Quiz-5
advertisement

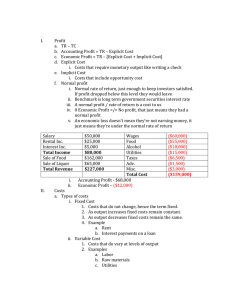
Quiz V Profit Maximization and Competition 1.Economic profit is defined as: A. B. C. D. Business profit minus explicit costs Total revenue minus total explicit cost Normal profit minus implicit cost Total revenue minus explicit cost minus implicit cost E. Total revenue minus average variable cost F. Price times quantity sold 2. To a small firm in a competitive market: A. The demand it faces is horizontal, reflecting a constant price B. The demand is vertical but supply is downwardsloping C. The price increases as it produces and supplies greater quantities of output D. The price is variable while the quantity is constant E. Profit is always zero 3. Which of the following is profit? (There may be more than one answer.) A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Total Revenue – Total Variable Cost Total Revenue – Total Cost Q ( P – TVC - TFC) Q ( P – AVC ) Q ( P – AFC – AVC) (P.Q) – Total Variable Cost (P.Q) – TVC – TFC (P.Q) – AVC -AFC 4. The short-run marginal cost of a single firm tends to become upward-sloping at some level of output because A. B. C. D. E. wages are not constant of competition of increasing returns to the variable input of diminishing returns to the variable input The market price increases as more output is produced and supplied to the market F. of principle of diminishing marginal utility 5. Which of the following is not one of the characteristics of a perfectly competitive market? A. Many buyers and many sellers B. Each firm determines the price it wants to charge according to its cost of production C. All firms produce the same (homogeneous) product D. All buyers and sellers have free access to market information E. Firms are free to enter and exit the industry









![[00:00:17.851] So in this module we're going to take another](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010080946_1-ea6bff0dbb200a44533d56f80da9cb6f-300x300.png)