Biochemistry test review
advertisement

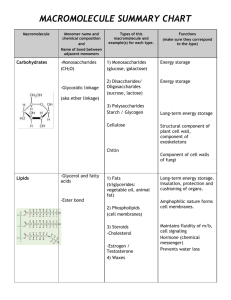
Name________________________________________________Date_______________Period______ Biochemistry Unit Exam Review – Just the basics 1. What do each of the following symbols represent? C _________________ H_________________ O __________________ N____________________P_________________ Carbohydrates CHO Source of energy Bread, fruit, pasta Monomer: monosaccharide 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Lipids CHO Store energy Wax, oil, butter Monomer: 1 glycerol, 3 fatty acids Protein Nucleic Acids CHON Build cells, metabolism Meat, muscle, milk Monomer: Amino acids CHONP Genetic information DNA, RNA; ATP Monomer: Nucleotide A chain of monosaccharides is a ________________________________. A chain of amino acids is a _______________________. A chain of nucleotides is a _________________________________. A chain of fatty acids makes a ____________________. What elements are carbohydrates made ot? __________________________________________. What elements are lipids made of? ___________________________________________________. What element inside proteins is different from lipids and carbohydrates? _______________. What element inside nucleic acids is different from lipids and proteins? _________________. Elements make up molecules. Molecules make up macromolecules. 10. Which of the following is an example of a molecule without carbon? (Circle one: Hydrogen, water, or protein) 11. Which of the following is an example of a macromolecule? (Circle one: Hydrogen, water or protein) 12. Circle the smallest of the following: element, molecule, or macromolecule. 13. Circle the largest of the following: element, molecule, or macromolecule. Monosaccharide = one sugar (glucose) Disaccharide = two sugars (maltose) Polysaccharide = three or more sugars (starch) Starch What macromolecules are you made of? Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids. Glucose Maltose Sugars end in “ose” Enzyme Type of protein Speeds up chemical reactions Specific for substrate 14. When 2 monosaccharides join together they form a ___________________________. 15. When 3 or more monosaccharides join together they form a ____________________. Enzyme - protein - speeds up chemical reactions - specific for substrate - ends in “ase” Name________________________________________________Date_______________Period______ 16. What type of macromolecule is an enzyme? __________________________________ 17. Enzymes (circle one: speed up or slow down) chemical reactions. 18. Are enzymes picky when they bond to substrates? (circle one: yes or no) 19. Where do substrates bond to enzymes? At the _____________ ______________. 20. The substrate that bonds to the enzyme is known as the (circle one: reactant or product) 21. Once the substrate is broken down by the enzyme it is known as the (circle one reactant or product). 22. Glucose and fructose are examples of (circle one: sugars or enzymes) 23. Lactase and catalase are examples of (circle one: sugars or enzymes) 24. Complete the table with the answer choices: Macromolecule Monomer Carbohydrate Protein Lipid Nucleic Acid STUDY STUDY STUDY STUDY STUDY STUDY STUDY STUDY STUDY STUDY STUDY STUDY STUDY!! Dehydration Synthesis Dehydration = removal of water Synthesis = join together Glucose + Glucose Maltose + H2O Hydrolysis Hydro = water Lysis= to separate Maltose + H2O Glucose + Glucose 25. When 2 molecules join and water is lost the process is called _______________ ____________________. 26. When 2 molecules split when water is brought back in the process is called _________________. 27. What does dehydration mean? ____________________ 28. What does synthesis mean? ________________________ 29. What does hydro mean? ___________________________ 30. What does lysis mean? _____________________________