanted to eliminate rituals and focus on the individual • Persecution of Puritans in England Puritans and the Settlement of New England • The Pilgrims and Plymouth Colony - want to build a orderly Puritan version of England - First Holland (to much vice) then onto America Plymouth Video English Migration, 1610-1660 The Founding of Massachusetts Bay Colony • Puritans obtain a Royal charter for most of Northeast of America - special provision: gov’t could be located in the colony instead of England • John Winthrop elected Governor and settled in Boston - “City Upon a Hill” sermon given • Native Americans- initially few around because of epidemics; relations will break down The Early Years of Massachusetts Bay Colony • Disease spread quickly and killed many. Starvation also an issue • Settlers kept arriving; especially when Church of England cracks down on Puritan ministers in England • Immigrants came from all parts of society and unlike Chesapeake many women/children The Evolution of New England Society Church, Covenant, and Conformity • Puritans influenced by John Calvin - strict discipline in behavior, & predestination • All town residents must attend church services • Everyone kept an eye on everyone else; trying to prove saintliness • Sabbath day taken seriously- fines issued for flute playing or visiting neighbors • Banned practices: Christmas, Easter, cards, dice, any games of chance, music, dance Government by Puritans for Puritanism • Transformed the joint stock company into a colonial gov’t • Freemen had voting rights on some issues & gov’t position - Freemen= male church members - “Contrary minded” men forced out Splintering of Puritanism • How long did you think it would last? • Different visions of Godliness; every town/church had different rules • Roger Williams • Anne Hutchinson vs. John Winthrop- Covenant of Grace vs. Covenant of Works • More divisions of churches Quakers and Salem Witch Trials • Quakers (society of friends) arrive in New England. Different beliefs. - God speaks directly to everyone; do not need preachers or Bibles - Refuse to conform to laws and government, Sabbath - As you can imagine there is conflict between the Quakers and Puritans. - Salem Witch Trials- 100 accused of witchcraft, 19 executed The Founding of the Middle Colonies- last 1/3 of 1600s • From New Netherland to New York - Dutch West India Company purchases Manhattan for goods worth 12 beaver pelts from local Natives. - New Amsterdam - Low population (although highly diverse) and low profits - Monarchy restored in England. Duke of York is given New Netherland as a land grant; sent warships and kicked out the Dutch - Early Governors struggle with controlling the colony because of its’ diversity Colonies in Eastern North America 1650 New Jersey and Pennsylvania • Duke of York subdivides his land grant • Quarrels between officials. William Penn (Quaker and prominent individual from a military/political family) – Jersey stays a propriety colony (focused on trade) – Penn given a land grant for a Quaker colony (Pennsylvania); given to rid England of Quakers Middle Colonies, 1685 Relations with Native Americans and King Philip’s War • Massachusetts settlers massacre Pequot’s 1637 • 1670s warfare erupts in both New England In New England - Steady encroachment on Native land - Wampanoags struck back; Chief is Metacomet/King Philip (settlers name for him) - Counterattacks and thousands are killed. - Colonists gain upper hand and defeated the Wampanoags with a scorched-earth policy. (see map on the next page) Aftermath: Hatred of Natives, large war debt, devastated frontier King Philip’s War, 1675 – 1676) Spread of Settlement: British Colonies, 1650–1700