Organ Systems of the Human Body
advertisement

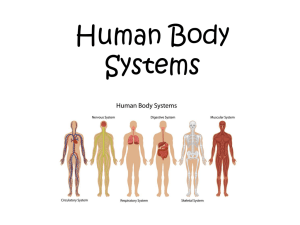
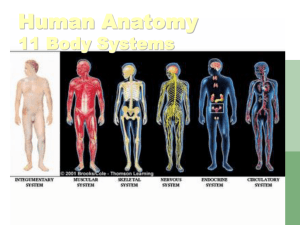
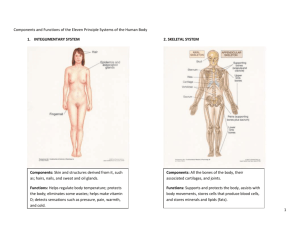
Organ Systems of the Human Body Ms Clark PVMHS Integumentary System Components: ◦ Skin and structures derived from it (hair, nails, sweat and oil glands) Functions: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Forms the external body covering Protects the body Eliminates some wastes Helps make vitamin D Detects sensations such as pressure, pain, heat, and cold. Integumentary System Skeletal System Components: ◦ Bones, joints, cartilages Functions: ◦ Protects and supports body organs ◦ Provides framework that muscles use to cause movement ◦ Blood cells are formed within bones ◦ Stores minerals Skeletal System Muscular System Components: ◦ Skeletal muscle tissue – muscle usually attached to bones Functions ◦ Movement ◦ Maintaining posture ◦ Producing heat Muscular System Nervous System Components: ◦ Brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sense organs such as eyes and ears Functions: ◦ Regulates body activities through nerve impulses by detecting changes in the environment ◦ Responds to changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands Nervous System Endocrine System Components: ◦ All glands and tissues that produce hormones (chemical regulators of body functions) Functions: ◦ Secrete hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism. Endocrine System Cardiovascular/Circulatory System Components: ◦ Heart, blood, blood vessels Functions: ◦ Transport blood throughout body Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells Blood carries carbon dioxide and wastes away from cells Cardiovascular/Circulatory System Immune/Lymphatic System Components: ◦ Lymphatic fluid and vessels; spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, tonsils Functions: ◦ Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood ◦ Protects body against disease-causing organisms Immune/Lymphatic System Respiratory System Components: ◦ Lungs, pharynx (throat), larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe), bronchus Functions: ◦ Keeps blood supplied with oxygen ◦ Removes carbon dioxide Respiratory System Digestive System Components: ◦ Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum, anus Functions: ◦ Breaks down food so that it can be absorbed into blood and distributed to cells ◦ Eliminates solid wastes Digestive System Urinary/Excretory System Components: ◦ Kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra Functions ◦ Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body ◦ Regulates volume and chemical composition of the blood ◦ Maintains body’s mineral balance ◦ Helps regulate red blood cell production Urinary/Excretory System Reproductive System Components: ◦ Female: Ovaries, uterine tube, uterus, vagina, mammary glands ◦ Male: Testes, penis, vas deferens, prostate gland, seminal vesicles Functions: ◦ Production of offspring Provides for conception and childbearing Reproductive System