Characteristics of Science Study guide for test on Metric and
advertisement

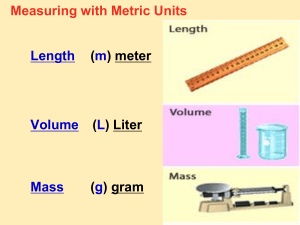
Characteristics of Science Test Date: October 8, 2015 Study guide for test on Metric and Scientific Method Part One BIG IDEAS Metric Measurement The Metric System was created by the French in an effort to standardize measurements. This system is used by almost the whole world. The United States is the only major country that still uses the English system of measurement. In science, the metric system is always used. This enables scientists all over the world to share test results and progress further in scientific research. The basic unit for length is the meter. The basic unit for mass is the kilogram. The basic unit for volume (capacity) is the liter. 1 gram per cubic centimeter is equal to 1 milliliter (also used in capacity) Common Prefixes (with abbreviations and values) used in the Metric system kilo (k) = 1000 hecto (h) = 100 deca (da) = 10 base unit = liter (L) or meter (m) or gram (g) deci (d) = 0.1 or 1 tenth centi (c) = 0.01 or 1 hundredth milli (m) = 0.001 or 1 thousandth Common Values 100 cm = 1000 mm = 1 m 1000 m = 1 km 10 mm = 1 cm (repeat this same pattern for other units) You will have four problems to convert in the metric system. Review your practice sheets and metric information examples. In addition, you will have to determine the volume, mass, and length of several things. Review your “How to Measure” packet. Remember that items that less than 1.0 g/cm3 will float while those that are more will sink. The density of water is 1.0 g/cm3. Part Two BIG IDEAS Scientific Method The scientific method is a way to ask and answer scientific questions by making observations and measurements Generally, there are five steps in the scientific method: ask a question (problem), form a hypothesis, conduct and design an experiment, analyze data (results), and draw a conclusion. It is important for your experiment to be a “fair” test. A “fair” test occurs when you change only one factor (variable) and keep all other conditions the same. The final step in the scientific method is the conclusion. This is a summary of the experiment’s results, and how those results match up to your hypothesis. Most hypothesis(es) turn out to be wrong when conducting experiments. You will have several science scenarios in which you will have to develop a hypothesis, identify a control, dependent, independent variable, analyze results, and make a conclusion. Vocabulary (expect to know these terms in context and as definitions) 1. Hypothesis – a prediction or an educated guess; a possible explanation which can be tested 2. Observation – a report of what the senses detect 3. Data – information gathered in an experiment; evidence 4. Conclusion – a statement which sums up what is learned in an experiment 5. Problem – a question that can be answered by gathering evidence 6. Experiment – a test or procedure to prove or disprove a hypothesis 7. Variable – any factor that can change in an experiment 8. Control – any factor that stays the same in an experiment 9. Independent Variable – the part of the experiment that is manipulated or changed in the experiment; also known as the manipulated variable (example: new toothpaste) 10. Dependent Variable – the part of the experiment that is affected by the independent variable; also known as the responding variable (example: whiter teeth)