(Intro to Extended definition)
advertisement

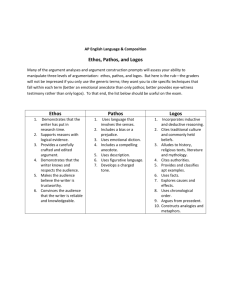
Critical Thinking Topic: “Your Topic” College Prep 2-25-13 Essential Question for the Unit “How do definitions shape our understanding?” Everything we do this unit will tie to this question Turn in those Topic Proposals I want em….. Did anyone struggle with this? What is an extended definition paper? The first consideration is that a word doesn’t have one “right” meaning. There are more ideas or concepts than there are words, so the same word has to mean different things at different times. Conversely, different words or phrases can be used to name the same concept. What is necessary for clear thinking is that the parties to the conversation know what concept they are dealing with at any time. Therefore, in writing an extended definition, don’t define the word—rather explain the concept, and show why it’s important that the reader have clearly in mind the same concept you have in mind. Maybe this dude can help VIDJA Extended Definition Papers (what I want to see) Introduction of the topic Definition of topic Criteria Examples Contrasting examples Warrants Discussing what the term means means for human conduct (connection to real life conduct). MUST be making an argument!!!! Claim, Evidence, Warrant Remember these?!?!? Claim: an assertion of truth Criteria Evidence: Facts on their own Examples Warrant: a statement that explains why a piece of evidence makes a claim factual. Your explanations Equation Warrant = claim + evidence Remember arguments?!!?!??! EVERYTHING is an argument (remember that?!) Therefore, your extended definition is an argument!! Ethos Ethos (Greek for 'character') refers to the trustworthiness or credibility of the writer or speaker. Ethos is often conveyed through tone and style of the message and through the way the writer or speaker refers to differing views. It can also be affected by the writer's reputation as it exists independently from the message--his or her expertise in the field, his or her previous record or integrity, and so forth. The impact of ethos is often called the argument's 'ethical appeal' or the 'appeal from credibility.’ PATHOS Pathos (Emotional) means persuading by appealing to the reader's emotions. We can look at texts ranging from classic essays to contemporary advertisements to see how pathos, emotional appeals, are used to persuade. Language choice affects the audience's emotional response, and emotional appeal can effectively be used to enhance an argument. Logos Logos (Logical) means persuading by the use of reasoning. This will be the most important technique we will study, and Aristotle's favorite. We'll look at deductive and inductive reasoning, and discuss what makes an effective, persuasive reason to back up your claims. Giving reasons is the heart of argumentation, and cannot be emphasized enough. We'll study the types of support you can use to substantiate your thesis, and look at some of the common logical fallacies, in order to avoid them in your writing Lets take a look at an example Lets read “What it is to be a teacher” Traditional definition Claim, evidence, warrant Types of arguments made Frayer Model (write these down on your sheet) In the Middle The word itself Definition What the word is in your own words Facts/characteristics Features of the word, what does the word do? Examples Manifestations of what it is Non-Examples Manifestations of what it is not What it looks like with “teacher” Watch a brother do a Frayer Model Help me analyze the argument? Contrasting examples? Your Turn Read “Love” Create your frayer model on LOVE On the back analyze the argument (theme) AND the types of arguments (claim, evidence, warrant structure) State contrasting examples…if there are any