10142011_Profit
advertisement

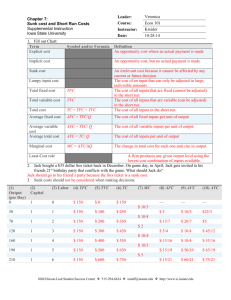
I. Profit a. TR – TC b. Accounting Profit = TR – Explicit Cost c. Economic Profit = TR – [Explicit Cost + Implicit Cost] d. Explicit Cost i. Costs that require monetary output like writing a check e. Implicit Cost i. Costs that include opportunity cost f. Normal profit i. Normal rate of return, just enough to keep investors satisfied. If profit dropped below this level they would leave ii. Benchmark is long term government securities interest rate iii. A normal profit / rate of return is a cost to us iv. 0 Economic Profit =/= No profit, that just means they had a normal profit v. An economic loss doesn’t mean they’re not earning money, it just means they’re under the normal rate of return Salary Rental Inc. Interest Inc. Total Income Sale of Food Sale of Liquor Total Revenue II. i. ii. $50,000 $25,000 $5,000 $80,000 $162,000 $65,000 $227,000 Wages Food Alcohol Utilities Taxes Adv. Misc. Total Cost Accounting Profit - $68,000 Economic Profit – ($12,000) ($60,000) ($55,000) ($18,000) ($15,000) ($6,500) ($1,500) ($3,000) ($159,000) Costs a. Types of costs i. Fixed Cost 1. Costs that do not change, hence the term fixed. 2. As output increases fixed costs remain constant. 3. As output decreases fixed costs remain the same. 4. Example a. Rent b. Interest payments on a loan ii. Variable Cost 1. Costs that do vary at levels of output 2. Examples a. Labor b. Raw materials c. Utilities b. c. d. e. iii. If you put output=0 if there’s a cost then that’s considered a fixed cost Total Cost = Total Fixed Cost + Total Variable Cost Marginal Cost i. Additional cost of producing one more unit of output ii. ΔTC/ ΔQ iii. Or iv. ΔTVC/ ΔQ Timeframes i. Short Run 1. At least one fixed cost of production 2. Firms can neither enter nor exit the industry 3. How long is the short run? a. It is unknown, however long it takes to get rid of the fixed cost b. For a kid running a lemonade stand it’s however long it takes him to get a new lemonade pitcher c. For General Motors it’s many years ii. Long Run 1. All factors of production are variable 2. Firms are free to enter or exit an industry 3. Difference between shutting down / exiting a. Shutting down i. You just stopped, you didn’t actually exit the industry b. Exiting L TPL i. Means you’re on a boat :P 0 Diminishing Returns 1 10 i. As you continue to add additional units of some 2 25 variable resource (i.e. labor) to some fixed resource, 3 35 eventually each additional unit of that variable 4 40 resource will yield less output. 5 42 ii. See table to right 6 42 iii. Diminishing returns raises output cost iv. ATC 1. Average Total Cost 2. TC/Q v. AFC 1. Average Fixed Cost 2. TFC/Q vi. AVC 1. Average Variable Cost 2. TVC/Q vii. TC = TFC + TVC 1. ATC = AFC + AVC MPL 10 15 10 5 2 0