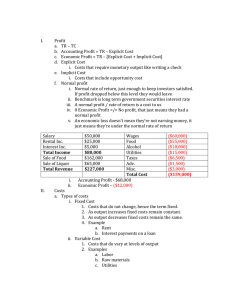
Type text here P$3 X 4 = 12 P$6 X 5= 30 12+ 30 = $42 logical or mathematical relation also known as price line consumer choice theory or income approach Budget line - shows the combination of two products that a consumer can afford to buy with a given income . $2 $1 P $2 P$1 PXQX + PYQY 2X 6 + 1X 0 = 12 2 X 5 + 1 X 2 = 12 shows real income Opportunity cost What are the factors that may effect budget line ? parallel shift pivotalshift No chnage in no change in price No change in income fall in price increase in price 12/2=6 12/4=3 real income falls due to rise in price level or inflation $5 $2 purchasing power falls if price increase 2y:px 2y:1x 12x = 24y 1x =24/12 y 1x = 2y CD line 1y:px 1y:0.5x 6x= 12y 1x= 12/6y 1x= 2y AB line if price decrease opportunity cost it is a technique for explaining how choices between two products/alternatives are made . slope negative convex satisfaction level will be equal isoquant Tangent means - a straight line that touches a curve. inferior good - ( demand falls when the consumer's real income rises.) Normal good - ( demand rise when the consumer's real income rises.) equal consumption backward bending 1x 6 = 6 shirts 2x 9=18 Trousers downward sloping due to fall in price of trouser if S.E is grester than I.E - inferior good if I.E is greater than S.E - Giffen goods TP= maximumat F MP = 0 fall - stay positive MP = 0 AT 6th unit MP negative at 7th init =TP/L tangent AP - Maximum shows total cost remain the same for the entire isocost line shows total ouptut remains the same nagative slope convex to origin no twol isoquant will intersect given up capital units to increase labour units isocost - total cost line tangent productive efficiency st Eo total ouput due to change in one factor 300-100=200 200/100X100 =200% SRTC TC=TFC+TVC 25 45 Short run TC/Q= TFC/Q+TVC/Q ATC=AFC+ AVC ATC- AVC=AFC 100 50 33.3 25 T TC/Q=TFC/Q+ TVC/Q ATC = AFC+ AVC ATC-AFC=AVC TANGENT AT RAY 3 OPTIMUM LEVEL OF PRODUCTION LOWEST AVC TANGENT TO TC ATC VERTICAL DISTANCE INCREASING RATE DECREASING RATE Analyse and evaluate the features . L: O- Analyse and evaluate the main characteristics of perfect competition . rice $6 $5 =D $4 might not able to cover cost $5 e.g- rice - wheat - Chapter 6 AC=AR Type text here T P=AR=MR=D P =D - Perfectly elastic P=AR=MR=D = AR= D 6-10-2020 =P Explicit - expenses implicit - opportunity cost normal profit- TR=TC tangent max profit at Q2 still generates marginal profit total profit maximisation output Perfect competition is a form of the market in which there is a large number of buyers and sellers and where homogeneous product is sold at a uniform priceA price taker firm means that it has to accept the price as determined by the .forces of market demand and market supply. Firm's demand curve under perfect competition is a horizontal straight line parallel to X-axis. Under perfect competition, AR is constant for a firm. Hence, AR = MR. AR= AC AR is greater than AC AR is less than AC Loss abnormal profit AR > AC AC>AR AR=MR=P=D AR=MR=P=D AR=MR=P=D AR=MR=P=D cease production at P1 AVC>AR LOSS Po Qo loss AR>AC AR=AC Reduce price AR=AC Conclusion mid point P= AR MR will not be equal to AR MR is less than AR Downward sloping profit maximisation MR=MC at Eo AR=AC satisficing - reach minimum target satisfying - satsify all stakeholders 1.Traditional frim's Thoery Examples of direct costs are direct labor, direct materials, commissions, piece rate wages, and manufacturing supplies. Examples of indirect costs are production supervision salaries, quality control costs, insurance. non - price demand factors 1REASON 2 3 4 2.Managerial Theory 3.Behavioral Theory The definition of a rule of thumb is a generally accepted guideline, policy or method of doing something based on practice rather than facts. ? In perfect competition, any profit-maximizing producer faces a market price equal to its marginal cost (P = MC). link to market failure Analyse and evalaute that is is always bad for the consumer . link to inelastic or elastic demand and revenue INELASTIC DEMAND Profit maximisation Profit maximisation link to AS economics willing to pay able to pay loss- AC > AR A sunk cost refers to money that has already been spent and which cannot be recovered. ? SUPER NORMAL PROFIT Economic efficiency= Productive & allocative efficiency minimum AC X- efficent what a society desires” P= Perfect competition P P=MC rise in real income lead to fall in working hours . shows negative relationship reading individual labour supply curve market supply curve always upward sloping positive realtionship Perfect competition market wage taker perfectly elastic reading extra power point notes Product market marginal physical product