Solutions 2 pH - Solon City Schools
advertisement

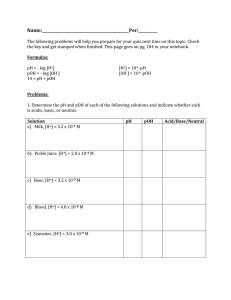
The Chemistry of Acids and Bases Acids and Bases: Define and Calculate pH/pOH At the conclusion of our time together, you should be able to: 1. 2. 3. 4. Define pH and pOH Explain the pH scale and what it means Change any pH reading to pOH Convert pH to concentration of hydronium ion concentrations, hydronium ion concentrations to pH Law of Probability -The probability of being watched is directly proportional to the stupidity of your act What is pH??? The pH scale is a way of expressing the strength of acids and bases. This scale is defined by: pH = - log [H+] Under Over 7 = acid 7 = neutral 7 = base What is pH??? p = count H = Hydronium ion (H3O+) In 1 Liter of water, (55+ moles of water), how many moles of hydronium ions are there??? Understanding pH gives me this number!!! If there was 1 mole of H3O+ in 1 Liter of water, (55+ moles of water), this count would be 1 mole. What is pH??? Remember: pH = - log [H+] pH = -log[1] Therefore, by definition, the pH of this solution is =0 What is the pH of water??? H2O + H2O ---> H3O+ + OH <=== This equation indicates that most water molecules stay as molecules, very few will form hydronium ions If we count the number of hydrogen ions in one liter of water (pH) we would get: .0000001 moles of H3O+/liter of water or 10-7 moles of H3O+/liter of water What is the pH of water?? pH = 7 What is the pOH of water??? H2O + H2O ---> H3O+ + OH <=== This equation indicates that most water molecules stay as molecules, very few will form hydroxide ions If we count the number of hydroxide ions in one liter of water (pOH) we would get: .0000001 moles of OH-/liter of water or 10-7 moles of OH-/liter of water What is the pOH of water?? pOH = 7 How High is the pH Scale?? Since 1 mole of OH- in one Liter of water would be a pOH = 0 And the pH and pOH of water is 7 or neutral, Therefore, the pH of a strong base with a pOH of 0 would be? pH = 14 Therefore, the pH scale goes from 0-14 Also, any pH can be converted to pOH by? Subtracting from 14. pH- The Amount Of H+ Ions In A Solution. 1 2 3 4 5 ACID extra H+1 ions (protons) 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 BASE fewer H+1 ions. extra OH-1 ions. 13 14 Where Do You Find a Dog With No Legs? Right Where You Left Him. Let’s Try Some Calculations by Not Using Calvin’s Approach to Math in Chemistry: Examples of Converting pH If an acid has a pH of 3, what would be the pOH? 14 – 3 = 11 If an base has a pOH of 2, what would be the pH? 14 – 2 = 12 Calculating the pH pH = - log [H+] (Remember that the [ ] mean Molarity) Example: If [H+] = 1 X 10-10 pH = - log 1 X 10-10 pH = 10 Example: If [H+] = 1.80 X 10-5 pH = - log 1.80 X 10-5 pH = 4.7 Try These! Find the pH of these: 1) A 0.15 M solution of Hydrochloric acid pH = 0.82 2) A 3.00 X 10-7 M solution of Nitric acid pH = 6.5 But Why Only 2 Significant Figures?? 2) A 3.00 X 10-7 M solution of Nitric acid pH = 6.5 Remember, we are working with logarithms. Therefore, we will use the pHAD principle. Add significant figures after the Decimal Point for pH. pH Calculations – Solving for H + If the pH of Coke is 3.12, [H+] = ??? Because pH = - log [H+] then - pH = log [H+] Divide both sides by log or Take antilog (10x) of both sides and get 10-pH = [H+] 10-3.12 = [H+] = 7.6 x 10-4 M *** to find antilog on your calculator, press “Shift” or “2nd function” and then the log button pH Calculations – Solving for H+ A solution has a pH of 3.78. What is the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution? (#1 on handout) pH = 3.78 = -3.78 = Inverse log -3.78 = 10-3.78 = 1.66 x 10-4 = -log [H+] -log [H+] log [H+] inverse log (log [H+]) [H+] [H+] What is the pOH? If an acid has a pH of 3.78, what would be the pOH? (#1 on handout) 14 – 3.78 = 10.22 pH Calculations – Solving for H+ A solution has a pH of 3.78. What is the concentration of hydroxide ions in the solution? (#1 on handout) pOH = - log [OH-] 10.22 = - log [OH- ] - 10.22 = log [OH- ] Inverse log -10.22 = inverse log (log [OH- ]) 10-10.22 = [OH-] 6.03 x 10-11 = [OH-] Calculating [H3O+], pH, [OH-], and pOH Problem 1: What is the [H3O+], [OH-], and pOH of a solution with pH = 3.78? Is this an acid, base, or neutral? [H3O+] = pOH = [OH-] = Acid 1.66 x 10-4 M 10.22 6.03 x 10-11 M Calculating the pOH pOH = - log [OH-] (Remember that the [ ] mean Molarity) Example #4 on handout: If [OH-] = 4.88 x 10-6 pOH = - log (4.88 x 10-6) pOH = 5.31 Calculating [H3O+], pH, [OH-], and pOH Problem 2: A chemist dilutes concentrated hydrochloric acid to make: 0.000 389 M HCl. Calculate the pH, [OH-], and pOH pH = pOH = [OH-] = Acid 3.41 10.59 2.57 x 10-11 M [OH-] [H+] pOH pH pH [H+] [OH-] pOH Acids and Bases: Define and Calculate pH/pOH Let’s see if you can: 1. 2. 3. 4. Define pH and pOH Explain the pH scale and what it means Change any pH reading to pOH Convert pH to concentration of hydronium ion concentrations, hydronium ion concentrations to pH The American Medical Association announced today that the Universal Choking Sign has been revised: Old Sign: New Sign: Get Your Clicker!!! The “p” in pH stands for? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Priority Count Number Molarity Not listed The “H” in pH stands for? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. House Hydrogen ions Acid Concentration Not listed If a solution has a pH of 6.5, what is the pOH of that same solution? 1. 4.5 2. 7.5 3. 6.5 4. 0.0 5. 12.5 6. Not listed If a solution has a pH of 6.2, what is the [H+] of that solution? 1. 6.2 2. 6.3 x 10-7 3. 1.0 x 106.2 4. 1.0 x 107.8 5. 7.8 6. Not listed If a solution has a pOH of 9.44, what is the [OH-] of that same solution? 1. 0.98 2. 1.00 x 109.44 3. 3.63 x 10-10 4. 4.56 5. 9.44 6. Not listed Let’s kick back and relax!! The Chemistry of Acids and Bases Acids and Bases: Strength and Indicators At the conclusion of our time together, you should be able to: 1. Determine the relative strength of acids and bases and the reason for the strengths 2. List the 3 basic types of indicators 3. Explain each indicator’s strengths and weaknesses 4. Use an appropriate indicator to determine the pH of a substance Remember: the pH scale is a way of expressing the strength of acids and bases. Under Over 7 = acid 7 = neutral 7 = base What makes an acid strong or weak?? Strong or Weak Acids/Bases The strength of an acid (or base) is determined by the amount of IONIZATION. HNO3, HCl, H2SO4 and HClO4 are among the only known strong acids. Strong Acids Generally divide acids and bases into STRONG or WEAK ones. STRONG ACID: HNO3 (aq) + H2O (l) ---> H3O+ (aq) + NO3- (aq) HNO3 is about 100% dissociated in water. Weak Acids Weak acids are much less than 100% ionized in water. One of the best known is acetic acid = CH3CO2H pH H2O H+ 0 55 1 1 550 1 2 5500 1 Strong ACID HCl Hydrochloric acid H2SO4 Sulfuric acid HNO3 Nitric acid Weak ACID CH3COOH H2CO3 Acetic acid Carbonic acid Citric acid Strong Bases Strong Base: 100% dissociated in water. NaOH (aq) ---> Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Other common strong bases include KOH and Ca(OH)2. CaO (lime) + H2O --> Ca(OH)2 (slaked lime) CaO Weak Bases Weak base: less than 100% ionized in water One of the best known weak bases is ammonia NH3 (aq) + H2O (l) NH4+ (aq) + OH- (aq) Weak Bases Strong or Weak Acids/Bases Summary Strong acids and bases dissolve in water Hydrochloric, Hydrobromic, Hydroiodic, (All Binaries) Nitric, Sulfuric, Perchloric Acids (Ternary Acids with 2 more O than H) Group I hydroxides Maybe Our Goals Aren’t the Exact Same, But They’re Similar!! There are Several Ways to Test for pH There are three basic types: Paper pH meter Liquid indicators (Some are natural liquid indicators like red cabbage, radishes) Paper Testing Paper tests like litmus paper and pH paper Put a stirring rod into the solution and stir. Take the stirring rod out, and place a drop of the solution from the end of the stirring rod onto a piece of the paper Read and record the color change. Note what the color indicates. Use a small portion of the paper. You can use one piece of paper for several tests. pH Paper Red Litmus paper Blue Litmus paper pH Meter Tests the voltage of the electrolyte Converts the voltage to pH Expensive, but very accurate Must be calibrated with a buffer solution pH Indicators Indicators are dyes that can be added that will change color in the presence of an acid or base. Some indicators only work in a specific range of pH Once the drops are added, the sample is ruined Some dyes are natural, like radish skin or red cabbage We’ll Chip Away at this a Little at a Time!! pH of Common Substances A Former Student Trying to Apply His Knowledge of Chemistry!! Acids and Bases: Strength and Indicators Let’s see if you can: 1. Determine the relative strength of acids and bases and the reason for the strengths 2. List the 3 basic types of indicators 3. Explain each indicator’s strengths and weaknesses 4. Use an appropriate indicator to determine the pH of a substance Get Your Clicker!!! Red litmus paper will turn what color in an acid? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Blue White Red Clear Not listed Which of the following would be the most accurate way to test for pH? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. pH meter Litmus paper Phenylthalein Cabbage juice Universal indicator Not listed Several liquids are tested for pH. Which of these liquids would be the weakest acid? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Liquid a, pH = 1.0 Liquid b, pH = 4.5 Liquid c, pH = 6.5 Liquid d, pH = 8.5 Liquid e, pH = 10.5 Liquid f, pH = 13.0 So – What did you think of today’s class?? If a solution has a [H3O+] of 6.20 x 10-8, what is the pH of that solution? 1. 6.79 2. 8.79 3. 5.21 4. 4.56 5. 7.21 6. Not listed If a solution has a [OH-] of 1.05 x 10-3, what is the pH of that solution? 1. 11.02 2. 2.98 3. 1.00 4. 3.02 5. 10.98 6. Not listed Converting pH to pOH If an acid has a pH of 6, what would be the pOH? 14 – 6 = 8 [H 3 O + ], [OH - ] and pH Page 14:5 What is the pH of the 0.0001 M NaOH solution? [OH-] = 0.0001 (or 1.0 X 10-4 M) pOH = - log 0.0001 pOH = 4 pH = 14 – 4 = 10 Try These! Page 15:9 The pOH of rainwater collected in a certain region of the northeastern United States on a particular day was 9.94. What is the H+ ion concentration of the rainwater? pH = 4.06 8.91 x 10-5 The OH- ion concentration of a blood sample is 2.88 x 10-6 M. What is the pH of the blood? pOH = 5.54 14.0 – 5.54 = 8.46 pH I wouldn’t do that if I were you!!!