B - Effingham County Schools
advertisement

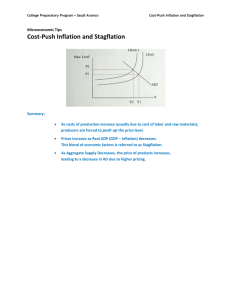
Grab a Calculator • (unless you already have one) Pepperonia & Anchovia And The Winner Is... Now, Do One On Your Own. You can do it! Clicker Quiz 1. GDP is the dollar value of all final goods and services sold in a ___ month period. • • • • A) 6 B) 10 C) 12 D) 24 2. Which of the following purchases is included in GDP? • • • • A) A haircut. B) A used car. C) An illegal drug. D) An oil refinery buys oil from a drilling company. 3. Which best describes GDP? • • • • A) a way to measure inflation B) a way to measure happiness C) a dollar value D) an indicator of what kinds of things we are producing 4. GDP = __ + I + G + (X-M) • • • • A) A B) B C) C D) D 5. Which actor in the economy is responsible for most of the investment that occurs? • • • • A) Consumers B) Businesses C) Government D) Military Is it counted & where?? A haircut from Regis at the mall. • • • • A) Yes, consumption B) Yes, investment C) Yes, government D) Not counted Is it counted & where?? The purchase of the scissors used to cut your hair. • • • • A) Yes, consumption B) Yes, investment C) Yes, government D) Not counted Is it counted & where?? A haircut Mom gave you. • • • • A) Yes, consumption B) Yes, investment C) Yes, government D) Not counted When Mr. Cook buys his Ferrari… • A) GDP & consumption will both rise. • B) Consumption & imports will rise, GDP will stay the same. • C) Consumption & exports will rise, GDP will stay the same. • D) Imports will rise, GDP will fall. • E) GDP will stay the same, and no sectors will be affected. Independent GDP Work Silently Answers Georgia Standard & Today’s Big Question(s) • How are we doing? – Compared to others? – Compared to how we’ve been doing? Scary! • The dollar has lost 56% of it’s value since 1992. • Or, a dollar today will buy the same amount of stuff as $0.64 would buy in 1992. From year to year, a dollar then vs. a dollar now. Macroeconomics Lesson 3 Inflation Part 1 Inflation • Inflation: P , $ value • Deflation: P , $ value • Stagflation: recession + inflation at same time. • For the last 50 years, the U.S. has had an avg. inflation rate of 4% /yr. • Do recessions have any effect on the rate of inflation? If so, what? • Are their any exceptions to your answer? When? So let’s say • You get a raise of 5% this year. • But inflation was 5% this year. • Your nominal pay rose. • What happened to your PURCHASING POWER??? • IT STAYED THE SAME Stories of extreme inflation Note those who are helped, and those who are hurt. Story Time • Once upon a time in Burgerland… • There were only four jobs: – Beefers (cowboys) – Bakers – Burger store managers – Bankers • And only one product… • BURGERS. For as long as anyone can remember… • The price of a burger has been $1. • All of the burger joints voluntarily charge $1. Bill the baker wants to expand his business • So he borrows – $10 from Brenda the banker, – at 20% simple interest (fixed rate), – to be paid back in one year. • That’s $12! • What is Brenda’s profit? • How many burgers will Brenda be able to buy with her profits? • (All of the burger joints voluntarily charge $1.) But, before Bill is due to pay Brenda… • The burger store managers (Bruce, Belinda, Barry, and Bedelia) unexpectedly raise their prices from $1 to $2 a burger!! • Who is hurt by this change of events? • Who is helped? • How could Brenda have kept from getting hurt? If Brenda had charged • 20% interest • PLUS • the rate of inflation (called an adjustable rate loan) • She would have come out better. • Prices doubled. That’s 100% inflation. • A loan of $10, paid back plus 120% interest would be $22 Unexpected Inflation • Hurts: –lenders at fixed rates –savers at fixed rates –fixed-income recipients • Benefits: –borrowers at fixed rates Helped, hurt, or neither?? • Service providers fulfilling long-term contracts • Workers with cost-of-living-adjustments in their contracts • Banks that have made fixed-rate loans • Banks that have made adjustable-rate loans • Borrowers of fixed-rate loans • Borrowers of adjustable-rate loans Helped or Hurt? A Competition Helped or Hurt? Individual Work Reminders/Hints • A bond is a loan. – If I buy a bond from Coca-Cola, I’m loaning them $. – They sold me a bond, so they’re borrowing from me. • Dividends are profits paid to stockholders. When prices rise, dividends rise. • Income tax is a percentage of your income. – When prices rise, incomes rise. Answers Clicker Quiz $1 dollar bought more stuff in 2009 than it did in 2008. The time between 2008 and 2009 was a period of • A) inflation • B) deflation • C) stagflation Stagflation is a period of • • • • A) Inflation and recession B) Inflation and deflation C) Deflation and recession D) Inflation and rising GDP Inflation MOST hurts • • • • A) lenders at fixed rates. B) borrowers at fixed rates. C) lenders at adjustable rates. D) borrowers at adjustable rates. Inflation MOST helps • • • • A) lenders at fixed rates. B) borrowers at fixed rates. C) lenders at adjustable rates. D) borrowers at adjustable rates. In order to protect themselves in case of unanticipated inflation, lenders often • A) make adjustable-rate loans. • B) make fixed-rate loans. Who is hurt MOST by unanticipated inflation? • A) savers at a fixed rate of interest • B) borrowers at a fixed rate of interest • C) workers with a union cost-of-living adjustment in their contracts • D) speculators in gold and other precious metals Who benefits MOST from rising inflation? • A) owners of stocks • B) service providers fulfilling long-term contracts • C) homeowners paying back fixed-rate mortgages • D) retired people living on Social Security (Social Security has an annual cost-ofliving increase) Of the following groups, the one hurt the LEAST by unanticipated inflation is • A workers who have cost-of-living adjustments in their labor contracts • B people who have saved money in accounts with a fixed interest rate • C banks that have made long term, fixed rate mortgage loans • D consumers who buy goods and services at prevailing market prices Sue got a 10% raise at work this year, & the rate of inflation was 12%. Sue’s • A) nominal pay rose and her purchasing power rose. • B) nominal pay rose and her purchasing power fell. • C) nominal pay fell and her purchasing power rose. • D) nominal pay fell and her purchasing power fell. Macroeconomics Lesson 4 Inflation Part 2 Auction Time! MV=PQ • • • • M: money supply V: velocity P: price Q: quantity (of goods and services) Causes of Inflation • Increase in money supply (MV=PQ) • War • More demand Constructing a Price Index • Inflation can distort GDP from year to year. • A price index measures P changes. • Select goods & services for a “market basket.” • Add the price of each of these goods, to get the “base-year market basket price.” • Find the market basket price at regular intervals (monthly, yearly, etc.). 1st Period Chad Seth Danielle Zack Michael Baggott Kyle Kendall Matth Nicole Arron Hillary Michael Brannen Shannon Lacey Haley Virginia Brandon Erin Morgan Taylor Teacher Desk/ Work Area 2nd Period Megan Justin Xavier Andrew Paige Cyndilee Chris Charlee Ryan Stacey Amanda Chelsea Brett Jessica Tim Courtney Kylie Forrest Lacey Alison Daniel Morgan Emily Teacher Desk/ Work Area Haley Jordan Alex Avery 4th Period Dee Dee Moriah Kristen Kayla Jade (Empty) Drew Steven Kara Amber Bethany (Empty) Kevin Harley JD Courtne y Nick Sonia David Melissa Jordan Edwards Jonatha n Jordan Marin Mandie Lauren Kayla Daylan Catherine Phillip Justin Raven Ryne Maggie Teacher Desk/ Work Area Andre’ Kelsea With Your Partner • With your partner, think of ten things that the average family spends money on in a month. • These things can be goods or services. • Write these down on a sheet of paper, along with your guesses as to quantity consumed. Item Quantity 1. Bread 4 loaves 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. …10. Math Review • Percent Change • the formula: [(new-old)/old] X 100 • so if something increases from 5 to 7, the percent change is • [(7-5)/5] = 0.4 = 40% Constructing a Price IndexContinued • Price index = • (selected basket price/ base yr. basket price)X100 • The base-year price index always = 100! • Inflation = • % change in price index, [(new-old)/old] Inflation between ‘84 & ‘98: (163-100)/100 = 0.63 = 63% Inflation between ‘98 & ‘03: (183.7-163)/163=0.13=13% Constructing a Price IndexContinued • Example: • The country of Spamelot only makes Spam and crackers. • 1960 2010 • P Spam 0.40 1.20 • P Crackers 0.60 1.80 • Mkt Basket P ____ ____ • P Index (base year 1960) 100 ____ • Inflation from 1960-2010 _____ On the back of your partner assignment... • Put these headings at the top: • Item Q P-item ‘99 Total P ‘99 P-item ‘09 Total P ‘09 • • • • Near the bottom of your page, write: Total Market Basket P ‘99 ___ Total Market Basket P ‘09 ___ % inflation ‘99-’09___ Assignment • Estimate the rate of inflation between 1999 and 2009. • 1st: create your market basket by – selecting AT LEAST 7 items from the list – determining quantities of each item used per month • 2nd: multiply Q of each item times the P for each year, and fill in your chart • 3rd: Add up your total market basket price for each year • 4th: Calculate percent change in your market basket prices [(new - old)/old] Prices in 1999 • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Peanut butter (lb.)- $1.77 • White flour (lb.)- $0.30 • White bread (lb.)- $0.87 • Chocolate chip Cookies (lb.)- $2.61 • Ground beef (lb.)- $1.38 • Pork chops, center cut, bone-in, per lb.- $2.95 • Bologna, all beef or mixed, per lb.- $2.41 • Chicken breast, bone-in, per lb.- $2.07 • Cheddar cheese, natural, per lb.- $3.75 • Apples, red delicious, per lb.- $0.86 • Bananas, per lb.- $0.49 • Tomatoes, per lb.- $1.90 • Lettuce, iceberg, per lb.- $0.65 • Beans, dried, any type, all sizes, per lb.- $0.69 • Coffee, 100%, ground roast, all sizes, per lb.- $3.44 • Average electric bill per month- $84 • Gasoline, unleaded, per gallon/3.785 liters- $0.97 • Movie ticket- $5.06 • US postage stamp- $0.33 • Bacon (lb.)- $2.59 • Dozen eggs- $0.89 • Average rent/housing payment per month- $645.00 • Prices in 2009 Peanut butter (lb.)- $2.14 White flour (lb.)- $0.52 White bread (lb.)- $1.38 Chocolate chip Cookies (lb.)- $3.11 Ground beef (lb.)- $2.36 Pork chops, center cut, bone-in, per lb.- $3.39 Bologna, all beef or mixed, per lb.- $3.11 Chicken breast, bone-in, per lb.- $2.46 Cheddar cheese, natural, per lb.- $5.01 Apples, red delicious, per lb.- $1.23 Bananas, per lb.- $0.63 Tomatoes, per lb.- $1.66 Lettuce, iceberg, per lb.- $0.94 Beans, dried, any type, all sizes, per lb.- $1.40 Coffee, 100%, ground roast, all sizes, per lb.- $3.68 Average electric bill per month- $126 Gasoline, unleaded, per gallon/3.785 liters- $1.79 Movie ticket- $7.50 US postage stamp- $0.42 Bacon (lb.)- $3.22 Dozen eggs- $1.37 Average rent/housing payment per month- $780.00 And the actual (according to the CPI) rate of inflation is... You figure it out! Major Price Indexes • Consumer Price Index (CPI)-90,000 items in 364 categories. • Implicit GDP Price Deflator- all goods/services. Base year 1996. Clicker Quiz When the value of money was based on its silver content, new discoveries of silver were frequently followed by periods of • • • • A recession B recovery C shortage D inflation The value of a price index in 2000 was 172. What was the value of that price index in it’s base year? • • • • A) 72 B) 100 C) 136 D) 152 The value of a price index in 2000 was 172. What was the rate of inflation between the base year and 2000? • • • • A) 72% B) 100% C) 136% D) 152% The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is an indicator of which of the following? • • • • A the size of an economy B the velocity of money C the level of inflation or deflation D the presence of a budget deficit or surplus If one wanted to know whether there had been inflation or not, the BEST measure to observe would be the • • • • A. GDP. B. business cycle. C. CPI. D. national debt Draw Your Basket • Draw the basket holding all of the items you picked. • To the left of the basket, list the base yr market basket P & the base yr P index. • To the right, list the current market basket P & this yr’s market basket P. • At the top-center, write the rate of inflation. • Include at least five colors. Inflation tends to increase at the end of expansions, & tends to decrease during periods of recession. II. Constructing a Price IndexContinued • • • • • • • Steps: Select items for a market basket. Record P of each item. 1st year total = base-year market basket P. Record P of same market basket each yr. P index = (new basket P/ base yr. basket P)X100 Inflation = % change in price index, [(new-old)/old] Inflation By Country Bell Ringer • Think about how we defined GDP a few days ago. • How could GDP be used to help tell us if we’re in a recession? Georgia Standard & Today’s Big Question(s) • How are we doing? – Compared to others? – Compared to how we’ve been doing? Ch 13, Section 2 pg. 350 GDP and Changes in the Price Level I. Real GDP • GDP adjusted for inflation. • Real GDP= • [GDP from year Y/(price index from year Y)]X100 • This formula sets dollars equal to base year. Listen • If we have inflation, what happens to the price index values from year to year? I. Real GDP • Listen: • If GDP in 2003 was $10.6 trillion, and the GDP deflator was 111.9, what was the Real GDP? • [$10.6 trillion/111.9]X100= $9.5 trillion • $9.5 trillion is 2003 GDP measured in 1996 prices. • • • • • • • • • I. Real GDP Listen GDP in 1999 was $9.22 trillion. Remember, the GDP in 2009 was $14.25 trillion. formula for percent change is: GDP increased by 55%. [(new-old)/old]X100 Assignment: Divide 2009 GDP by your 2009 price index. Multiply this value by 100. Now you have 2009 GDP in 1999 dollars! Determine the % change in YOUR Real GDP between 1999 and 2009. II. New Graph • P level measures P of everything. • RGDP measures Q of everything. III. Aggregate Demand • D for all goods/ services. • AD increases if – C, I***, G, or Nx – money supply II. Aggregate Supply Continued • Increases if: – input costs or i – productivity or technology Decreases in the prices of oil, steel, etc. can cause Ag. Supply to increase. Causes of Inflation • Demand-pull inflation • Cost-push inflation - during stagflation • Growth in money supply. • Wage-price spiral - higher Ps, then higher wages, then higher Ps... Mr. Cook’s Crazy Argument • Listen: • Inflation isn’t necessarily bad. In fact, a little inflation is often a good thing. • Think about the AS/AD curves. • An increase in AD reflects a growing economy, yet causes a higher price level. Inflationland • In Inflationland, they have inflation at the relatively high rate of 7% a year. • The inflation rate is always 7%. • Banks expect inflation to stay at 7%, and make decisions accordingly. • Businesses give all workers a 7% raise every year. • The government raises taxes 7% every year. • Who does inflation hurt in this country???? III. Costs of Inflation • Shoe-Leather • Menu Inflation By Country Inflation By Country It’s a Mystery! • What was happening to prices in Spamelot between 1960 and 2010???? • P index = • (new basket P/ base yr. basket P)X100 • Base Year price index is ALWAYS 100! • Inflation = % change in price index, • Percent change = [(new-old)/old] Listen • If we have inflation, what happens to the price index values from year to year? Review • P index = • (new basket P/ base yr. basket P)X100 • Base Year price index is ALWAYS 100 • Inflation = % change in price index • Percent change is always: [(new-old)/old] Review • Example: • The country of Spamelot only makes Spam and crackers. • 1960 2010 • P Spam 0.40 2.50 • P Crackers 0.60 1.50 • Mkt Basket P ____ ____ • P Index 100 ____ • Inflation from 1960-2010 _____ VII. Major Price Indexes • Consumer Price Index (CPI)-90,000 items in 364 categories. • GDP Deflator- all goods/services. 1. GDP is the dollar value of all final goods and services sold in a ___ month period. • • • • A) 6 B) 10 C) 12 D) 24 2. Which of the following purchases is included in GDP? • • • • A) A haircut. B) A used car. C) An illegal drug. D) An oil refinery buys oil from a drilling company. 3. Which best describes GDP? • • • • A) a way to measure inflation B) a way to measure happiness C) a dollar value D) an indicator of what kinds of things we are producing 4. GDP = __ + I + G + (X-M) • • • • A) A B) B C) C D) D 5. Which actor in the economy is responsible for most of the investment that occurs? • • • • A) Consumers B) Businesses C) Government D) Military GDP Worksheet • Follow all directions Real GDP • GDP adjusted for inflation. • Real GDP=[GDP/(GDP deflator)]X100 • This formula sets dollars equal to base year. The oil crisis of 1973 caused stagflation. High oil prices caused a recession and inflation at the same time. High inflation + falling real GDP = STAGFLATION GDP- 2007 Real GDP Growth - 2007 Inflation Review • Inflation: P , $ value • Deflation: P , $ value • Stagflation: recession + inflation at same time. • Listen: • U.S. has had inflation for 50+ years, avg. rate = 4% /yr.