Respiratory System
advertisement

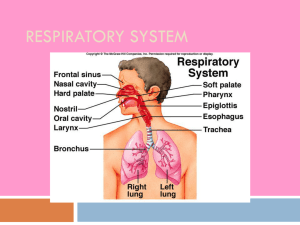
Respiratory System Functions Provide large area for gas exchange between air and circulating blood Move air to and from the gas exchange surfaces of the lungs Protect the respiratory surfaces from dehydration and temperature changes and defending against invading pathogens Produce sounds permitting speech, singing, and non-verbal auditory communication Provide olfactory sensations to the central nervous system for sense of smell The Respiratory Tract Conducting portion Begins at entrance to nasal cavity Continues through the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and larger bronchioles Delivers air to lungs Filters, warms, and humidifies the air Protecting alveoli from debris, pathogens, and environmental extremes Respiratory portion Includes smallest bronchioles and alveoli Gas exchange Structures Nose Air enters through external nares (nostrils), which open into nasal cavity Coarse hairs across nostrils protect from large airborne particles Mucus coats lining of nasal cavity Protects from small airborne particles Promotes filtration, warming, and humidifying of incoming air Pharynx Throat Shared by respiratory and digestive systems Extends between internal nares and entrances to larynx and esophagus Structures Larynx Air leaves pharynx and enters larynx through opening called glottis Voice box Epiglottis extends above glottis to protect during swallowing Houses vocal cords Trachea Windpipe Bronchi Structures Bronchioles Alveoli Lungs Lungs have spongy consistency due to air-filled passageways and alveoli Pleural Cavities Cavities that house the lungs